Good day, dear reader! Pipelines designed to supply water or heat to a room require high-quality protection from heat loss, mechanical stress and the negative effects of moisture, especially when it comes to their external areas. For these purposes, when assembling pipelines and distributions of private systems, galvanized pipe insulation is widely used, which effectively prevents the rapid wear of thermal insulation on the pipeline, freezing, the appearance of condensation and corrosive formations on its parts.
Why is insulation needed at all?
Galvanized steel insulation is a protective coating on the outer surfaces of pipes, which increases their resistance to corrosion, mechanical damage and harmful environmental influences.
It also gives the structure a more aesthetic appearance, helps to increase the operating temperature range of the transported substance, reduces heat losses and fire hazards.
What materials are used
This type of insulation is made of thin galvanized steel in the form of cylinders or shells of different diameters, from which you can choose the right option for any external pipeline.
Installation of galvanized protective shells is carried out on previously fixed heat-insulating material:
- polyurethane foam. This insulator has a low thermal conductivity coefficient, hygroscopicity, durability, good adhesion to steel and shell material, and is applied by spraying. By agreement with the customer, pipes in polyurethane foam insulation (PPU) are equipped with an ODK (operational remote control) system. It allows you to obtain real-time information about damage to the steel pipe and shell, the appearance of places where the thermal insulation layer is moistened, and malfunctions of the signal wire;
- PPU shells are products made of polyurethane foam, made in the form of detachable cylinders, half-cylinders, prefabricated elements. Fixed on the pipe using a tie;
- foam polymer mineral. The material has a low water absorption coefficient and retains heat well in the pipeline. The cost of foam-polymer-mineral insulation (PPM) is lower than other thermal insulator options;
- extruded polyethylene. Pipe insulation using extruded polyethylene is considered reinforced insulation (RUS). It is applied in a factory and forms a completely waterproof layer that is resistant to temperature changes and the effects of various chemical compounds and aggressive environments;
- rubber - bitumen mastic. Performs the function of waterproofing metal pipes without affecting the reduction of their thermal conductivity. The technology of insulation with rubber-bitumen mastic involves the application of several layers: a primer that increases the adhesion of metal surfaces, polymer-bitumen mastic and non-woven fabric for reinforcement. Polymer film or galvanization is used to wrap the insulated surface of the pipes.
What is zinc pipe casing?
The use of polyurethane foam insulation on pipes is necessary to protect against two negative factors: the influence of the external environment and physical stress, leading to compression of the insulation and, accordingly, reducing its thermal insulation properties.
Also, the use of an outer shell is an important part of the technological process, in which a liquid polyurethane foam mixture is poured into the space between the inner steel pipe conducting the working environment and the outer one, forming a layer of insulation of the required thickness and shape.
The outer protective shell is made of polyethylene or steel, which is protected from corrosion by galvanizing.
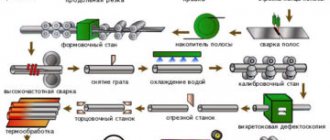
To produce external heat-insulating galvanized pipes, thin-walled steel up to 1 mm thick is used; during production, rolled pipe is dipped into a bath of hot zinc (hot galvanizing method) - thus obtaining a double-sided protective anti-corrosion shell. In production, zinc grades Ts0 and Ts1 are used according to GOST 3640-94; aluminum and lead are added to the bath (melted with zinc grade Ts2).
To increase strength, the outer pipe is produced with stiffening ribs; often a copper wire is built into the shell, which is necessary to monitor the integrity of the pipeline, the insulating coating and its outer shell.
Rice. 2 Rolled grades for the manufacture of PPU pipe coatings with galvanized steel
Polyurethane foam, from which the thermal protective shell is made, is found in everyday life in the form of foam rubber; it is used to make polyurethane foam, which is widely used in the construction industry. The component is obtained from the combination of two products of chemical oil refining - polyol and polyisocyanate; when a small amount of water is added to the mixture, carbon dioxide CO2 is formed, and its intense release causes foaming.
Purpose of galvanized protective covers
A galvanized casing is a cylindrical product with knurled drainage stiffeners. It is installed as a protective waterproofing shell on open pipelines with a thermal insulation layer of mineral wool or polyurethane foam shells coated with a waterproofing film.
Products are also produced in which the outer shell is made of polyethylene.
Requirements and standards for polyurethane foam OC pipe
The above requirements are regulated by GOST. According to GOST 30732-2006, OC polyurethane foam pipes are required to be produced using rigid polyurethane foam that meets the given standards.
Accordingly, the diameter and length of pipes are manufactured strictly in accordance with GOST. Excellent sizes are made only to order, and coordination will become problematic when used on construction sites.
For the outer shell, only first class galvanized steel is used. In this case, the thickness of the outer shell sheet should not be less than 1 centimeter. Galvanizing must be applied completely sealed.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: Insulation for protecting pipes, made of foamed polyethylene (thermal insulation)
Polyurethane foam should have a homogeneous texture with fine-grained pores. There should be no voids in the insulation layer. If the size of the voids exceeds 1/3 of the thickness of the polyurethane foam, then the product is defective.
Sometimes you can see double pipes of polyurethane foam OC. Most often, such pipes are used to save money, but a double pipe does not comply with GOST 30732-2006.
Requirements, Properties and technical characteristics of the coating
When laying pipelines openly, to protect the thermal insulation of the pipes, they are made using a spirally rolled shell made of thin-sheet galvanized steel of class 1 or 2 (GOST 14918-80), in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.0414-88.
The surface of the shell, according to GOST, should be perfectly smooth on the outside or with slight longitudinal stripes and waviness that does not take the pipe wall thickness beyond the permissible limits, and rough on the inside. Both surfaces should be free of bubbles, cracks and foreign matter.
Main technical characteristics of the products:
- wall thickness - 0.55 - 1.0 mm;
- range of outer diameters - from 100 to 1600 mm;
- the length of straight sections is 8 -12 m for pipes with a diameter of less than 219 mm and 10 - 12 m for products with a diameter of 273 mm or more.
Pipes PPU OTs
PPU (polyurethane foam) - gas-filled plastic (foam) comes in two types: rigid and elastic.
When creating polyurethane foam OC pipes, a rigid variety is used, since it has a low thermal conductivity coefficient.
The production of polyurethane foam OC pipes takes place in the factory. First, a metal pipe is manufactured and placed in an outer shell of galvanized steel, which reduces the water permeability coefficient to a minimum and increases the service life of the pipe.
The outer shell protects the insulation from mechanical stress, fire and moisture. Polyurethane foam is poured into the gap between the steel pipe and the outer shell. After the insulation hardens, the finished product is obtained.
In essence, the product is a “pipe within a pipe”, and the space between the shells is filled with insulation.
After manufacturing, the pipes undergo a series of checks to ensure compliance with quality standards:
- Full check of welds for leaks, unless a seamless production method was used.
- Material axial shear compliance tests.
- Compliance of materials with GOST: the thickness of the insulation, the degree of polishing of the pipes, the diameter of the product must comply with the standards.
Galvanized steel is resistant to corrosion and costs less than stainless steel. The use of galvanized steel in the manufacture of the outer shell increases the service life of the product and makes it expedient to use polyurethane foam OC for creating external communications.
Properties and characteristics
The characteristics of finished products are regulated by state regulations. In this case, each element of the polyurethane foam OC pipe must comply with GOST.
The galvanized shell is moisture resistant, which expands the scope of application of the product. In combination with low thermal conductivity, polyurethane foam OC pipes become the best option for external water and heat supply.
Note! Of the insulation materials, polyurethane foam has the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient, and at the same time, its price can compete with other types of insulation materials. The combination of characteristics has made polyurethane foam a universal means of insulation, used in almost all areas of construction.
We recommend that you read: Using paint for the surface of galvanized pipes
The characteristics of the finished product must correspond to the table below:
| Properties | Measure | Index |
| Insulation layer density | Kg/m3 (kilogram/cubic meter) | Minimum 60 |
| Density at 10% radial compression | MPa (megapascal) | From 0.3 |
| Thermal conductivity at 50°C | W/m*K (watt/meter*Kelvin) | No more than 0.033 |
| Shear strength at (23±2)°С Shear strength at (140±2)°С | MPa (megapascal) | Minimum 0.2 Minimum 0.13 |
| Indicator of radial creep of thermal insulation with maximum temperature (140±2)°С | Mm (millimeters), within 100 hours Mm (millimeters), within 1000 hours | Up to 2.5 Up to 4.6 |
| Water absorption in boiling water over a period of 90 minutes | % by volume | Maximum 10% |
OC polyurethane foam pipes reduce heat losses to 1–2%, which is an excellent indicator that is superior to other types of insulation. The production cost is quite high, but the characteristics and durability allow the material to pay for itself.
Polyurethane foam is highly flammable upon contact with an open fire; in accordance with GOST 30244, it belongs to the highly flammable group G4.
OC polyurethane foam pipes are non-toxic and do not harm health or the environment, but polyurethane foam can release extremely toxic impurities when burned. However, the galvanized outer shell is a reliable means of protection against open fire.
The pipes are also equipped with copper indicator conductors with a cross-section of 1.5 mm2. These indicators allow you to monitor the status of communications remotely and find problem areas with high accuracy.
Advantages and disadvantages of protective coating
The advantages of galvanized casings include:
- light weight (galvanized steel sheets have a large area and at the same time weigh little);
- simplicity and ease of installation on already assembled structures;
- fully ready for installation;
- having high strength;
- durability;
- compliance with all fire safety rules and building codes;
- compactness and ease of transportation;
- aesthetic appearance;
- Possibility of use both outdoors and indoors.
The disadvantage is the need for periodic inspections during operation to identify damage, followed by replacement of the unusable part with a new product of the same dimensions.
Designs and types of shaped products
Utility networks have a complex spatial configuration and include shut-off, control and control valves. Therefore, to insulate such structures, not only straight sections are needed, but also various shaped elements: tees, bends, transitions, plugs, etc.
Straight section
This is a ready-to-install product in the shape of an open cylinder. It is mounted overlapping with other segments, secured with locks - latches, self-tapping screws or rivets.
Main standard sizes of straight sections of shells:
- length – from 470 mm to 1000 mm;
- outer diameter – from 60 mm to 500 mm (in 10 mm increments), from 90 mm to 1000 mm (in 10 mm increments);
- holes for fastening – 4-6 pcs. with a diameter of 2.7 mm for screws or in quantities of 3-6 pcs. with a diameter of 3.2 mm for installing rivets or snaps.
Retraction
Bends - parts made of galvanized steel with a thickness of 0.55; 0.7; 1.0 mm with a bend radius of 90 or 45 degrees. They are used in places where the pipeline changes direction to protect the thermal insulation of shaped elements.
Tee
Tees protect branching points of pipeline networks. Available in several versions:
- round T-shaped 90 degrees;
- straight with the same length of pipes;
- with shortened shoulder length at 30 and 45 degrees.
They are installed in the same way as rectilinear products with an overlap, fastened with metal screws (such as bugs) or rivets.
Plug/transition
End caps - designed to protect the heat-insulating layer at the end of pipelines. They consist of two parts with ridges, mounting holes and screws.
A transition is a straight section of a shell of concentric or eccentric shape, ready for installation. It has one longitudinal and two transverse ridges, holes for fasteners and the required number of screws. It protects a shaped product installed at the junction of pipes of different diameters or made of different materials.
Zeppelins
Zeppelins are round shaped products made up of segments (petals).
Along the edge of each segment there are ridges and holes for rivets (screws). Zeppelins are used to insulate the ends of tanks and reservoirs.
Casings for valves and flanges
They are made in the form of a split box with the necessary ridges and special locks - latches, for rigid and reliable fixation of parts of the product. They serve to protect the heat-insulating layer from the negative effects of the environment in places where shut-off devices, various instrumentation and flange connections of the pipeline system are located.
Cones
Cone shells are a type of galvanized coating of a cone shape with the presence of longitudinal and transverse ridges. They perform the function of protecting the thermal insulation layer on the end surfaces of containers, on chimney pipes and ventilation outlets from the street side.
Insets
The shell for insertion is a straight section that has longitudinal and transverse ridges and a curved connection for mating with the main insulation element, holes for fasteners and the required number of screws. It is used to protect the insulation layer at the junction (branch) of lines from the main pipeline.
approximate cost
The approximate cost of straight sections of galvanized steel casings is given in the table.
| Outside diameter | Price per piece, in rubles |
| Ø 100 | 180 |
| Ø 125 | 230 |
| Ø 160 | 300 |
| Ø 200 | 370 |
| Ø 250 | 460 |
| Ø 315 | 565 |
| Ø 400 | 880 |
| Ø 450 | 992 |
| Ø 500 | 1110 |
| Ø 560 | 1225 |
| Ø 630 | 1378 |
| Ø 710 | 1686 |
| Ø 800 | 2058 |
| Ø 1000 | 2572 |
| Ø 1250 | 3200 |
Scope of application and installation features
Shells made of galvanized steel have high performance characteristics and an affordable price, therefore they are widely used in:
- hot and cold water supply systems
- sewer lines;
- pipelines of the oil and gas industry;
- thermal routes laid underground, in trenches, and above ground;
- ventilation systems;
- arrangement of stoves, fireplaces (chimney insulation);
- fire-fighting water supply systems;
- systems of supply and discharge pipelines with circulating process fluid;
- to protect open working parts of machines and mechanisms.
The process of installing a galvanized shell is quite simple, does not require the use of special technological equipment and can be easily done with your own hands.
Non-professionals can use the following step-by-step instructions for isolating a separate section in an already operating highway:
- clean the surface of the required section of the pipeline from dirt;
- degrease it with white alcohol or solvent;
- apply an anti-corrosion coating of bitumen primer to the surface of the working pipes;
- remove wetted parts of polyurethane foam insulation at the ends of adjacent pipe sections;
- heat the protective shell at the joint to a temperature of about 80°C - a special adhesive tape (bitumen-rubber MBR) is placed in this place;
- fix the protective galvanized shell at the joint, securing the product with special clamps or cuffs;
- drill several holes for pouring polyurethane foam;
- mix the foaming agent and pour it into the prepared holes;
- Seal the holes with Abris sealing tape.
The main condition is that installation must be carried out at an ambient temperature of at least + 20°C and in dry weather.
In rainy weather, work should be done under a canopy or other type of shelter, otherwise moisture may penetrate in the form of condensation or precipitation into the inner layer of insulation.
Installation of galvanized polyurethane foam protection
The installation of pipes is carried out by welding; to seal the joints, a polyurethane foam mixture is used, which is poured into the empty space using formwork made of galvanized sheets. To connect galvanized pipelines, a two-component polyurethane foam composition, a cover sleeve made from a segment of zinc shell and bitumen-rubber adhesive tape are used, the work is carried out in the following sequence:
- After checking and inspecting the quality of the weld, prepare a workplace to ensure free access for the worker to the joint, construct a temporary shelter from precipitation, the air temperature should not fall below -25º C.
- Clean, wash and dry the surface of the zinc shell, clean the pipe from dirt, paint, traces of scale and rust with a stiff brush until it has a metallic shine, degrease the inner surface of the casing and the galvanized shell in the contact area with solvent grade No. 646.
- Remove the waterproofing from the ends of the pipes to a depth of 15 - 20 mm; if it gets wet, remove the layer until a dry surface appears.
- The conductors of the operational remote control system (ORS) of adapters and pipes are connected or paired together.
- Cut out two strips of adhesive tapes with a pipe circumference length of 50 mm, heat the pipe ends with a gas burner to 80 - 90º C and glue the strips onto the surface, which melt slightly upon contact with the metal.
- In the same way, glue the strip to the longitudinal surface of the metal casing after heating the contact point with a gas burner.
- Install the protective casing on the surface of the pipes overlapping so that one edge goes from top to bottom, fix it at the edges with tightening belts.
- Using gas burners, the surface of the casing is heated along the edges and at the place of the longitudinal connection, gradually tightening the belts, the procedure is continued until the steel casing tightly fits the joints and extruded adhesion appears at the edges. To bleed air and fill, a hole with a diameter of about 10 mm is drilled in the upper part.
- Using a screwdriver and self-tapping screws, connect the edges of the casing along the entire length and circumference in increments of 100 - 250 mm, with a distance of 10 -15 mm departing from the edges.
Rice. 9 Adhesive tape, which is installed at the joints of the PPU pipeline - The joint is filled at a temperature of 20 - 25º C, if the ambient temperature is below -10º C, the casing is heated with a burner in the range from 20 to 40º C, two drainage holes with a diameter of 3 mm are drilled on top along the edges of the cuff.
- The PU foam components are mixed at a temperature of 18 - 25º C in the amount necessary to cover a given volume, first pour out the contents of the container with composition A and add a standardized amount of B, mix for 20 - 30 seconds until a homogeneous composition is obtained using an electric drill and a mixing nozzle.
- The composition is poured through the upper 10 mm hole of the metal casing, and the entrance is closed with a small pre-cut metal plate (140x50 mm).
- The appearance of foam in the drainage holes signals that the volume is completely filled; after 20 - 30 minutes, remove the lid and remove excess polyurethane foam from it, and clean the 3 mm drainage channels from the polyurethane on top.
- Heat the casing in the area of the filler hole to a temperature of 80 - 90º C, apply adhesive tape and then a lid to it, press the cover with a tightening belt and fix it in the corners with four self-tapping screws (rivets).
- Using pieces of 40x40 tape, cover the drainage 3 mm external outlets along the edges, applying them to a surface preheated by a gas burner, after which the holes are closed with plugs using self-tapping screws or rivets.