Main characteristics
This type of rolled pipe is capable of withstanding high pressure of the transported medium, and the enhanced wall thickness parameters and high quality of the alloys used allow it to be used on the most critical pipelines, in complex components of machines and ships.
Products are made from carbon, alloy or low-alloy steel.
Classification of a pipe as thick-walled is determined by the ratio of the external section and wall thickness. A coefficient from 6 to 12.5 is a sign that the rolled product belongs to this class. An indicator less than six indicates a particularly thick-walled product.
Standardized parameters for seamless steel pipes are:
- Outer diameter.
- Wall thickness.
- Length.
When choosing a product, the manufacturing method is important.
Pipe connection methods
The most common are welded joints. Pipes of any size are connected by welding; For convenience and reliability of the weld, pipes for welding are supplied with chamfers.
Large-diameter pipes (from 50 millimeters or more; the division by diameter is quite arbitrary - flanges are found on pipes with a diameter of 40 millimeters and on thinner ones) use flange connections. A paronite gasket is used as a means of ensuring tightness.
Large diameter pipes can be connected with flanges
Small diameter pipes use threaded connections. GOST also regulates how threaded fittings for steel pipes are produced, and more than one.
So,
- GOST 8966-75 regulates the production of couplings;
- Steel nipples are produced in accordance with GOST 8967-75;
- Locknuts are made according to GOST 8968-75 standard;
- Squeegees must be manufactured taking into account the requirements of GOST 8969-75.
Materials for threaded fittings include brass (often chrome-plated), stainless steel and cast iron. Fittings are also made from black steel, but their use is not recommended: as they rust, they stick tightly to the pipe, and it is very difficult to disassemble such a connection without annealing.
Classification and types
Seamless thick-walled pipes are divided into two types: hot and cold rolled.
According to their characteristics and manufacturing methods, they are divided into 4 categories:
- “B” - made from steel standardized in terms of chemical composition with a minimum degree of oxidation.
- “B” – using heat treatment.
- “E” – without hardening.
- “D” – with passing hydraulic tests.
Difference between hot and cold rolling
The main difference is the operating temperature. With the hot method, the metal is easier to process, but the surface quality and geometric accuracy of the product produced will not be of the highest level.
Cold wire rod allows you to obtain a smooth, even surface and maintain the specified accuracy parameters. The products are distinguished by higher strength and quality. But their cost will be higher.
Application area
The high strength and low specific weight of seamless steel pipes make them in demand in many economic sectors. When constructing pipelines intended to move gases and liquids under high pressure, most bends are used without longitudinal seams.
Mining of oil and gas
In the gas and oil production sectors, thick pipes are used for transporting gas and liquid media over long distances, as well as for drilling. At great depths of excavation, the risks of increased soil pressure and rock shifts increase, which requires the use of a particularly strong casing structure. Seamless channels with reliable walls, made of high-quality alloys, will ensure trouble-free operation of drilling equipment.
Arrangement of hydraulic systems
Hydraulic systems are present in many lifting installations, important components of automobiles, and are used in industry and construction. Their work is distinguished by extreme temperature and high pressure force. Thick-walled steel pipes, which have a large margin of safety, successfully withstand these conditions.
Chemical industry
In the chemical industry, pipes with both thick and thin walls are used. Durable, thick-walled ones are used for transporting gases and toxic substances where there is high pressure. Thin-walled tubes are actively used in laboratories and medical instruments.
Energy production
Power plants are characterized by constant changes in internal excess pressure and high ambient temperatures. In these extreme operating conditions, the use of thick-walled seamless pipelines is optimal.
Shipbuilding and aircraft manufacturing
In these industries, one of the main tasks of designers is to minimize the weight of the main product. For this purpose, materials are used that must be reliable in operation and have low weight. The highest tensile strength and light weight of the seamless pipe fully meet these requirements of aircraft and shipbuilders, so the products are widely used among them
Advantages and disadvantages
Solid-drawn pipes produced by the cold rolling method are distinguished by greater strength and better workmanship than the hot rod range.
Treated with galvanizing and chrome plating, they perfectly resist corrosion.
Thick walls allow them to be used in difficult operating conditions.
According to experts, there is only one drawback - the high price per ton, almost twice as much as that of hot-deformed analogues.
No seam plus or minus
Seamless pipes are more reliable compared to electric welded ones. However, they are significantly more expensive.
Suture products can be made with a larger diameter and longer length than seamless products. The range of their diameters and sections is significantly wider.
Both types are in demand in their niches. Electric-welded ones have fully justified themselves for water and heat supply, primarily from an economic point of view. Seamless rolled steel is used where there is high pressure and greater strength is needed.
Standards and regulations
The production of seamless thick-walled pipes is carried out in accordance with the requirements of state standards and other regulatory documents. Standardized:
- Standard sizes.
- Weight.
- Limit deviations.
- Manufacturing methods.
- Structure of the chemical composition of alloys.
Guests
For the manufacture of BT, two main GOST standards are used.
GOST 8732-78 regulates the range of hot-rolled pipes, GOST 8734-75 applies to cold-rolled products.
For the production of rolled tubular products for special purposes (for example, for PJSC Gazprom), other state standards or technical conditions are used.
From 2010 to 2015, the national standard GOST R 53383-2009 was in force, which was subsequently replaced by GOST 32528-2013.
Weight and tolerances
Accurate determination of the mass of products is necessary for calculating loads in structures and selecting suitable lifting equipment for transporting products.
The weight is calculated per unit length of the pipe. It depends on the outer diameter and wall thickness. The tables of the relevant GOSTs indicate the standard weight values of rolled products for each standard size.
Standardized deviations in weight do not exist, but in case of deviations in size, the mass is calculated based on the arithmetic average of the minus and plus tolerances indicated in the corresponding GOST tables.
Dimensions
The diameters of hot-rolled pipe products according to GOST 8732 78 are calculated in the range from 2 to 55 centimeters. Wall thickness – from 25 mm to 75 mm. Pipe lengths from 4 to 12.5 meters are cut.
Cold-rolled products according to GOST 8734-75 are presented with slightly smaller diameters: from 5 to 250 mm. The wall thickness ranges from 0.3 to 24 mm.
Measured and unmeasured rolled lengths are allowed from 4m to 12.5m.
Formula for calculating mass
State standards provide a formula for calculating the theoretical mass of one meter of a product in kilograms.
M=0.02466 x S (D - S),
wherein:
- D – external section in mm.
- S – wall thickness (mm).
- M – mass.
The steel density value taken for calculations was 7.850 g/cm3.
Duration of operation
The service life of steel water pipes is very impressive. For these reasons, they have become the undisputed leader for highways for various purposes. In the heating system it is better to use pipes made of black steel, and in the water supply it is more appropriate to install galvanized types.
When using these products in metal communication systems, it is necessary to pay attention to the features of their production. This is reflected in the duration of use.
Rolled pipes can be electric welded and can be installed in water supply, heating and gas supply networks. Their problem is that their throughput volumes are smaller than those of similar copper or polymer pipelines.
The reason for this is the surface inside steel plumbing systems, it is rough and creates eddy currents in the distilled liquid. Thus, the flow of the medium is hampered.
A distinctive feature of these pipes is that their service life is not affected by hydraulic load. High loads of this kind do not reduce the service life of a steel pipeline.
Often such a network operates in difficult conditions: underground and at a coolant temperature close to boiling point, and with hydraulic shocks reaching up to 15 atmospheres.
Plastic and metal-plastic pipelines cannot cope with this operating mode. They would fail after 10-15 minutes of such work, but the steel structure will reliably last for a long time.
Dimensions
Steel pipes have the following standard sizes, which are taken into account during design developments:
- Conditional pass. This is a conditional indicator that is used to describe the highway. This is the actual designation of the internal diameter, rounded to the nearest standard number. In accordance with GOST 28338-89, the value is rounded in the direction of increase. Measurements are taken in inches or millimeters. For water supply pipes, the range of sizes ranges from 1 to 15 cm.
- Inner diameter. This is an exact figure for the volume inside, which is obtained by direct measurement. It is set in millimeters.
- Outside diameter. This is the volume value with the calculation of the wall thickness.
- Wall thickness. This value is regulated.
The length in such a situation is not a constant value; in calculations it is taken into account as a pressure regulation factor and as an economic one. These systems are produced in measured short lengths, which means in the form of standard pieces. And they can be produced in a non-measured version. In this case, the dimensional values are from 4 to 12 meters.
Video: consider the characteristics
Comparative characteristics of water pipes
In systems for measuring water pipes, the inch system is used, and the dimensional values of pipes in all other cases are indicated in millimeters. For greater convenience, millimeter notations are used in practice along with inch notations.
In the metric version, mm is considered the standard of measurement, and this value is stable. In the imperial system, inches show not only standard measurement options, but also conditional ones. This is based on the characteristics of the carving.
The difference between the two types of products is visible at first glance. This is indicated by the size of the thread and the roundness of the threads on the pipe.
IMPORTANT! Inches are converted to mm as follows. Knowing that 1 inch equals 2.54 cm, you can accurately calculate the millimeter value of the pipe diameter. Round everything in the direction of increase.
Diameter table
The diameters of steel pipes for water supply are shown in the table.
| Conditional passage (DU) | Thread volume |
| 10 | 3/8 |
| 15 | 1/2 |
| 20 | 3/4 |
| 25 | 1 |
| 32 | 1 ¼ |
| 40 | 1 ½ |
| 50 | 2 |
| 65 | 2 ½ |
| 80 | 3 |
| 90 | 3 ½ |
| 100 | 4 |
| 125 | 5 |
| 150 | 6 |
The standard diameters of these pipes, which are regulated by GOST, are shown in the following table.
| Conditional passage (DU) | Diameter volume outside |
| 6 | 10,2 |
| 8 | 13,5 |
| 10 | 17 |
| 15 | 21,3 |
| 20 | 26,8 |
| 25 | 33,5 |
| 32 | 42,3 |
| 40 | 48 |
| 50 | 60 |
| 65 | 75,5 |
| 80 | 88,5 |
| 90 | 101,3 |
| 100 | 114 |
| 125 | 114 |
| 150 | 165 |
Which pipes to choose for water supply.
The volume needs to be known exactly. Such knowledge makes it possible to calculate the amount of medium carried through the pipeline. Such knowledge is especially valuable when arranging household systems.
For example, these indicators will be needed when working with a heating system, when you need to calculate the network so that in winter all rooms in the house are heated evenly. For each specific situation, such calculations are made using special tables.
If in doubt, it is better to call specialists for help. A properly and correctly installed steel network will serve uninterruptedly for a very long time. In this way you can save not only nerves and time, but also finances.
An improperly installed water supply system can quickly become unusable, and repair work in this case is costly. It is for these reasons that competent, qualified assistance from craftsmen can save money.
Size chart of different water pipes
The following table shows the sizes of different water pipes.
| Conditional passage (DU) | Seam pipes (mm) | Seamless products (mm) |
| 6 | 10 | 10,2 |
| 8 | 13,5 | 13,5 |
| 10 | 17 | 16 |
| 15 | 21,3 | 20 |
| 20 | 26,8 | 26 |
| 25 | 33,5 | 32 |
| 32 | 42,3 | 42 |
| 40 | 48 | 45 |
| 50 | 60 | 57 |
| 65 | 75,5 | 76 |
| 80 | 88,5 | 89 |
| 90 | 101,3 | 102 |
| 100 | 114 | 108 |
| 125 | 114 | 133 |
| 150 | 165 | 159 |
Assortment
The range of steel pipes is shown in the table provided. Here is the data on how much the pipe weighs. The same regulatory standards determine the thickness of metal water pipes. It can also be found in the table provided.
| Conditional passage (DU) | Lungs | Ordinary | Reinforced | |||
| Wall thickness | Weight | Wall thickness | Weight | Wall thickness | Weight | |
| 6 | 1,8 | 0,3729 | 2 | 0,4044 | 2,5 | 0,4747 |
| 8 | 2 | 0,5672 | 2,2 | 0,6131 | 2,8 | 0,7389 |
| 10 | 2 | 0,7398 | 2,2 | 0,8030 | 2,8 | 0,9805 |
| 15 | 2,35 | 1,098 | — | — | — | — |
| 15 | 2,5 | 1,159 | 2,8 | 1,277 | 3,2 | 1,428 |
| 20 | 2,35 | 1,417 | — | — | — | — |
| 20 | 2,5 | 1,498 | 2,8 | 1,657 | 3,2 | 1,862 |
| 25 | 2,8 | 2,120 | 3,2 | 2,391 | 4 | 2,910 |
| 32 | 2,8 | 2,728 | 3,2 | 3,086 | 4 | 3,778 |
| 40 | 3 | 3,329 | 3,5 | 3,841 | 4 | 4,340 |
| 50 | 3 | 4,217 | 3,5 | 4,877 | 4,5 | 6.159 |
| 65 | 3,2 | 5,706 | 4 | 7,053 | 4,5 | 7,879 |
| 80 | 3,5 | 7,337 | 4 | 8,336 | 4,5 | 9,322 |
| 90 | 3,5 | 8,442 | 4 | 9,598 | 4,5 | 10,74 |
| 100 | 4 | 10,85 | 4,5 | 12,15 | 5 | 13,44 |
| 125 | 4 | 13,42 | 4,5 | 15,04 | 5,5 | 18,24 |
| 150 | 4 | 15,88 | 4,5 | 17,81 | 5,5 | 21,63 |
Steel water pipes are very common and there will be no problems purchasing them. This can be done through platforms for selecting the purchase of building materials.
Such places provide a large variety of offers. After carefully reading them, you can choose the most suitable option for purchase.
Seamless steel pipe production
When ordering, you can choose a transportation option, and if necessary, you can rent equipment for installing a steel main.
Despite the increased popularity of plastic highways, steel still remains one of the most popular materials, and durable steel networks are the best proof of this.
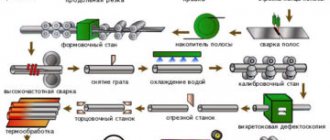
Manufacturing methods and technologies
Seamless pipes made of ferrous metals are produced in one of two ways:
- Hot rolling.
- Cold deformation.
The process takes place in industrial conditions on pipe rolling units. The basis is a cylindrical metal blank, which is heated until the steel crystallizes and acquires the required degree of ductility. Next, on a piercing machine, a through hole is pierced with a mandrel and a hollow pipe blank is obtained.
Hot deformed
Then the billet is rolled out at high temperature in a rolling mill, where, using rolling, a pipe of the required diameter with the required wall thickness is obtained from it.
The product is cooled with water.
The final calibration is performed using rolling.
The process is completed by cutting standard sections in accordance with GOST standards, as well as taking into account the customer’s requirements.
The entire production process is carefully controlled. Defective products must be melted down. Manufactured products are tested according to established methods.
Cold-worked
The process of manufacturing cold-deformed pipes at the first stage is similar to the production of hot-rolled pipes. But here the cooling procedure is carried out immediately after manufacturing the workpiece on a piercing machine. At the same time, for cold wire rod, hot-rolled products with a slightly larger diameter are used - the so-called “roll”.
The cold deformation process is carried out either by rolling (stretching the workpiece on a rolling mill until the desired diameter and wall thickness are obtained) or by drawing the workpiece through a hole of a smaller cross-section (drawing ring). The second method takes longer, since pulling is carried out in several cycles through a ring that gradually decreases in cross-section.
During manufacturing, cold-rolled pipe is annealed to improve its performance.
Production
Welded pipes
The raw material for any welded pipe is a flat steel sheet; however, most often it is delivered from the metallurgical plant rolled into a roll.
- The sheet is cut into narrow longitudinal strips;
- The strips are welded into an endless narrow strip;
- The tape is rolled by rollers into a round piece with an open seam;
- After which the seam is boiled;
- The pipe is calibrated in the next rolls;
- The seam is tested for leaks. Eddy current flaw detection is most often used, but ultrasonic flaw detectors are also available;
- The pipe is cut into pieces of the required length and sent to the warehouse.
Important: pipes welded with TIG - a tungsten electrode in an inert gas environment - are considered the most durable.
However, HF-welded pipes made using induction welding with high frequency currents are noticeably cheaper. The reason is the welding speed is approximately 20 times higher compared to TIG.
At one end of the line you can see a narrow steel sheet. On the other are finished welded pipes. The presence of a person is only necessary for control
Seamless pipes
The production of a hot-deformed pipe in general looks like this:
- A monolithic cylindrical workpiece—a rod—is heated in a furnace to a temperature above the recrystallization point of steel; in this case the metal becomes plastic;
- On a piercing mill, the workpiece is transformed into a hollow cylinder . Externally, it is already a pipe, but rather irregularly shaped and with dimensions far from the target;
- After which the actual rolling of the workpiece in rollers begins - its hot deformation. The future pipe acquires the required diameter and wall thickness, then cools and calibrates;
- The finished pipe is cut into pieces of the required length and stored.
All operations are carried out with hot workpieces
The production of cold-deformed seamless pipe differs in only two aspects:
- After the piercing mill, the workpiece (it is called a sleeve) is cooled with water and all further operations are carried out cold;
- Before final calibration, a mandatory production step is annealing - heating to the recrystallization temperature and cooling. In this case, the internal stresses accumulated during deformation leave the metal; in addition, it becomes more viscous.
Please note: thick-walled steel pipes are produced seamlessly.
The walls of a hot-deformed pipe can reach a thickness of 75 millimeters, and of a cold-deformed pipe - 24 mm.
If necessary, it is possible to produce extra-thick-walled pipes outside the standards. It is carried out by drilling a calibrated workpiece.
Galvanizing
If it is necessary to provide a pipe with an anti-corrosion coating, so-called galvanizing is used.
There are quite a few ways to coat a pipe with a layer of zinc; on an industrial scale, however, only two methods are used in the production of pipes:
- Hot galvanizing . The pipe is immersed in molten zinc. It has a melting point much lower than steel; after it cools, a thin, uniform film forms on the surface of the pipe;
- Galvanic galvanizing . In an acid solution environment, a significant potential difference is created between the zinc electrode and the pipe; the electrode dissolves and zinc settles on the surface of the pipe. The main disadvantage of the method is the need to dispose of toxic electrolyte containing zinc salts.
This is what galvanizing baths look like
Where can I buy
It is better to buy products from reputable manufacturers.
The leader in Russia in terms of the volume of pipe products produced is TMK (Pipe Metallurgical Company). The company has 28 enterprises with an annual volume of about 4 million tons of products.
OMK (United Metallurgical Company), which ranks second in the ranking of manufacturers, specializes in the production of large-diameter pipes.
About 17% of pipe products in Russia come from ChTPZ, an association of metallurgical enterprises headed by the Chelyabinsk Pipe Rolling Plant. It produces and sells almost all types of seamless pipes, including stainless steel.
A wide range of seamless pipes is produced at the Ural Pipe Plant, Volzhsky and Sinarsky Pipe Plants.
All of these companies sell their products both directly and through their dealers.
The price of hot-rolled pipes starts from 31.5 thousand rubles per ton, cold-rolled pipes – from 45 thousand.
A brief overview of the most popular brands
The greatest demand is for products made from steel grade 20. It belongs to the group of high-tech alloys and is easy to process and stamp. Welding does not require initial heating, the seams are strong.
In the production of pipe metal products, the 09G2S grade is widely used. It has high mechanical strength, easy weldability, and resistance to low temperatures.
About 70 percent of stainless products are seamless pipes made from 10Х17Н13М2Т alloy. Its constituent nickel, titanium, chromium, and molybdenum provide the rolled product with anti-corrosion properties, ductility and strength. Products from this brand are in demand in medical institutions, chemical and food industries.
Features of installation of pipes and their connections
The designs of thick-walled pipes make it easy to cut threads at their ends for subsequent connections. The process is facilitated by the absence of a weld and sufficient wall thickness.
Welding joints require preliminary preparation of the end. The edge should be cleaned, dirt should be removed, and the chamfer should be removed. First, the joints are grabbed at two or three points on opposite sides. The weld is made in several layers, depending on the thickness of the walls. The reliability of the connection must be checked by a test run of the working environment.
Pipe classification
How are the pipes different?
- Linear dimensions . The length, diameter and wall thickness of the pipe can be measured with simple instruments; The assortment can be viewed in the corresponding standard. Corresponding to what? The method by which the pipe was produced. Hence the next point.
- Production method . There are welded spiral and straight-seam pipes; seamless hot-deformed and seamless cold-rolled;
- Presence of anti-corrosion coating . This is usually a layer of zinc applied to the inner and outer surfaces of the pipe.