When manufacturing pipelines for various purposes, it is very important to correctly select the throughput of the structure in accordance with the pressure in the line. Moreover, this parameter very often depends on the diameter of the materials used, but in almost all tables a completely different value is used. That is why the question of how to calculate the cross-sectional area of a pipe is of great interest to modern designers.
Amateur photo of the material from the end side, where measurements are required
Online calculator for calculating the area of workpieces
Using an online calculator you can find the area of blanks having the shape:
- Circle,
- Rectangle,
- Cross section of a round pipe,
- Cross section of a square pipe,
- I-beams (beams),
- channel,
- Corner.
For ease of use, each calculation contains a graphical representation with symbols. To calculate, you need to enter data in the fields corresponding to the designation on the graphic image of the product.
The result of the calculation is the area of the workpiece or the sum of the areas of several workpieces with the same data.
Please note that the input data and the calculation result are presented in millimeters.
The calculator also automatically selects machines for processing selected for calculating the workpiece. By clicking on the link, you will be taken to a page with a description and technical characteristics of this machine.
You can use the obtained data to calculate the cutting time of the workpiece.
You can make this calculation on the page with the calculator “Calculation of workpiece cutting time”
Source
Financial operations
A clear financial structure, as well as the presence of a specific production plan, allows the company to accurately purchase products for industrial production. The second stage is the correct distribution of structures along trade routes, covering the costs of replenishing costs, or repairing problem areas of highways.
Without calculating the pipe area, it is difficult to calculate other parameters, so this parameter plays a key role in industrial calculations.
Instructions for the calculator for calculating the area and volume of a pipe by diameter
Enter the dimensions in millimeters:
d1 - The internal diameter of the pipe is determined by its purpose. The internal diameters of commonly used pipes are 6, 10, 15, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 65, 80, 100, 110, 125, 200 mm.
d2 – External diameter, depends on the type and application of the pipe.
L – Pipe length, here indicate the length of the pipe blank.
The main parameters of pipes d1 , d2 , L can be gleaned from the following regulatory documents:
GOST 24890-81 “Welded pipes made of titanium and titanium alloys. Technical conditions"; GOST 23697-79 “Straight-seam welded pipes made of aluminum alloys. Technical conditions"; GOST 167-69 “Lead pipes. Technical conditions"; GOST 11017-80 “High pressure seamless steel pipes. Technical conditions"; GOST R 54864-2011 “Hot-deformed seamless steel pipes for welded steel building structures. Technical conditions"; GOST R 54864-2016 “Hot-deformed seamless steel pipes for welded steel building structures. Technical conditions"; GOST 5654-76 “Hot-deformed seamless steel pipes for shipbuilding. Technical conditions"; GOST ISO 9329-4-2013 “Seamless steel pipes for work under pressure. Technical conditions"; GOST 550-75 “Seamless steel pipes for the oil refining and petrochemical industries. Technical conditions"; GOST 19277-73 “Seamless steel pipes for oil and fuel lines. Technical conditions"; GOST 32528-2013 “Hot-deformed seamless steel pipes. Technical conditions"; GOST R 53383-2009 “Hot-deformed seamless steel pipes. Technical conditions"; GOST 8731-87 “Hot-deformed seamless steel pipes. Technical conditions"; GOST 8731-74 “Hot-deformed seamless steel pipes. Technical requirements" and GOST 8732-78 "Hot-deformed seamless steel pipes. Assortment".
It is important to know that 1 inch is approximately equal to 2.54 cm, since the system for measuring pipe diameters in inches is very often used.
Information
After completing the installation of pipe communications, above-ground or underground pipelines, the need arises to paint the pipes. This is done to avoid corrosion and destruction of steel pipelines. The online calculator will help you calculate the area of the pipe, as well as the paint consumption for painting the pipe surface. The program will quickly and without errors determine the area to be painted on the pipe; you just need to enter the available dimensions into the calculator menu bar.
Calculator functions for calculating pipes
The pipe area calculator for painting is an online program consisting of the following blocks:
- two lines for entering pipe sizes;
- additional function “Count paint consumption”;
- two lines of output of finished calculation results;
- reference information with a pipe sketch, formula and explanation of symbols.
The pipe painting calculator allows you to calculate:
- pipe surface area;
- required amount of paint.
In addition, the finished result can be saved as a PDF file or printed with one click.
How the calculator works
To get a ready-made calculation of the pipe area and paint consumption, you need to enter the following data in the program menu lines:
- indicate the outer diameter, in mm;
- indicate the length, in meters;
To obtain the amount of paint required, you need to tick the “Calculate paint consumption” box and:
- indicate paint consumption based on the average consumption rate (i), in g/m2;
After this, the calculator will automatically produce the finished result: calculation of the pipe area in square meters; the amount of paint required in grams.
IMPORTANT! In order to use the pipeline for a long time and without repairs, several rules must be followed: remove rust, degrease the surface of the pipe, apply at least two layers of paint: base primer and main finish. You can avoid all these procedures, with the exception of degreasing, and use a special 3in1 rust paint, which includes primer, paint and a rust converter.
Pipe (water and gas) is a type of rolled metal, a long hollow welded product of round cross-section. It is used for water and gas pipelines, heating systems, as well as for the manufacture of parts for water and gas pipelines.
Heat loss
In this system, there is a clear pattern that must be followed to prevent losses. The fact is that the greatest absorption of heat occurs at those points where contact with the outside world is closest. That is, the thinner the inner and outer layer of the pipe and the smaller the diameter of the structure, the greater the heat loss when transporting natural resources and other substances. This suggests that it is necessary to compact the highway as much as possible. But, a complete lack of absorption leads to overload and possible damage to the system, so you should not abuse the expansion of the outer diameter, or deliberately increase the area in order to reduce losses.
As for calculations, they help in establishing measurements and additional equipment. By calculating the cross-sectional area, you can find out in which places control is required using heating equipment.
Online calculator for calculating the characteristics of an annular section (pipe)
The online calculator calculates the geometric characteristics (area, moments of inertia, moments of resistance to bending, radii of inertia) of a flat section in the form of a ring (pipe) based on known linear dimensions and displays a detailed solution.
- calculation of the moment of inertia of the ring relative to the OX axis
calculation of the moment of inertia of the ring relative to the OY axis
calculation of the moment of resistance to bending of the ring relative to the OX axis
calculation of the moment of resistance to bending of the ring relative to the OY axis
calculation of the radius of gyration of the ring relative to the OX axis
calculation of the radius of gyration of the ring relative to the OY axis
Assistance for the development of the premierdevelopment.ru project
Send mail and we will know that we are moving in the right direction.
Thank you for stopping by!
I. Procedure for calculating the characteristics of an annular section (pipe):
- To carry out the calculation, you need to enter the outer diameter of the section d and the wall thickness s.
- Based on the entered data, the program automatically calculates the internal diameter of the section d1.
- The results of calculating the area, moments of bending resistance, moments and radii of gyration of the annular section are displayed automatically.
- The figure on the right shows the required dimensions of the section elements.
- The source data block is highlighted in yellow, the intermediate calculation block is highlighted in blue, and the solution block is highlighted in green.
Source
Thermodynamic parameters
The purpose of these physical and chemical quantities is to carry out accurate calculations of heat absorption and heat release of individual sections of highways. Having learned the costs, it is possible not only to develop a scheme for a new design that involves less losses in the transport of matter, but also to draw up a new financial plan for production and volume of products.
Heat network
In order to carry out the necessary calculations, it is necessary to create an individual formula based on operating with the total area of the structure.
Types of pipe sections.
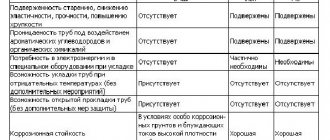
To lay water supply or sewerage systems in construction, pipes of various shapes and sections . For classic water supply, round, square, rectangular, triangular, elliptical and other pipes can be used. For sewerage, pipes of round, semicircular, elliptical, semi-elliptical, ovoid, rectangular, trapezoidal and other shapes and sections are used.
The most popular are pipes with a round cross-section . The production of such pipes is low-cost, they have good technical characteristics, as well as a number of excellent technical and operational qualities.
To calculate the weight of a pipe or the length of a pipe, you can use a pipe calculator.
The types of pipeline sections can be different:
The following are the cross-sectional shapes of gravity pipes and channels, such as:
- a) - Round,
- b) - Semicircular,
- c) - Tent,
- d) - Banquet,
- d) - Ovoid (ovonal),
- e) - Elliptical,
- g) — Semicircular with straight inserts;
- e) - Ovoid inverted,
- i) - Tray,
- j) - Pentagonal,
- l) - Rectangular,
- m) - Trapezoidal
Calculation of pipeline cross-section.
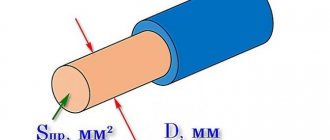
The formula for the cross-sectional area of a pipe will depend on what the shape of this section is. To calculate the cross-section of a pipeline, it is necessary to calculate the area of a circle with a diameter that is equal to the outer diameter of the pipe, and then subtract the thickness of its walls.
The area of a circle is calculated by the formula: S = Pi*(R^2) or S=Pi*(D/2-N)^2,
- R is the radius of the circle, equal to half its internal diameter;
- S is the desired value;
- Pi is the number pi, which is usually rounded to 3.14.
- D and N are the outer diameter and wall thickness of the pipe.
As an example, we calculate the internal cross-sectional area of a round pipeline with an internal diameter of 100 mm.
The radius of this pipe will be 50 mm, or 0.05 m.
The area of the pipe will be 3.14 x 0.05^2 = 0.00785 m2.
Attention: when calculating the permeability of gravity pipelines (for example, domestic sewage), take into account not the total, but the so-called live flow cross-section , which is limited by the average water level.
- a) - total cross-section,
- b) - live flow cross-section in a partially filled pipe,
- c) — live cross-section of the flow in the tray.
All necessary data on the internal diameter of VGP pipes, which are used when installing internal communications, can be found in GOST 3262-75, according to which these pipes are manufactured.
Table of external diameters of pipes.
Outer diameter, mm
Pipe wall thickness, mm
Ordinary
Why do you need careful calculations?
After determining the purpose and type of production, it is necessary to establish the vector of trade development, or carefully consider the branches for the modernization of finished structures. The goals are always different: from providing heating in residential buildings to creating an international or domestic highway for the transportation of natural resources. Based on the desired task, calculating the area of steel pipes can serve in several directions.
- Setting the values of the thermodynamic parameters of the system.
- Calculation of heat absorption during chemical reactions occurring during transportation.
- Calculation of volumes of industrial materials and raw materials for carrying out operations for the manufacture of highways.
- Conducting financial transactions without the risk of costs or unnecessary expenses.
- Reconnaissance of permeability of steel pipes.