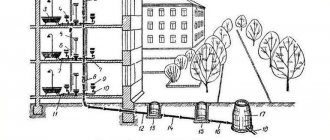
The sewer is the main channel of the network. It is part of the city sewerage system, responsible for receiving sewage and its centralized supply to pumping stations, water treatment or to the point of direct discharge.
History has been familiar with collectors since the times of Ancient Rome. For their laying, various materials were used, from stone and clay to cast iron pipes. In the twentieth century, cast iron and reinforced concrete took the lead. Today, expensive and rather difficult to operate systems are being replaced by HDPE sewer pipes. The manufacturers' range includes products with a diameter of up to 3000 mm with ring stiffness up to SN16, which allows you to find a solution for absolutely any soil and volume of wastewater.
Areas of application
The easiest answer would be: everywhere. Sewage now exists in all cities and towns, in all industries, in agriculture, in mines and oil production complexes, sinter plants and farms, railway stations and airports.
Almost all underground infrastructure of cities falls under the concept of “sewage” - after all, communication lines, the Internet, underground power networks laid in a shell or in boxes are also called sewerage. Houses without sewage systems now remain mainly in small villages and towns, but even there, septic tanks and systems are gradually being built for each house.
Polyethylene is the most popular material for external and internal sewage systems. It is durable and at the same time plastic. With slight movements of the earth, polyethylene communications will retain their integrity when steel or, especially, cast iron pipes break.
In cases of very heavy loads - depths of more than 10 m, aggressive or toxic wastewater and special requirements for the integrity of pipelines - polyethylene pipelines are not used.
Welding with heated equipment
The pipelines are then removed and checked for parallel alignment. When there is no gap between the ends, they are heated using a specialized tool. When the surfaces are fused, the tool is removed from the area to be welded. Next, both parts are pressed, increasing the pressure at the junction. After a certain time interval, the seam cools.
Specifications
Polyethylene sewer pipes are characterized by diameter, length, wall thickness and ring rigidity. In addition, polyethylene pipes are single-layer and double-layer, with a smooth wall and corrugated.
The SDR (Standard Dimension Ratio) coefficient of pipes is the standard ratio of the outer diameter to the wall thickness. Applicable to smooth-walled polyethylene pipes for pressure sewerage. SDR is taken from tabular data; the thickness of the pipeline wall, its annular rigidity, and strength depend on it.
Polyethylene is chemically inert and resistant to organic solvents at room temperature. The density of polyethylene is 0.94–0.96 g/cm³, it is lighter than water.
Laying sewer lines made of polyethylene products
Due to such qualities of polyethylene pipes as high speed and ease of installation, such products are in high demand among plumbers.
Black polyethylene sewer pipe is good for creating indoor type piping. Moreover, you do not need any special equipment to install it. The joining of pipes whose cross-section is within 110 mm is made using compression fittings.
Pipelines made of polyethylene pipes for external sewerage are connected by butt welding. This process occurs several times faster than welding work with metal products and does not require additional consumables or complex equipment. Moreover, after work, an even, high-quality weld seam is obtained, providing sufficient tightness for the full functioning of the system.
The presence of special installation equipment for sewerage pipes made of polyethylene makes it possible to simplify the installation of the pipeline as much as possible, and the number of joints in this case can be minimized in comparison with similar pipelines made of rolled steel.
Sewer communications made of polyethylene pipes can be laid in two ways: in a previously prepared trench in compliance with all standards for such work; inside an existing sewerage system made of steel pipe products.
Production Features
Scientists have created many varieties of polyethylene. In relation to polyethylene pipes for sewerage, three names are usually mentioned: low-pressure polyethylene (LDPE), high-pressure polyethylene (HDPE), and medium-pressure polyethylene (MPD).
The concept of “pressure” in this case describes the features of PE production. PE produced by low and medium pressure methods has approximately the same density and molecular weight. LDPE has lower density and greater ductility. The methods differ in the catalysts and temperatures used.
Types of shaped parts
Among the many shaped elements with which you can join pipes, there are:
- transition pipes, saddle pipes, compensation pipes, instrument pipes;
- various tees;
- bends;
- audits;
- crosses;
- couplings;
- union nuts;
- plugs;
- sealing gaskets and rings.
The selection of each element is made based on the actual dimensions of polyethylene pipes, taking into account the standards for such products.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of using polyethylene sewerage systems:
- Durability. When laid without exposure to ultraviolet radiation, you can count on 50 years of operation.
- Durability, resistance to crushing.
- Plasticity, tear resistance.
- Resistance to aggressive wastewater, corrosion, biological pollution, chemical inertness.
- Harmless to humans.
- Frost resistance. Polyethylene pipelines can withstand freezing with liquid inside, and after defrosting they return to their original shape.
- The pipeline does not become overgrown with calcium and magnesium salts from the inside.
- The smooth inner surface facilitates faster evacuation of contents.
- Low weight facilitates transportation and installation.
- The industry produces fittings of any shape and purpose. From bell-shaped or corrugated polyethylene products, you can easily assemble a sewerage system of any shape.
- Installation is quite simple and does not require highly qualified installers.
- Bell-shaped communications and pipelines on couplings with collet clamps can be disassembled and reassembled if necessary, pressure welded pipelines can also be used after disassembly (the sections will simply have to be increased).
One of the most significant advantages of polyethylene is its price. This is the most inexpensive plastic.
A serious drawback of polyethylene products is their instability to ultraviolet radiation. But for underground sewerage this drawback does not matter. In addition, polyethylene has a high coefficient of thermal expansion - during summer installation it is necessary to provide a small margin in length so that in winter the cold and reduced pipe does not experience stress.
Polyethylene seems to have been created for underground installation - this material has some advantages and no disadvantages at all.
Basic properties
All polyethylene pipes are created from a thermoplastic polymerization product of a lower hydrocarbon - ethylene, which gives products made from it similar characteristics:
- Pipe material density - 0.94-0.96 g/cm
3,
- Operating temperature ranges from -60 to +90
0C, optimal mode – from 0 to 40
0
C,
- Permissible operating pressure of the contents – up to 16 atm,
- The diameter of polyethylene pipes can be from 20 to 1600 mm,
- The wall thickness varies from 2 to 60 mm.
ATTENTION! The indicated numbers are correct for most brands of polyethylene, but there are exceptions. There are types of polyethylene materials, products from which can withstand much higher loads - mechanical, chemical and temperature.
Advantages
Polyethylene pipes have a very long service life - more than 60 years under standard conditions, which is explained by the following capabilities of this material:
- Elasticity, due to which the pipe does not deteriorate even when its contents freeze. In this case, it can only be slightly deformed - stretched in diameter.
- Resistant to common chemical reagents - various acids, alcohols and alkalis, and for some types even to fats and gasoline products. Polyethylene cannot withstand contact only with liquid fluorine and chlorine, but these substances are extremely rare in their pure form, so such contact is unlikely.
- Resistant to biodegradation through rot and fungus, as well as destruction by insects and rodents.
- The period of natural decomposition is more than 100 years.
- Absolute absence of toxic emissions, which allows them to be used in direct contact with food products and laid without additional protection.
- The ability to be an excellent insulator for liquids and gases, which allows nothing unnecessary to pass in or out.
- Smoothness of the inner walls. This factor determines the small percentage of their contamination and the appearance of growths.
- Low weight of products. Polyethylene is even lighter than water, due to which the installation of communication systems involving polyethylene pipes does not require strengthening the supports, especially strong fasteners and the use of great physical force.
- Ease of installation work. To connect individual sections of pipes, gentle heating or fastening with sockets and couplings is sufficient.
INTERESTING! Polymerized ethylene can serve as an excellent sound insulator. The use of polyethylene pipes instead of their metal counterparts helps to significantly reduce the level of noise coming from communications.
Flaws
Despite all the versatility of PE pipes, they have disadvantages associated with the structural features of the material:
- The products do not withstand high temperatures; they are intended mainly for transporting cold liquids and gases.
- Pure polyethylene becomes brittle after prolonged exposure to sunlight. To protect against ultraviolet radiation, pipes are treated using one of the following methods: coated with paint (preferably acrylic),
- blocked with protective materials,
- Even at the manufacturing stage, special protective substances are added to polyethylene.
This is interesting: Storm sewer calculation - algorithm and online calculator
Kinds
All types of sewerage systems are divided into pressure and non-pressure according to the pressure in the pipelines.
By design - bell-shaped or smooth; smooth or corrugated. The design determines the installation method.
According to the material - from HDPE, LDPE, and other types of plastic.
By purpose - for sewerage in the traditional sense of the word (for transporting wastewater); for power, information networks, communication networks; for storm drainage; for drainage.
Plastic
For sewage systems, pipes made of different types of plastic are used: HDPE, LDPE, polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene. Cross-linked polyethylene is not used - it is too plastic and does not have sufficient ring rigidity. Besides, it's expensive. But my story is about polyethylene pipes, then we will talk only about them.
Gravity
When you hear the word “sewage”, what comes to mind is the traditional gravity flow system of socket elements. This is just a non-pressure sewer system - wastewater, rain or flood waters flow towards a lower level, along a slope. This system is used for small sewers in a private home, as well as when constructing urban infrastructure.
A remarkable advantage of gravity sewer systems is their reliability. Gravity exists everywhere; liquid, under the influence of gravity, tends to find the lowest place, flowing downhill.
If the sewer system is designed correctly and installed with high quality, then it works for many years, requiring virtually no human intervention, except for rare cleaning of pipelines and wells. Constant monitoring is not required.
Structurally, such a system consists of polyethylene pipes laid with a slope and wells. The wastewater is collected in a centralized collector and discharged outside the populated area or to treatment facilities. The distance between wells is limited to 50 m, the pipeline should not have more than one turn (so that it can be cleaned from the well).
The slope in external sewerage systems is 1-2 (5) mm per linear meter. You should not exceed the slope, otherwise the sewage system will go deep into the ground, the volume of excavation work will increase, and a pumping station will be needed to transport the wastewater.
Nadornaya
A pressure sewer system is much less common. Pressure sewerage is used only in exceptional cases:
- If the central collector is located above the level of the receiving well or storage tank.
- If there is an obstacle on the pipeline path that cannot be bypassed in any other way except by raising the level (rock, basement, structures, railway track, highway).
- If it is necessary to use a pipe of small diameter and increase the speed of movement of the wastewater.
The design of a pressure sewer includes polyethylene pipelines, a pump or pumping station that pumps contaminated wastewater from a storage well into a gravity collector, storage tank, and municipal treatment facilities. A shredder must be installed in front of the pump to process large waste so that it does not clog the pump.
The pressure system requires frequent human inspection, the chopper and pump require constant attention (however, automation saves the day). But in any case, the equipment requires maintenance and complex repairs. If the chopper malfunctions, the system becomes clogged.
The advantage of the system: the possibility of constructing a long or narrow pipeline, application in conditions of height differences between the well and the collector or treatment facilities.
HDPE
HDPE, or HDPE – low-density polyethylene (high density, HDPE). This is the most inexpensive and widespread type of polyethylene. The phrase “low pressure” refers to the production conditions of PE, and not to the technical characteristics of the material.
Undyed PE is white, thin polyethylene products are transparent. Sewer pipes are painted: external ones are red, drainage pipes are painted green, internal pipes are painted gray or white.
Products made from HDPE have low cost, high plasticity, frost resistance, and do not burst when frozen. The strength of HDPE is sufficient to lay communications to a depth of about 5-6 m. HDPE is usually undesirable to use for internal wiring from a sink - at a temperature of 70-80 ° C it softens and loses strength.
PVD
High-density polyethylene (LDPE), or low-density polyethylene, is less durable than HDPE. It is not used for sewer pipes - it will collapse under soil pressure.
Corrugated
For sewerage pipelines operating in harsh conditions, the industry produces a durable two-layer polyethylene pipe with a corrugated outer layer and a smooth inner layer. Corrugation is a change in the diameter of the outer layer with a certain step. Corrugation gives the structure strength, rigidity, and at the same time flexibility.
There are rigid and flexible corrugated pipes. For underground communications, two-layer rigid corrugations are used - they have higher strength. The inner layer of corrugation is made of HDPE or LDPE. The outer one is made of less plastic HDPE, polyvinyl chloride or polypropylene.
The use of polyethylene corrugated pipes for underground communications has many advantages:
- increased strength;
- high resistance to deformation, rupture, crushing;
- easy installation;
- the ability to bend communications without fittings.
Corrugated pipe is used in situations where the sewerage system experiences heavy loads - when laid at a depth of more than 6 m, in rocky soil. During subsidence, cast iron communications can burst, and plastic corrugated pipes can stretch.
A serious disadvantage of corrugated pipes is their considerable price.
Material
To the greatest extent, the properties of any object are determined by what it is made of. Polyethylene pipes are no exception.
And they are made from a material that is the most common plastic in existence.
Its physical properties are:
- Polyethylene does not react with acids, alkalis and alcohols. But it can be destroyed by liquid chlorine and fluorine. However, this usually does not threaten the vigilant owner of a polyethylene water supply: the probability of encountering fluorine and chlorine in a free state is much less than the probability of encountering the British Queen in the restroom of the Zhmerinka bus station.
- Polyethylene is somewhat lighter than water
. Its density is approximately 0.94-0.96 g/cm3. Note: the fact that he does not drown in water does not characterize him in a bad way. It's just lightweight plastic. The weight of a polyethylene pipe of small and medium diameter will seem manageable even to a person who is far from the world record in powerlifting. - Polyethylene begins to soften and lose its original shape at a temperature of 80 C
. - He is afraid of the light
. Under natural conditions, polymerized ethylene turns into dust in about a year. Don’t rush to mourn your new canister: to prevent this from happening, the industry uses special modifiers that make polyethylene almost eternal. Environmentalists are crying at this point.
How much cleaner it would be if all polyethylene decomposed within a year...
Advice: after all, it is advisable to deepen the entrance to the house below the freezing point of the soil. If the internal water supply warms up as soon as the temperature in the room rises above zero, then in the snowdrifts at -30 outside it is still a pleasure.
In addition, during the winter absence, it is advisable to drain the water from the pipes for one more reason: ice is not harmful to the pipes, but it will break the faucets.
Dimensions, diameters and markings
Socket products in accordance with GOST 22689-2014 have a range of nominal diameters: 32, 40, 50, 63, 75, 80, 90, 100, 110, 125, 160, 200, 250, 315 mm. Wall thickness varies from 3 to 13.6 mm. The effective length of the elements ranges from 0.3 m for small products to 6 m for large diameter products.
Smooth-walled polyethylene pipes for pressure sewerage are produced in accordance with GOST R 54475-2011, Ø from 10 to 2000 mm. Diameters up to 180 mm - in coils and sections, larger sizes - only in sections.
Corrugated pipes in accordance with GOST R 54475-2011 are produced in lengths from 1 to 12 m. The diameters of corrugated two-layer polyethylene sewer pipes reach 2200 mm (starting from 110 mm).
Marking
Markings are applied to the surface of pipes and fittings at a distance of at least 1 m. The code includes the following symbols:
- manufacturer's name;
- international designation of the product brand (PE100, PE80, PE63 or PE 100, PE80, PE63);
- standard dimensional ratio SDR;
- dash;
- nominal diameter and nominal wall thickness;
- purpose - drinking or technical;
- standard.
For example: drinking pipe PE 63 SDR 21 – 32×3 GOST 18599-2001.
On gray and red products the markings are applied to the surface, but not always on black pipes. Marking of socket products:
- product name – TK (sewage pipe);
- nominal diameter (external) in mm;
- name of the material;
- Date of issue.
For example: TK 110-PE – sewer pipe, diameter 110 mm, PE – polyethylene.
Corrugation markings include:
- the word “pipe” or the name of the fitting;
- nominal size DN/OD or DN/ID (inner or outer diameter);
- nominal ring stiffness SN;
- abbreviated name of the material (Latin or Cyrillic);
- standard designations.
For example:
- PE polyethylene pipe with a nominal internal diameter DN/OD 200 mm, nominal hardness SN6;
- pipe OD 200 SN6 RE GOST R 54475;
- 90° tee made of PP polypropylene for pipes with a nominal outer size of DN/ID 300 mm, nominal hardness SN8;
- tee 90° ID 300 SN8 RR GOST R 54475.
Plastic products for sewerage are painted - this helps with their installation, storage and transportation. Bright red, blue, red and green communications are also easier to find during excavation work.
Applicable colors for polyethylene pipes:
- Pure black or black-gray are used for technical purposes.
- Products for internal sewerage are painted white, black, gray.
- The drainage is painted bright green.
- External sewer pipes are painted bright orange, red, or orange-brown.
- Black with a blue stripe and bright blue are used for drinking water supply.
- Yellow and black with yellow stripes are used for natural gas.
- Red color is used for protective pipes for laying electrical cables.
How to choose a diameter for connecting plumbing fixtures
The diameters for connecting indoor plumbing facilities are standardized: for a toilet - 110 mm, bathtubs, showers and Jacuzzis - 40-50 mm, bidets - 40 mm, sinks and sinks - 32-40 mm. If a pipeline is laid into a bathroom with several appliances, then all outlets are connected to a 50 mm pipe, while the outlets can have a smaller diameter, just select the appropriate adapters and tees.
A dishwasher or washing machine is connected through a tee to the outlet of a sink or sink of any diameter, or together with the sink to a 50 mm pipe.
The diameter of the drain pipe in a high-rise building is 100 mm; for a riser from kitchen sinks it can be 85 mm. For a riser in a two-story house, 50 mm or a vacuum valve is sufficient. The water consumption even from two vertically positioned toilets is small, so you don’t have to worry about pulling water plugs out of the sinks.
Installation methods
The popularity of PE products is largely due to ease of installation and low financial costs.
In addition, they are great for creating an internal system. There are two methods for connecting polyethylene pipes:
- detachable - for large diameter pipes (performed using steel flanges or compression fittings;
- one-piece (carried out with a heated tool or welding machine).
The most common type of detachable connection is flange.
It involves the use of slip-on metal flanges and bushings for them, which are welded to the ends of the pipes. Compression fittings are rarely used, mainly when the previous method cannot be used for some reason.
Requirements for polyethylene pipes according to GOST
GOST standards according to which polyethylene sewer pipes are produced:
- socket pipes and fittings are produced in accordance with GOST 22689-2014;
- smooth – GOST 18599-2001;
- corrugated - GOST R 54475-2011.
All types of pipes must comply with GOST in shape, size, fit within dimensional tolerances, have nominal dimensions from the size range according to GOST, and have strength in accordance with regulatory documents. The most important parameters are the external and internal parameters, dimensions, shape of the socket, wall thickness, ring stiffness.
Regulations
It must be said that GOST is not established for corrugated polyethylene sewer pipes; this type of pipe is produced according to specifications after agreeing on the properties of the material with customers. Conventional pipes are produced in accordance with GOST 22689.2 - 89. The main provisions of this document:
- For the manufacture of pipes, both HDPE and LDPE can be used.
- The lengths of produced pipes are 2000, 3000, 5500, 6000 and 8000 mm.
- The diameters of the produced pipes are 40, 50, 90, 110 mm.
- The standards strictly regulate the sizes of sockets on pipes, as well as the sizes of shaped parts - tees, crosses, etc.
- The pipes are designed to work with transported liquid having a temperature of up to 45 degrees. Short-term increases in ambient temperature up to 60 degrees are allowed.
Advice! GOST 22869.2 regulates the manufacture of pipes intended for the creation of gravity sewer systems. Pipes intended for installation of pressure pipelines are manufactured according to different standards.
Tips on how to choose
Almost all sewerage pipes are made from inexpensive and fairly durable HDPE. The choice of a specific type of product and installation method depends primarily on the conditions of laying the sewerage system - depth, pressure; its type - pressure or non-pressure. For pressure pipes, long polyethylene pipes are always chosen and installed like water supply pipelines.
For conventional non-pressure pipes, socket pipes and fittings are used. For very deep sewers, in places with the risk of landslides, land subsidence, in regions with increased seismic hazard, a two-layer corrugation is used.
The diameters for internal wiring are described above. For external systems in private houses, pipelines with a diameter of 110 mm are used; for risers and horizontal sections in a private house, 110 mm is also sufficient; to collect wastewater from several wells, communications with a diameter of 160 mm or more are laid. Large diameter pipelines are used for municipal sewers.
Cleaning the drainage system
Cleaning sewer pipes
Horizontal sections of the pipeline must have a slope to ensure gravity flow of water to the riser. The slope is also important for self-cleaning of the internal surface of the sewer. The need to clean a plastic pipeline occurs infrequently, since its smooth internal surface provides high throughput. But if this blockage has formed, then it can be eliminated in several ways.
- A plunger is useful if the blockage is minor. This is the most gentle cleaning method.
- A plumbing spiral cable will help if you are unable to clear the blockage with a plunger. It is better to use thin cables so as not to damage the system.
- You can also clean the drain with a special liquid. The instructions on the bottle label should indicate that it is suitable for plastic products.
- There is a hydrodynamic method for eliminating blockages using special installations. To clean the system with such a device, the owner will have to contact a competent plumber. This method is very effective, especially in case of clogged risers.
Proper selection and installation of polymer sewer systems for the home, as well as their careful operation, will allow residents to safely remove used water for many decades. This means the house will be clean and tidy.
Direct supply of PE 100 pipes from the manufacturer.
We produce and sell PE 100 technical pipes. We have solid production capabilities, in particular several production lines that can operate in parallel and fulfill several different orders. We always have pipes of popular diameters in stock. Our plant has the capabilities to produce PE 100 pipes of any shape: for example, triangular or trapezoidal. By purchasing pipes directly from the manufacturer, you can be sure that you will get them at the best price. In addition, only the manufacturer of PE 100 pipes can guarantee consistent high quality products.