Gas is one of the resources widely used for the needs of the population. It is used in heat supply systems, in factories, in food preparation, etc. It is difficult to imagine modern housing or an industrial enterprise without gas. But various types of overpasses can be used to supply it.
What is a gas pipeline?
Gas pipeline
is an engineering structure designed to transport gas and its products (mainly natural gas) using a pipeline. Gas is supplied through gas pipelines and gas networks under a certain excess pressure.
The need to classify gas pipelines is a logical consequence of the development of gas technologies in everyday life and industry. The very concept of classification presupposes a clear structuring and systematization of methods for laying gas networks for various operating conditions and needs.
The classification of gas pipelines of gas supply systems - assignment to one or another type of gas distribution (gas control) technology - is carried out according to certain rules and criteria. Among the characteristics by which networks are divided:
- Pressure (its level in the network).
- Execution material.
- Dislocation.
- Resource (pumping volumes), etc.
Safety precautions during operation of the main gas pipeline
Follow safety regulations in areas where the main gas pipeline is being installed.
A main pipeline is a potentially dangerous structure that can only be used in accordance with special instructions governing the construction and operation of main gas pipelines.
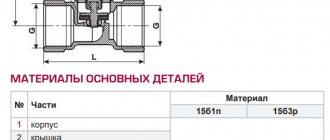
Industrial organizations using it are required to monitor the operation of the gas pipeline. They must also obtain a special passport in two copies. They are accompanied by a diagram on which all pipeline parts are shown, their type, manufacturer, material, and installed fittings are indicated.
The frequency of walking or flying around the entire territory of the structure is established depending on the maintenance standards. In the event of a natural disaster that could damage the pipes, an emergency inspection must be carried out. Inspections of pipeline crossings across highways are carried out annually.
Features of structures
Features of laying gas pipelines in cities
The frame of the station building is a lightweight steel structure. Its roof and walls are made of lightweight panels with two or three layers. In the second version, the parts are equipped with a special frame, which is covered on both sides with zinc, asbestos-cement or aluminum sheets.
According to the level of pressure in the manifolds, stations can operate according to plans that include from one to three superchargers installed one behind the other, which can also be connected in groups of several elements.
What pipes are used for installation?
Gasification of buildings is a complex task that is dangerous to life and health. Pipes must withstand pressure, be resistant to mechanical damage, and withstand climatic and temperature changes.
The material must be completely sealed, mostly homogeneous (joining by welding is allowed, but it is better to avoid this).
Pressure options:
- low up to 0.05 kgf/cm2;
- average up to 3 kgf/cm2;
- high up to 6 kgf/cm2.
At low pressures, thin-walled metal structures are used. They are suitable for carrying blue fuel to garden plots and private houses.
Such pipes are easily bent, soldered, and connecting elements can be installed. The top of the gas pipeline is coated with oil paint to avoid the appearance of condensation and, as a result, corrosion.
Another popular option for underground installation is plastic pipes. Made from polyethylene or polypropylene. Such designs are used for small plots, country houses, and outbuildings.
You cannot use a polyethylene model:
- with high blood pressure;
- in hot regions where temperatures rise above 45 degrees;
- there is a danger of ground movement, earthquakes, seismic activity;
- indoors, underground communications (tunnel and the like).
The main advantages of such pipes are: their low cost, ease of installation, and good performance characteristics.
If the gas line is under high pressure, monolithic metal is used . Soldering on such structures is not allowed. Copper pipes weigh lighter and meet all safety requirements.
Types of construction of gas overpasses
The classification according to the construction scheme includes 3 types of gas pipelines .
- Dead-end systems (one-way supply - gas transportation in one direction).
- Ring networks (gas flow is supplied through 2 or more lines due to the construction of closed circuits, of which there can be different numbers in different overpasses).
- Mixed.
The second point of this classification table, as practice has shown, is both more reliable and more convenient to use. In particular, during repair work or upgrading of the network, there is no need to disconnect all consumers of the ring gas supply system (it is enough to stop the gas supply only to the section that is being served).
All communication between gas pipelines of various types and consumers passes through gas control points (in short - GRP). The same structure includes gas control cabinets (GRC) and gas control units (GRU).
Pressure classification
In all cases, pressure remains one of the defining characteristics of the overpass. The rules of its operation, as well as the reliability, safety and power of the entire system depend on what type of gas pipelines
As for the purpose of networks in the table for classifying gas pipelines by pressure , then:
- High-pressure gas pipelines serve industrial enterprises and gas control points of medium-pressure pipelines.
- The medium-pressure gas pipeline supplies gas to utilities and small production facilities (as well as low-pressure systems).
- Low pressure overpasses serve the residential segment and utilities.
Is it advisable to lay a gas wire in a rut for a private home?
Gasification of a building is a costly and bureaucratic matter. All work on main wiring and gas pipeline connections is carried out by specialists. The organization must have permission and a license.
There are 2 ways to supply gas to buildings:
- Overhead . An inexpensive option, the pipe is laid on supports, used when it is necessary to carry blue fuel from the distributor to the building in close proximity. It is more convenient for gas service employees to maintain and repair such structures. If a leak occurs, it is detected and repaired faster. Disadvantage: it is much easier to damage such a gas pipeline, there is a danger to health and life, and constant monitoring of the integrity of communications is required.
- Underground . In this case, it is necessary to dig a trench. It is used in places of public buildings where there is a high risk of damage to open gas pipelines, in gardens and summer cottages, in order to hide and secure communications. Another option is trenchless construction. The gas pipe is laid using special equipment without opening the top layer of the earth. This is relevant in places where the road passes, so that there is no need to re-lay asphalt or paving slabs.
An open trench helps to clearly see the path along which the communication runs and the absence of damage to the gas pipeline itself. The wire material can be non-metallic, stainless, does not require painting and is better preserved, not exposed to temperatures and weather conditions.
Despite the fact that underground gasification is more expensive, the work will pay off during operation. There will be no costs for repairs and maintenance, the likelihood of leakage is reduced significantly. In large cities and regional gardening associations, overhead communications are rarely allowed, only if it is not possible to lay a trench.
Key points in network operation
First, performance. It is calculated taking into account the fuel and energy balance of the areas where transportation will take place. Maximum loads are predicted. You also need to take into account that a particular region may develop in the future, so the volume of delivered gas will increase.
Gas pipeline looping is used to increase productivity. If the pipeline operates at medium power, then centrifugal blowers do not particularly affect efficiency. But their role increases with increasing load.
Secondly, automatic adjustment. When designing a network, the features of managing gas mains are analyzed. To do this, determine the stability of the system and detect processes that are not sufficient for balanced functioning.
The importance of automatic adjustment increases in direct proportion to the transport distance
Modern technical means allow you to change productivity automatically. If the necessary equipment is not available, then the speed and efficiency of transportation drops to literally zero.
On the one hand, the movement of matter occurs under the influence of inertia. But on the other hand, the system slows down the movement both due to the rounding of the pipes and directly due to internal resistance. Given the complexity of the equipment, both factors require an individual approach.
A state-owned company is responsible for managing the gas pipeline. In Russia it is OJSC Gazprom
The third key point is notation. Special characters perform informational and warning functions. Placing signs is a mandatory rule for the use of main gas pipelines.
Designations allow you to identify objects, zone and depth of the pipeline. In fact, these are columns with two information blocks. The vertical area indicates the area of special danger, location and other important features.
And the horizontal one, with information about the location of the dangerous area, is installed at an angle of up to 30 degrees relative to the surface of the earth. It shows the distance in kilometers along the entire route.
Main structures included in the gas pipeline complex
According to SNiP, the main gas pipeline includes a pipeline and all branches with a pipe diameter of no more than 1420 mm. The excess pressure of the transmitted gas should not exceed 10 MPa.
The gas pipeline complex includes the following facilities:
Composition of main gas pipeline structures
- gas well with a “plume”;
- gas collection point;
- gas field reservoir;
- treatment plant;
- gas compressor station;
- main gas pipeline;
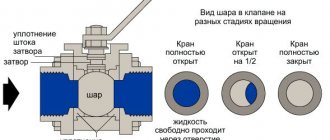
- locking devices;
- transition compressor station;
- transitions;
- communication line;
- spare set of pipes;
- along the highway with access roads;
- gas distribution stations;
- bends;
- protective structures;
- looping;
- city gas networks.
Looping is pipes that are laid parallel to the main pipeline. Loopings are constructed if it is necessary to increase the productivity of the pipeline. Their location does not matter.
Gas pipeline looping
Classification of gas pipeline by location
The classification of main gas pipelines based on location divides gas networks:
- For external and internal. The first ones are located on the street, they can be inter-shop, yard, or intra-block. Internal gas pipelines are located inside premises and workshops. Schematically, they represent a section of the gas supply system from the input to the connection point of devices that are supplied with gas (stove, radiator).
- Aboveground and underground (overwater and underwater, respectively).
Classification of gas pipelines by purpose in the gas supply network includes:
- Gas inlet pipelines. These include the section of the network from the internal highway to the disconnecting device at the input.
- Distribution - external sections of the gas pipeline, responsible for transporting gas from the main line to the entry point (can be separate pipelines in the supply systems of one facility).
- Gas pipeline inlet - a section from the point of connection with the distribution network to the shutdown system at the inlet.
- An inter-settlement gas pipeline is a distribution network located outside populated areas.
- Discharge.
- Purge systems.
Pros and cons of underground installation
Advantages of the underground installation method:
design safety, safety from damage, human factors, climatic phenomena;- aesthetic appearance;
- possibility of using plastic pipes;
- long service life;
- difficulty of unauthorized connection.
Flaws:
- the event is costly;
- it is necessary to clear the area of plants and trees, often the asphalt is opened at the site of communications;
- abundance of documentation for approval.