Composition and distances from construction sites to utilities, i.e. security zones are defined in SNiP 2.07.01-89* , the current valid edition of this SNiP is SP 42.13330.2011. Actually from this SNiP it follows:
- Security zone for domestic sewerage
- Water pipeline security zone
- Security zone of heating networks
- Security zone of cables and communication networks
- Power line security zone
- Security zone of residential buildings and public buildings
- Protected zone of trees and shrubs
- Gas pipeline security zone
- Minimum distances between utilities
Water pipeline security zone
The security zone of the water supply system is 5 meters from the foundation of the facility to the network. The security zone from the foundation of the fence of enterprises, overpasses, contact and communication supports, railways to the water supply system is 3 meters.
In addition, from SP 42.133330.2011 Table 16 (see below for more details), you can glean the following information regarding the laying of water supply and sewer pipes:
"2. The distances from the domestic sewerage system to the drinking water supply should be taken, m: to the water supply system made of reinforced concrete and asbestos pipes - 5; to the water supply from cast iron pipes with a diameter of up to 200 mm - 1.5, with a diameter of over 200 mm - 3; to the water supply system made of plastic pipes - 1.5.
The distance between the sewerage networks and industrial water supply, depending on the material and diameter of the pipes, as well as the nomenclature and characteristics of the soil, should be 1.5 m.”
Limitations and their reasons
Almost no work can be carried out in the sewerage area. If something needs to be done, it must be agreed upon.
Wells in the country
Well, if the territory is entirely private, it is still worth consulting with an engineer. Do not forget that even when owning a plot of land, the owner is responsible for its condition.
And this is normal, because in the Earth’s ecosystem everything is dependent on each other. If an infestation occurs in one place, it will affect nearby areas.
The cycle of substances in nature is of global importance. A sewerage system that breaks somewhere will affect the ecosystem as a whole, even if it is almost unnoticeable.
Pressure system repair
If we talk about the consequences near the accident and the sewer protection zone, they are by no means inconspicuous. This leads to problems for the environment, and therefore for people. The consequences also negatively affect surrounding buildings, communications, including the water supply.
Power line security zone
The current rules for determining the security zone for power lines are determined in accordance with Decree No. 160 of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 24, 2009. And in general, they say that the security zone for overhead power lines is a vertical plane at a given distance from the outermost wires of the power line.
The distance itself varies depending on the line power and is defined in the Appendix. According to paragraph a) of this appendix, for overhead lines, depending on the power, they will be:
| up to 1 kW | up to 12 meters |
| 1-20 kW | 10 meters |
| 35 kW | 15 meters |
| 110 kW | 20 meters |
| 150-220 kW | 25 meters |
| 300-500 kW | 30 meters |
| 750 kW | 40 meters |
| 1150 kW | 55 meters |
However, according to the same paragraph, if power lines are laid within the boundaries of populated areas under the sidewalk then:
- up to 1 kW, the permissible security zone from the outermost wires is 0.6 meters to the foundation of the building and 1 meter to the roadway.
- For lines over 1 and up to 20 kW, the security zone will be 5 meters .
According to the same annex, in places where power transmission lines cross navigable rivers , the security zone for them will be 100 meters . For non-navigable rivers, protection zones do not change.
In the security zones of power lines, a special land use procedure has been defined. Within the security zones, the land is not seized from the owner, but encumbrances are imposed on its use - do not build, do not store, do not block, do not hammer piles, do not drill pits, carry out work using heavy equipment only in agreement with the Network Organization, etc. P. for more details, see the resolution.
Security zones, although determined according to the application, are ultimately established by the owner of the networks , information about them is transmitted to the cadastral chamber. Paragraph 7 of the resolution states that the network organization must, at its own expense, place information about the presence, danger, and size of security zones, in these very zones - i.e. install appropriate information signs.
Specifics of prohibitions within the boundaries of ZSanO
The most stringent requirements are imposed on strict security zones (the first zone). On their territories it is forbidden to erect buildings and structures, dig trenches or otherwise go deep into the ground, store any materials, apply fertilizers, litter, cut down green spaces, graze livestock, go fishing, arrange moorings for boats, or swim.
Prohibition signs are attached next to the warning sign, indicating what is strictly forbidden to do in the sanitary protection zone
An extensive list of prohibitions has also been compiled for the second security zone. Construction and blasting work, driving piles and other actions that create vibration are prohibited. You cannot dump wastewater, develop the bowels of the earth, cut down forests, place warehouses for pesticides, fertilizers, fuels and lubricants, plow up virgin lands, or drain swamps.
It is not allowed to allocate space for cattle burial grounds, silage and manure pits, livestock and poultry breeding complexes, etc. The use of the protected area for living, active recreation, and sporting events is prohibited. It is prohibited to pull water pipelines through landfills, filtration fields, or near cemeteries.
Gas pipeline security zones
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated N 878 (ed. from ) “On approval of the Rules for the protection of gas distribution networks” Clause 7. The following security zones are established for gas distribution networks: a) along the routes of external gas pipelines - in the form of a territory limited by conditional lines running at a distance of 2 meters on each side of the gas pipeline; b) along the routes of underground gas pipelines made of polyethylene pipes when using copper wire to mark the gas pipeline route - in the form of an area limited by conditional lines running at a distance of 3 meters from the gas pipeline on the side of the wire and 2 meters on the opposite side; c) along the routes of external gas pipelines on permafrost soils , regardless of the pipe material - in the form of an area limited by conditional lines running at a distance of 10 meters on each side of the gas pipeline; d) around separate gas control points - in the form of a territory bounded by a closed line drawn at a distance of 10 meters from the boundaries of these objects. For gas control points attached to buildings, the security zone is not regulated; e) along underwater crossings of gas pipelines through navigable and floating rivers , lakes, reservoirs, canals - in the form of a section of water space from the water surface to the bottom, enclosed between parallel planes spaced 100 m on each side of the gas pipeline; f) along the routes of inter-settlement gas pipelines passing through forests and trees and shrubs - in the form of clearings 6 meters wide, 3 meters on each side of the gas pipeline. For above-ground sections of gas pipelines, the distance from trees to the pipeline must be no less than the height of the trees throughout the entire life of the gas pipeline.
List of regulatory documents
The mandatory creation of ZSANO, divided into zones, is provided for by the law “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population” ( No. 52FZ, 03/30/99 ). According to this law, the development of a water source protection system must be added to the water supply operation project and formalized as a separate project.
The design of ZSanO is based on SanPiN with code 2.1.4.1110-02 . This regulatory document determines how to calculate sanitary protection zones and describes the requirements for them from the perspective of sanitation and epidemiology. Ignoring the rules and regulations prescribed in SanPiN 2.1.4.1110-02 is fraught with a high probability of outbreaks of serious infectious diseases, mass poisonings, and epidemics.
Documents with the abbreviation SNiP will also be useful: 40-03-99 (new version 2.04.03-85), 2.07.01-89*, 2.07.01-89*, 2.05.06-85*, 3.05.04-85* , 2.04.02-84 (section 10 - Sanitary protection zones). In the building codes and regulations with the specified codes you can find the necessary information on the design of water supply and sewerage networks, on the development of populated areas, and on main pipelines.
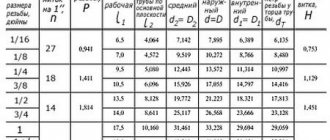
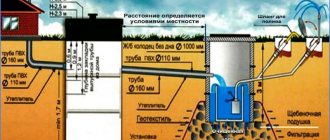
The standard depth for laying the water supply system is at least 0.5 m from the top level of the pipe, excluding soil freezing in winter. To the left and right of the trench there is land allocation for a sanitary security strip 10-20 m wide
Regulatory materials are the basis for developing standards taking into account the local characteristics of a particular region. City and rural administrative authorities are responsible for approving and adjusting norms for Sanitary and Sanitary Safety Inspections.
Minimum distances of gas pipelines.
Gas pipelines are distinguished by design (overground, underground), pressure inside the pipe (from several kilopascals to 1.5 megapascals) and pipe diameter. The distance from the gas pipeline to the building is determined in SP 62.13330.2011 in Appendix B. Here are excerpts from this application for underground and aboveground gas pipelines.
What is external sewerage
The meaning of “sewer protection zone” refers to external networks. This is a pipeline system through which domestic and industrial wastewater collected by internal drainage systems, as well as rain and melt water, are transported to pumping stations, and then to treatment facilities.
External sewer networks include:
- pipelines of various diameters
- wells: inspection wells
- differential
- rotary
When designing a sewer system, several significant factors are taken into account. Define:
- waste volume
- terms of Use
- distance to the nearest pumping station
- Possibility of connecting to an existing collector
- composition and properties of soils at the site of the proposed pipeline laying
- terrain
- groundwater level
- climatic conditions
- soil freezing index
Unlike the internal one, the external sewerage system is operated under more severe conditions. In addition to the impact of wastewater on the inner surface of the pipes, they are influenced from the outside by external factors - wet soil, aggressive environment, temperature changes. Installation of external sewerage is carried out from metal, plastic, as well as concrete and asbestos-cement pipes.
The sewer system diagram can be:
- separate - separate installation of rain and domestic sewerage
- semi-separate - separate collection of rainwater and domestic wastewater with further transportation in a common collector
- common - joint sewerage system
When designing and laying utility networks, you must adhere to the mandatory requirements of SNiP. Properly completed work on laying the external sewerage network will be the key to its long-term and trouble-free operation.
Annex 1
Recommended
Drinking water supply research program
1. Underground springs
1.1. Geological structure of the area where the source is located and general characteristics of its hydrogeological conditions; type of selected aquifer (artesian - confined, ground - unconfined), depth (absolute elevation) of the roof of the aquifer, thickness, water-bearing rocks (sands, gravel, fractured limestones); conditions and places of recharge and discharge of the aquifer; general information about the water abundance of the horizon (operational reserves); information on the current and future use of the aquifer for water supply and other purposes.
1.2. General information about the hydrogeological conditions of the area (field), recharge conditions of aquifers proposed for use for water supply, topographic, soil and sanitary characteristics of the water intake area, characteristics of the aquifer planned for exploitation (lithological composition, thickness, protection of the aquifer by overburden rocks, dynamic water level at calculated water withdrawal).
1.3. Data on the water permeability of layers, overlying layers, data on the possibility of influence of the recharge zone on water quality.
1.4. Sanitary characteristics of the area directly adjacent to the water intake; distance from the water intake to possible sources of water pollution: abandoned wells, absorption craters, sinkholes, wells, abandoned mine workings, storage tanks, etc.
2. Surface sources
2.1. Hydrological data: drainage basin area, surface flow regime, maximum, minimum and average flow rates, speed and water level at the point of water intake, average periods of freeze-up and break-up, estimated flow rate of water used and its compliance with the minimum flow rate at the source, data on the characteristics of tidal currents.
2.2. General sanitary characteristics of the pool in that part of it that can affect the quality of water at the water intake:
• the nature of the geological structure of the basin, soil, vegetation, presence of forests, cultivated lands, populated areas;
• industrial enterprises (their number, size, location, nature of production);
• reasons that influence or may influence the deterioration of water quality in a water body, methods and places for disposal of solid and liquid waste in the area where the source is located; the presence of domestic and industrial wastewater that pollutes the reservoir, the amount of wastewater discharged, facilities for its treatment and their location;
• distance from the wastewater discharge point to the water intake;
• the presence of other possible causes of source pollution (shipping, timber rafting, watering, winter dumps on ice, swimming, water sports, reclamation work, use of fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture, etc.).
2.3. Characteristics of the self-cleaning ability of a reservoir.
2.4. For reservoirs, in addition, the following is indicated:
• surface area and volume of the reservoir, useful and “dead” volume, feeding and use regime, water release in the reservoir, layout of the reservoir, its maximum and minimum depth, nature of the bottom, banks, bottom sediments, presence of blooms, overgrowth, siltation, direction of dominant winds and currents, the speed of water movement in the reservoir.
3. General information
3.1. Data on the possibility of organizing a sanitary protection zone for a water supply source, approximate boundaries of the sanitary protection zone for its individual belts.
3.2. Data on the need to treat source water (disinfection, clarification, deferrization, etc.).
3.3. Data on adjacent water intakes having the same supply area (location, productivity, water quality).
Design differences
Hydraulic pumps come in the following design types:
- Piston. Now they are practically not used for small pumping stations due to their bulkiness, low efficiency, and low lifespan.
- Centrifugal. One of the most popular and in demand due to its simplicity of design, efficiency and high reliability.
- Turbine. Similar to centrifugal ones, but with axial rather than lateral blades. More powerful and productive. They are mainly used in industrial hydraulic structures.
- Rotary or so-called screw pumps. They are distinguished by their small diameter dimensions, therefore they are most suitable for lifting water from wells.
- Vibrating or membrane. Cheap, but low-performance. The “Rucheek” and “Baby” models, which have been produced for summer residents for a long time, are known.
Types of double sockets
The main elements of an electrical outlet are the outer protective casing and the working part, which includes the base and contacts.
They are connected to each other by screw terminals - clamps necessary for connecting the cable of electrical equipment.
The only drawback of double sockets is that it is problematic to connect two high-power electricity consumers through them simultaneously
There is a misconception that double sockets are identical to assembled or dual models and represent several independent devices located close to each other, interconnected by cables.
If a double socket is connected to one power circuit, then electrical installation work is carried out according to a scheme similar to connecting a single socket. The only difference is the serial connection of two contact pairs within the electrical installation product
Technological progress does not stand still. Modern models are more advanced designs. In terms of rated voltage and current, they are strikingly different from the sockets that were ubiquitous during the Soviet era. For example, if in old-style models the permissible current did not exceed 10A, then for modern electrical installation equipment this figure is 16A.
Each part of a double socket can be connected to a separate power circuit if you first remove the brass jumper connecting them at the terminal
In reality, a double socket has one clamp and several distribution strips. Due to this, the electric current is supplied to both sockets equally, but its level will be divided depending on the power of the devices powered from the network.
Therefore, when replacing a failed old device with a new one, it is worth knowing its design features, which require certain nuances during installation.
The distance between the output contacts, as well as the diameter of the plug pins, in modern models is larger than in traditional analogues, and is 4.8 mm instead of 4 mm
According to modification, double sockets are classified into the following main types:
- Open and closed execution. In closed models, the holes are hidden behind curtains, which move to the side when the device is turned on. Devices of this type are indispensable for homes where there are small children. The curtains only work when pressed at the same time. Thanks to this, even if a foreign object is deliberately inserted, nothing dangerous happens.
- Without grounding and with grounding contacts. In models of the second type, grounding contacts are installed on the socket body, which protect electrical appliances and the user from breaking currents that accidentally “exit” the plastic body.
- For installation in rooms with high humidity and outdoor installation. Models of the first option are marked IP-44. They are equipped with a housing that protects the device from moisture penetration. Devices for outdoor installation are marked IP-55. Their highly durable housings are protected from dust contamination and moisture penetration.
Each type has a corresponding letter marking. For example: “A” indicates that this is an American double socket, “B” indicates the presence of a grounding contact.
Depending on the type of design and material of manufacture, devices are also divided into standard and polar, overhead and custom-made
Among the latest developments, programmed sockets are especially popular. Devices equipped with a timer turn on and off independently from the power supply after a set time interval has elapsed.
The protective housing of modern sockets is made of heat-resistant, unbreakable plastic. To enhance its decorative qualities, it is decorated with various inserts.
Thanks to the variety of design options, you can choose devices that will be invisible in the interior or, on the contrary, act as a worthy decoration.
When planning to install a double socket yourself, experts recommend choosing simple models without any modifications. Or give preference to double sockets with a spring-loaded plug ejector. Such models are convenient because they are equipped with springs that are activated when the plug is removed from the device.
To protect yourself by minimizing the risk of accidents, you should choose products from proven companies, ABB, and Legrand.
Responsibilities of the work producer
Working sewer systems are the key to good life support for city citizens, therefore, when carrying out work in the protected zone, the organizer of this work is obliged to:
- adhere to strict adherence to rules and regulations;
- ensure through their actions the safety and integrity of sewerage structures in the work area;
- in case of detection of inconsistencies in kind with the analysis provided by the water supply and sewerage organizations, take precautionary measures and suspend the work until a further decision;
- remove snow, ice, and debris in a timely manner to ensure free access to sewerage facilities;
- When handing over the object, invite a representative of the body that issued the permit to the commission.
These measures apply to producers operating in open areas.
General concepts
Sewer protection zones are areas that surround sewer network structures, bodies of water and airspace, where in order to provide protection to sewer systems, the use of certain actions or immovable objects is limited.
In such areas, it is necessary to refrain from such actions that contribute to harm to the structures of the sewer system:
- plant trees;
- obstruct passage to communication structures of the outlet network;
- produce a warehouse of materials;
- engage in construction, mining, blasting, piling work;
- carry out lifting work near buildings without the permission of the owner of the sewer network;
- carry out near networks located near water bodies, moving soil, dredging the bottom, immersing solids, pulling logs, chains, anchors of water vehicles.
The security zone + sewerage have their own boundary limits, which are set taking into account:
- location;
- appointments;
- diameter of buildings;
- gasket depth.
As a rule, boundaries are prescribed in a decree issued by the Minister of the Environment, but exact information can be obtained from local governments or water and sewerage organizations.
Summary
Land owners are required to pay attention to drawing up a thorough plan for the wastewater system, as well as to accurately implementing the finished project on the ground. It is also important to remember about decree number 578, aimed at coordinating the boundaries within which the telephone sewer security zone runs. This distance must be at least two meters on both sides.
If the state inspection reveals violations, the owner of the site will be obliged to carry out conversion work. Naturally, relocating the sewer system will result in serious financial expenses. And it is not always possible to do such work technically.
Everything useful about sewerage -
GidKanal | Yandex Zen
Standards for private housing construction
Directory SN 456-73 considers only main lines and collectors. It does not apply to areas allocated for individual housing construction. It is impossible to fulfill the requirements of SN 456-73 and comply with the standards for drainage of sewerage and water supply systems in private housing construction, since the dimensions of the strips for highways are too large. In addition, the size of the plots depends on several factors:
- the region in which construction is taking place;
- building density;
- the presence of sanitary or security zones;
- ground conditions.
In addition, other factors are taken into account:
- demand for plots;
- amount of vacant land;
- procedure for occupying areas;
- general development of the region, needs, standard of living of the population.
Based on these factors, the sizes of plots are adopted by local governments. Therefore, there is no standard in this matter. The minimum size is 3 acres, the maximum can reach several tens of hectares. It is impossible to use the same regulatory document in such conditions. It is impossible to determine the norms for land allocation for local sewerage, since the entire system is located on the site area and does not extend beyond its boundaries. Therefore, in such cases, only permissible distances to buildings, drinking water supply facilities, other structures or infrastructure elements are considered. For local water supply lines, the standards are more lenient, but for wastewater or disposal systems there are very stringent requirements. This is due to the specifics of the operation of autonomous treatment facilities and their potential danger to drinking wells or wells. At the same time, the construction of private systems is carried out within one site, so the use of standard standards becomes impractical. The only condition is maintaining distances to objects and structures, as well as correct installation of containers and pipes.
Regulation of laying pipeline networks
Pipelines for water supply systems are usually oriented towards serving a clean environment with minimal inclusion of foreign elements. Therefore, if the sanitary and hygienic standards are met, the installation of a water supply system is permitted in the first zone of protected areas. But, again, after careful research of the sources and consumers with whom he will have to work.
There are also prohibitive measures in place that completely exclude the organization of third-party networks within protected areas. First of all, this concerns the installation of water pipelines for main networks, regardless of their purpose. The same rule applies to other communications that interact with cleaning, industrial or agricultural facilities.
Vacuum valve for sewerage: Operating principle, installation + Photo and Video
With the installation of a sewer system, many questions arise.
Why this or that element, what function does it perform, is it really necessary in the wastewater disposal system. In the article we will consider such a detail as a vacuum valve for sewerage.
Before considering an air valve, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the operation of the sewer system.
Determination of standards for a drinking source
Sanitary protection zones for water supply facilities are spaces that allow the protection of aquifers and adjacent soils from polluting factors, as well as contributing to the complete safety of technical structures. Options for the parameters of such safety belts are described in detail in SanPiN 2.14.1110-02.
After an artesian well is drilled, water quality tests need to be done.
The following parameters are checked:
- Organoleptic and physical properties of drinking water: taste, color, degree of transparency, presence of various inclusions.
- Chemical composition, presence of inorganic and organic compounds, their concentration.
- Radiometric control, absence of dangerous isotopes.
- Microbiological composition, the presence of pathogenic bacteria, viruses, protozoa.
The conclusion is issued by the territorial division of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision. If there are no deviations from sanitary standards in all research protocols conducted by a certified laboratory, the water is recognized as suitable for drinking and cooking. If minor inconsistencies with the requirements are identified, the operation of the well is allowed only as a source of water for technical needs.