Add to bookmarks
One of the skills required for high-quality and quick replacement of pipes at home is accurately determining their diameter using available tools.
Before making measurements, you should understand in what units they are made. It is generally accepted that the diameter of pipes is always measured in inches (1 inch = 2.54 cm).
Whether it's problems with the plumbing or plumbing in the bathroom or problems with the water supply in the kitchen, knowing how to determine the diameter of a pipe using available tools will come in handy.
Of course, there are special tools for measuring, such as a ruler-circometer, laser meter, etc. But everything can be much simpler.
Before making measurements, you should understand in what units they are made. It is generally accepted that such values are always measured in inches (1 inch = 2.54 cm), and the standard size, for example, of steel products is most often 1 or 0.5 inches. By the way, the diameters of plastic, steel and metal-plastic parts vary.
The next step is to select the measured value. External - more important, because It is on it that threads and threaded connections are installed. This diameter directly depends on the thickness of the pipe walls. The dimensions of the wall thickness are determined by the difference between the external and internal diameters of a given pipe.
Pipe diameters external and internal
Before you find out how the diameter of a pipe is calculated, you need to determine what diameter you need to calculate.
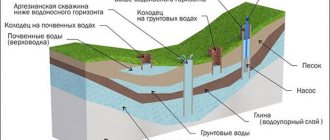
All pipe products that are used for gas and water supply, as well as for sewage disposal, are classified by internal diameter. This indicator is also called conditional passage, since the throughput of the entire system depends on it. The inner diameter is designated Dу, the outer diameter is Dн, and the wall thickness is h. Such designations allow you to conveniently carry out calculations and design a wide variety of pipelines for residential and commercial premises. With the same outer diameter, the inner diameter can vary depending on the wall thickness. The last indicator is selected based on the required mechanical strength of the product. For more precise standardization, GOST 355–52 was introduced, which regulates the nominal flow rate of pipe products. Each subsequent standard nominal diameter provides approximately 50% greater pipe capacity than the previous one.
Nominal or nominal diameter is a term that is often used instead of the concept of nominal bore. Often the internal diameter of the pipe and its nominal bore are different. The difference can be from 1 to 10 mm. The conditional or nominal diameter is the main characteristic of the product. It is this parameter that is decisive for the design and installation of any type of pipeline.
The diameters of pipes for water and gas are usually calculated in inches. Due to the fact that the metric measurement system is widespread in the post-Soviet space, difficulties often arise with the correct calculation of the width of pipes. Such situations arise when connecting pipelines made of different materials. To avoid mistakes, you should use special tables that are created specifically for quick and accurate calculation of sizes. Next, we will learn how to measure the diameter of a pipe using available tools.
Why do you need to calculate pipe parameters?
Preliminary calculation of pipe parameters is necessary in many cases. For example, for proper communication of the pipeline with other elements of the system. When working with pipes, designers and installers use indicators such as:
- pipeline permeability;
- heat loss;
- amount of insulation;
- amount of material for corrosion protection;
- roughness of the inner surface of the pipe, etc.
As a result, it is possible to determine the exact number of pipes required for a particular system, as well as their optimal characteristics. Correct calculations eliminate unnecessary costs for purchasing and transporting material and allow the substances in the pipeline to move at a given speed for the most efficient use of the system.
This table provides some useful information about the characteristics of different types of pipes that will help you select the appropriate designs needed to create a pipeline
In heating systems, the diameter of the pipes significantly depends on the permissible speed. An example of this kind of calculation is presented in the video:
Let's understand the terminology
Our country has a metric number system. And we measure everything in meters, centimeters and millimeters. Traditionally, the diameter of steel pipes is measured in millimeters. But the pipe has two diameters - internal and external, and is also characterized by wall thickness. So what diameter are we talking about when we talk about the size of steel pipes? Depends on the standard to which they are made. In some cases this means the outer diameter, in others the inner diameter. That's how difficult it is.
Nominal and nominal diameter
Pipes are used at different pressures. For a higher one, greater strength is required and this is achieved due to the wall thickness. In this case, the outer diameter of the pipe is left fixed. Otherwise, it will not be possible to connect the segments, and difficulties will arise with threads, fittings, etc. So the outer diameter is only an external parameter. Therefore, such a concept as conditional passage was introduced. In general, this is an outdated name and according to modern standards they say “nominal diameter”.
The nominal diameter of the pipe (nominal diameter) is a calculated value that is calculated during design. This value approximately corresponds to the internal diameter of the pipe in millimeters. Approximately, because the walls, with the same outer size, are of different thickness. This means that the clearance is changing. To somehow harmonize all this, a nominal diameter was introduced. This is a specific list of quantities defined by GOST 28338-89. They are shown in the table. Actual dimensions are rounded to the nearest nominal.
A number of standard nominal values of the nominal diameter of gas and water pipes and fittings for them
The designation of this value is DN, sometimes the Russian version is called Dn. After these letters there is a number without metric signs: DN30 or DN150. This is read as a nominal pipe diameter of 30 or 150, or a nominal diameter of 30 and 150. There are no units of measurement, since this is a conventional value.
Once again: all existing elements of water supply and gas pipeline systems are marked in accordance with the list of standard values - nominal diameters Dn. The actual size of the internal cross-section of a pipe or fitting may be larger or smaller. It is rounded to the nearest standard value.
In fact, the nominal diameter of a pipe or nominal size is a value that reflects the throughput. It is approximately equal to the inner diameter. After all, when you assemble a system, you use elements from different materials, with different wall thicknesses. Therefore, it is more reasonable to focus not on the diameters of the internal part, but on the nominal diameter. This will make it possible to ensure the same throughput of all elements of the system.
If the pipe is built-in
When the end part of the product is not accessible for measurement, for example, if it is an element of an existing gas or water supply system, this must be done.
- A caliper is applied for measurements to the side surface of the water pipe.
- Using this method, you can measure a pipe when the length of the tool legs exceeds half its diameter.
How to measure a large pipe
This is very easy to do, knowing the length of its circumference and the number π, approximately equal to 3.14.
- First, use a tape measure or cord to measure the pipe around its circumference to determine the circumference.
- Next, substitute the values you know into a simple formula: d=l:π, where the symbols mean: d is the diameter you are looking for, l is the found circumference.
For example: l is 31.4 cm. In this case, d=31.4:3.14. We get 10 cm, which corresponds to 100 mm.
What are the diameters (+ table with sizes)
It is important to navigate not only the types of pipes, but also the types of diameter. If you use the wrong data for calculation, the entire system may fail. To avoid common mistakes, it is important to familiarize yourself with all the rules and concepts.
It is extremely unprofessional to use exclusively the theoretical pipe diameter for calculations. Yes, it is convenient, fast, but unreliable. To understand how to measure the diameter, you need to decide which parameter needs to be determined. There are several values required for correct calculations:
- Conditional pass. This is the wall-to-wall size of the pipe, measured in millimeters. When using an inch measuring system, rounding is necessary, which may adversely affect the accuracy of the results. The concept is necessary when connecting several elements, for example, a pipe and a fitting.
- The thickness of the walls plays an important role in the accuracy of the calculations. Thanks to the concept, you can easily determine the strength and reliability of the system, calculate the maximum loads and determine the suitability of the pipe for a particular application.
- Outer diameter is the inner diameter to which the wall thickness is added.
- The nominal diameter is an analogue of the nominal diameter, calculated using more accurate methods.
Pipe diameter measurement
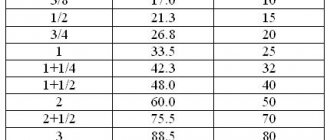
It is important to determine in which unit of measurement the result should be. This can be either inches or millimeters. It is much more convenient to use the metric system. This approach makes it possible to more accurately determine the final characteristics of the resulting system. Despite this, inches are most often used. Thanks to them, the result can be easily rounded, which simplifies the task, but reduces the accuracy of the indicators. It is worth noting that the difference is completely insignificant. For a clearer understanding, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the pipe sizes in inches and millimeters. The table will allow you to easily adapt and learn to understand unfamiliar sizes. Steel pipe diameter table:
| Nominal diameter | Inches |
| 150 | 6 |
| 200 | 8 |
| 250 | 10 |
| 300 | 12 |
| 350 | 14 |
| 400 | 16 |
| 500 | 20 |
The steel pipe diameter sizing chart is designed to allow capacity to increase by up to 50 percent as the index increases. In general, 1 inch is 25.4 millimeters. For example, 86.36 millimeters is a pipe size of 3.4 inches. The diameter of the pipe is 1-2 inches - 25.4 - 50.8 millimeters.
You can often read that in this situation a medium size is perfect. Sometimes it is not entirely clear which size is large and which is small. The first step is to determine what diameter is indicated in the recommendations. When it comes to external diameters, you should rely on the following parameters:
- less than 102 – small ;
- 102 – 246 – average;
- 425 and more are large .
The inner diameter is often not very different from the outer diameter; this does not mean that its measurement can be neglected.
The thicker the wall, the more loads the pipe will withstand. Unfortunately, it is not often that the walls are truly thick.
Calculation of the internal diameter of the pipe
To determine the internal dimensions, you need to know the external data. To do this, take a tape measure and circle it around the pipe. Afterwards, the resulting number should be multiplied by 3.1415 (number P).
To determine the internal diameter, you need to know the wall thickness. This value must be multiplied by 2, and then subtract the result from the outer diameter.
Before purchasing pipes, it is necessary to determine the tasks that the installed system will perform. If high resistance to internal pressure is required, it is best to use a seamless option. If the loads are minimal, the choice increases significantly; the seam can be either small or huge. This is a weak point that may not withstand serious stress. When relying on data obtained over time, it is better not to use the cheapest options.
The diameter of the pipes also plays a big role in further operation. To measure, you should use a simple formula: length multiplied by the number P. If we are talking about the internal diameter, it is enough to subtract the wall thickness multiplied by 2 from the results obtained.
Before purchasing a pipe, it is important to determine specific tasks. If this is a small or irregular load, budget options are suitable. Otherwise, only seamless models are needed. Thanks to its reliable structure, such a pipe will not need repairs for as long as possible.
Monitoring pipe parameters in production conditions
The outer diameter of water or sewer pipes in large production conditions is controlled and checked using a more complicated formula: D = L: 3.14 - 2∆p - 0.2 mm.
In this formula, in addition to the already known values, the symbols ∆p mean the thickness of the tape measure in mm, which you use to measure the diameter, and “0.2 mm” from the formula are the permissible deviations that take into account the fit of the tape measure to the pipe. The permissible deviation value for pipes with a cross-section of 200 mm is ±1.5 mm.
When measuring large diameter pipes, permissible deviations are measured as percentages. Example, for products ranging in size from 820 to 1020 mm, permissible deviation = 0.7%. For such measurements, an ultrasound-based measuring system is used.
In large production conditions, the wall thickness of pipes is measured with a caliper with a scale division of 0.01 mm. The permissible deviation from the nominal thickness towards reduction should not exceed 5%.
The values of pipe curvature are also subject to control, which should not be higher than 1.5 mm per linear meter of pipe length. The total curvature of products in relation to its length should not be more than 0.15%. The ovality of the pipe ends is determined by the ratio of the difference between the largest and smallest diameters to the nominal diameter of the pipe.
The value of this parameter should not exceed 1% for pipes with a wall thickness of up to 20 mm and not higher than 0.8% for walls above 20 mm.
The ovality of the pipe can be determined by measuring the diameter of the pipe end using an indicator clamp or bore gauge in two mutually perpendicular planes.
Simple school knowledge and careful use of simple tools will significantly simplify your task - how to measure the diameter of a pipe using improvised means.
Metric and inch units
Before measuring the size of the assortment, you should take into account that the technological features of laying and carrying out calculations when working with steel and plastic lines are different.
For this reason, it is necessary to first gain an understanding of the standard sizes of pipe-rolling materials for pipelines, and only then measure them. Without this knowledge, it is impossible to determine the size of the assortment in millimeters or inches.
Rolled steel pipes are primarily determined by their internal volume, measured in inches. In accordance with these units, you can find the names “inch” and “half-inch” pipe materials. One inch is equal to 25.4 mm, and half of it is correspondingly defined as 12.7 mm.
Plumbing fixtures are in no hurry to measure the outer diameter. Often installation can be done without it. It is necessary to measure this value in cases where it is necessary to measure a pipeline fastened with joints on a threaded connection.
It is usually cut on the outer part of the tubular product, and its size depends on the dimensions of the wall of the tubular product. During these actions, you should remember that if you measure pipes with different internal volume indicators, the wall size will be different.
To make it easier to measure and calculate the amount of materials needed for a pipeline, you can use a special thread system to indicate the external volume of pipe products. These values differ from the usual indicator, which can be measured in mm.
To correctly determine the size of pipe products in millimeters or find out their dimensions in inches, you need to take into account the following information.
For example, if the diameter of the metric thread knurling is designated M16, then the tubular product has an outer volume of 16 mm. In the version with pipe threads, all this is different. In inches these calculations are slightly different.
The outside diameter of a half-inch product does not reach 21 millimeters, and its thread knurling is the same in size. And this product gets its name “half-inch” because of the volume inside. In inches this value is denoted - ½. To make it easier to convert inches to mm, it is recommended to use special tables.
Volume of water in the pipeline
Knowing the volume of water that can be in a pipe is useful in many situations. This calculation can be useful when working on the heating system, water supply, and sewerage. The formula for an ordinary round pipe is not complicated. To carry out the calculation, you need to arm yourself with a caliper and a tape measure. To make the calculations easier, a calculator would be helpful.
First, measure the diameter of the pipe along the inner edges with a caliper. Divide the resulting value in half to find the inner radius. Based on the radius, we find the cross-sectional area of the pipe.
Next, you need to measure the length of the pipe with a tape measure. We multiply the resulting parameter by the previously calculated cross-sectional area. Ready! We found the volume of water that can be in the pipe. The volume can be expressed either in cube. m, or in l. These units correspond like this: 1 cubic meter. m = 1000 cubic meters dm = 1,000 l. However, this formula is only suitable if the pipe is completely filled with water.
For incomplete filling of pipes with water, much more complex geometric constructions and formulas are used to calculate the volume of liquid. We offer a drawing for your reference that shows how to make such calculations:
The throughput capacity of various pipes is determined using special tables. So, a pipe with a cross-section of 25 mm per minute passes up to 30 liters in 1 minute. If the pipe has a diameter of 32 mm, it is already capable of flowing up to 50 l/min. However, most faucets are capable of passing through no more than 5 liters of water in 1 minute.
It is also worth making allowances for the material from which the pipe is made. The fact is that polypropylene pipes have significantly smoother walls than metal pipes. This means that their ability to pass water with the same diameter will be higher. Limescale deposits that accumulate in metal pipes can have an even greater impact on throughput. Therefore, any table shows throughput only approximately.
How to measure using a ruler or tape measure
Before you measure the diameter of the pipe with a tape measure or a flexible ruler, you should know that this option is simple, and this task will be feasible even for inexperienced craftsmen. Here you only need to take one measurement.
It is necessary to measure the circumference of the pipeline. The resulting value is divided by the value of Pi. To measure and get more accurate numbers, you should use not 3.14, but 3.1416. But, for the task of finding the outer diameter of a pipe with a large volume, a ruler will not be enough. You will need to take a tape measure to work.
To determine the volume of a pipe, they also use the method of measuring the dimension of the wall at the cut. This can be measured with the same instruments. It is also possible to use a caliper. The wall thickness indicator is subtracted from the dimensional indicator of the volume outside.
When installing highways, it is important to know that to determine the internal volume of the assortment imported to us, it is necessary to determine that it is supplied with accompanying documentation.
Watch the video
It indicates the internal volume in inches. To convert internal or external dimensions to centimeters, they need to be multiplied by 2.54. For a similar conversion of the internal and external diameters back, you should multiply the indicator by 0.398.
Below is another interesting way.
How to measure with a caliper
If you ask a professional plumber how to measure with a caliper, the answer to this question will be as follows: “a caliper for such actions is the most convenient device, and you can use it to measure the required dimension very easily without making additional calculations. But only pipes with dimensions up to fifteen centimeters can be measured in this way.”
You need to press the jaws of the device firmly against the wall of the assortment, but it is not recommended to apply much force. Then you can measure and determine the dimensions in centimeters, and, if necessary, in millimeters.
Also, using a caliper, you can measure and determine the size of the end part. If this part of the highway is located in a hard-to-reach place, and the connection here is permanent, then this device will even come in handy.
But, the length of its legs should not be more than half the volume of the pipeline. To determine the measurement, the measuring device is applied to the pipe at its widest point.
Watch the video
Before determining the diameter of a steel pipe using this method, you should remember that experienced craftsmen recommend using only a high-quality device for work. Only he can guarantee accurate sizing.
Laser sensors
The diameter of a metal or any other round pipe can be measured using scanning laser sensors. How is the pipe diameter determined by these devices? Everything is simple here.
Such devices consist of a receiver and a receiver. These devices use a plane of light produced by a laser, which is deflected by a rotating prism and directed through a lens.
In the receiver, the laser is focused on the diode. It takes time for the laser to pass through a metal or other system.
How to measure with a micrometer
If the diameter of a metal or any other pipe is determined, then each measurement can be made with high accuracy (up to 0.01 mm) using a micrometer.
In appearance, the device resembles a bracket. On one side there is a heel - a support, and on the other there is a stem and a high-precision thread equipped with a microscrew. The microscrew contains a metric scale. To find out how to find the volume indicator of the assortment using a micrometer on a metal or other pipe, you need to place the part between the heel and the end, then start rotating the screw.
Continue until 3 clicks are heard. Next, you need to find the readings on the stem, where there is a scale in millimeters, and the data from the second scale of the device (these are hundredths of a millimeter) are added to the obtained figures. The sum of these two indicators determines the required value. And, as you can see, finding it is not at all difficult.
Micrometers equipped with an electronic digital readout function allow you to most correctly measure the diameter of a pipe. They are the most convenient to work with and allow you to determine the result with an accuracy of 0.001mm. If the battery in such a device runs out, you can measure it with it, just like with a regular micrometer.
The only disadvantage in this case is the high cost of the devices, which is not always acceptable for a home craftsman. Therefore, in order to correctly measure at home, such devices are used extremely rarely.
If the pipe is in your hands
If it is necessary to measure the diameter with minimal requirements for accuracy, and the cross-section of the product is completely accessible for measurements, then you can use a regular ruler or tape measure. The measuring instrument is applied at the widest part and the number of divisions is counted. This method allows you to determine the outer diameter with an accuracy of a few millimeters.
To measure small diameter products, use a caliper. To do this, the legs of the tool are applied to the end and pressed firmly, but without force, against the outer walls of the pipe. Using the instrument scale, the diameter is determined with an accuracy of tenths of a millimeter.
To calculate the internal diameter, the thickness of the pipe walls is measured along the cut.
Double the wall thickness is subtracted from the outer diameter to obtain the inner diameter.
Steel water pipes are defined by their internal diameter, which is often measured in inches. How to find out the diameter of a pipe in inches if this value is known in centimeters?
To do this, you need to multiply the diameter in centimeters by 0.398. To convert back, the diameter in inches is multiplied by 2.54
. That is, the internal diameter of a one-inch pipe is equal to 2.54 cm or 25.4 mm, and, for example, a ½-inch diameter is approximately 12.7 mm.
Source: vsetrybu.ru
Diameters of some popular pipe types
The only pipe size that, regardless of their material of manufacture, purpose, or cross-sectional shapes, is the same for everyone is the nominal DN (or conditional bore DN). If we add the wall thickness S to the nominal diameter, which is different for all types of pipes, it is easy to obtain their Dout.
Therefore, only the nominal diameter is regulated, the typical values of which are given in GOST 28338-89 and are mandatory for all types of pipelines and fittings.
Dimensional parameters of uPVC pipes for domestic sewerage
Unlike metal lines, sections of which are connected to each other by welding, the main type of joining of non-pressure sewer pipelines is a socket connection. The essence of the method is that one pipe fits into the expanded socket of another, which has an elastic rubber ring inside to ensure sealing of the joint.
That is, the main technical dimensions for this joining method are the outer pipe or internal socket, and the parameters of the width of the passage channel are of secondary importance.
Therefore, GOST 32412-2013, which regulates the technical conditions for internal sewer pipelines made of unplasticized PVC-U polyvinyl chloride, indicates only their Dout. from a standardized series and wall thickness S (Fig. 5).
Polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene PP pipes are connected to each other by soldering, simultaneously melting the shells on the outside and inside of the parts, and then inserting them into each other. Therefore, it is logical to assume that PP pipes of different standard sizes should be joined to each other and related in such a way that the internal diameter of the first part approximately corresponds to the external diameter of the second.
This rule is confirmed in the table of standard sizes of PP pipes (Fig. 6), where the dimensions along the outer circumference of any group almost completely coincide with Dout. previous and Dint. subsequent.
For example, a PP pipe of size Dout. 32 mm and Dint. 26 mm can be put on by soldering on a product of the previous standard size with Dout. 25 mm or place inside the subsequent one with Dinternal. 32 mm.
It should be noted that PP pipes are manufactured with shells of different thicknesses in view of the fact that they are designed to operate at different pressures in the system with a range from 10 to 25 bar. Therefore, with large wall thicknesses, the difference between the internal and external diameters of the joined parts can reach several millimeters. There is nothing critical about this, since all soldering irons have heating tips of a standardized size.
Rice. 7 Standard sizes of PP pipes
uPVC pressure pipes
One of the types of pipelines used for transporting cold water and wastewater in pressure sewers is PVC-U pipes, the technical conditions for which are specified by GOST R 51613-2000.
PVC-U pipes are produced with or without sockets, respectively, the methods of their connection are socket or glued into sockets or onto couplings.
The dimensions of the products are given by the average outer diameter (obtained by dividing the circumference by pi equal to 3.142), nominal outer diameters and wall thickness S.
Since one of the main methods of connecting uPVC pipes is adhesive, the dimensions of their sockets from the inside must match the external pipe sockets; according to the standard, the former are 0.3 - 0.4 mm larger than the latter. From the tabular data in Fig. 8 it can be seen that all standard sizes of uPVC pipes correspond to the standard series 10, 12, 16, 20, 25, 32, etc.
Rice. 9 Characteristics of pressure uPVC pipes according to GOST R 51613-2000
Pipes made of polyethylene and metal-plastic
GOST R 52134-2003 regulates the dimensional parameters of all plastic pipes used in households, dividing them into groups according to the dimensional ratio SDR - the quotient of the outer diameter divided by the wall thickness S.
The main method of joining PEX pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene is the use of fittings with tension sleeves; the technology is that a fitting fitting is inserted inside the PEX pipe, and the sleeve is forcefully pulled onto the outer shell at the joint. As a result, the elastic pipe shell is clamped between the fitting and the sleeve, providing a strong and tight connection.
To connect rigid metal-plastic pipelines, press sleeves are used; in contrast to the tension technology, a fitting fitting inserted inside a PEX pipe is pressed against the pipe walls with an outer sleeve, which is compressed with press pliers.
The third way to connect any type of thermoplastic pipelines is the use of compression fittings, which are pressed against the internal fitting inserted into the pipe with an external union nut (one of their varieties is a Push fitting, which is fixed with one click).
It should be noted that all companies supply their products with different internal diameters due to different wall thicknesses. This leads to the fact that for compression, tension or press connections using sleeves with fittings that are inserted inside pipes, products of a similar brand from one manufacturer are better than others.
If you use pipelines, fittings and fittings from different manufacturers, the likelihood of problems during installation of communications due to small differences in size increases significantly.
Rice. 8 Characteristics of series 5 thermoplastic pipes for domestic use according to GOST R 52134-2003
Dimensions of polymer pipes for water supply, heating
Polymer pipes are leaders in the use of hot and cold water supply and heating in domestic communications; when laying pipelines, various joining methods are used depending on the material of their manufacture.
The method of connecting pipes is directly related to their dimensions, which manufacturers must comply with when manufacturing their products.
Rice. 6 Standard sizes of PVC-U sewer pipes according to GOST 32412-2013
Dimensions of water and gas steel and copper pipes
GOST 3262-75 regulates the range of welded pipes made of non-galvanized and galvanized steel for water supply, heating and gas communications.
Rice. 4 Assortment of water-gas pipes according to GOST 3262-75
The standard also applies to products with cylindrical threads obtained by cutting or rolling technologies.
If you look closely at the tabular data in Fig. 4 dimensional and weight characteristics of water and gas pipes, you can see that products with the same nominal bore DN and outer diameter have different wall widths S.
This is theoretically impossible, unless you take into account that the previously given definition of the nominal bore indicates its approximate correspondence to the internal diameter.
For example, for an ordinary light steel pipe with Dout. 17 mm and S walls 2 mm, Dint. will be equal to 13 mm. For a heavy 17 mm product with S walls 2.8 mm Dinternal. – 11.4 mm, while the nominal bore DN in both products is the same and is equal to 10 mm according to the table in Fig. 4.
Sometimes, when installing heating systems and laying heated floors, copper pipelines are used, the technical conditions for which are given in GOST 617-2006. Gosstandart directly specifies the method for specifying their dimensions Doutside, wall thickness and length; the document also notes that by agreement between the manufacturer and the customer, Dinside can be taken as a basis. At some points, the document also refers to the average diameter of the product, which is defined as the arithmetic mean of its largest and smallest values in one section plane perpendicular to the axis.
Rice. 5 Characteristics of copper pipes GOST 617-2006
What tool do you need for each method?
Before choosing the diameter of a heating pipe, or any other system, you need to know what is used in such situations.
The well-known caliper
used for measurement more often than other instruments. But, it may not be among the set of home tools. Therefore, we have to solve the question of how to measure the diameter of a pipe without a caliper.
It is also not possible to find out the exact dimensions of a product with a large diameter for heating or water supply using this device. In such situations, it is possible to measure the required length of the volume of the tubular product using simpler devices:
- flexible ruler;
- tape measure;
- knowledge of the value of Pi, which is 3.14.
If access to the network is not difficult, a better option for calculating the value would be a tape measure or a metal ruler. But, with a hard ruler it is easy to calculate the size of only the end parts of the line that is being measured.
Watch the video
Another option for measuring the circumference of a pipe inside or outside is the copying method. In such a situation, for example, a ruler is brought to the pipe. This section of the highway is then photographed. Further measurements in order to obtain the entire set of necessary information should be taken from the photograph. Figures that correspond to reality are obtained after scaling the photographs taken.
In addition, you can find the diameter using the following formula:
In it, D indicates the diameter, and L is the circumference of the tubular product. In a simple example it looks like this. The circumference of the pipe is 62.8 cm. This number is divided by 3.14. The result is 200 mm.
It's not just home plumbers who work with this formula. It is also used in production conditions, only in this case there is a slight amendment. The formula for the work remains in the same form, only the double thickness of the tape measure and the value of 0.2 are subtracted from the final result. This number includes a correction for the adherence of the tape measure to the surface of the highway.
Pipe measurements using improvised means
Most often, the well-known caliper is used to measure the diameter of a pipe. But you may not have it, or if you do have it, it may not be possible to measure a large pipe diameter with it. In this case, the simplest set of tools and knowledge is used:
- flexible ruler (similar to the type of measuring tape used in sewing);
- roulette;
- school knowledge of the number Pi (it is equal to 3.14).
Using a similar set of tools, you can measure the diameter of not only a pipe, but also any other round object - a rod, column or garden bed.
We only need to make one measurement - determine the circumference of the pipe using a tape measure or flexible ruler. To do this, a measuring tape or tape measure is placed on the surface of the pipe in its widest part. The resulting circumference value should be divided by 3.14. For more accurate dimensions, use the value 3.1416.
It should be noted that imported supplies of pipes are accompanied by documentation that already indicates the pipe diameters in inches. To convert these values to centimeters, they are multiplied by 2.54. Similarly, to convert centimeters back to inches, multiply by 0.398.
Calculations of various pipe parameters
- the material from which the pipe is made;
- type of pipe section;
- internal and external diameter;
- Wall thickness;
- pipe length, etc.
Some of the data can be obtained simply by measuring the structure. A lot of useful information is contained in certification documents, as well as in various reference books and GOSTs.
How to find out the diameter and volume of a pipe?
Some calculation formulas are familiar to every schoolchild. For example, if you need to determine the diameter of a specific pipe, you should measure its circumference. To do this, you can use a measuring tape that seamstresses use. Alternatively, wrap the pipe with another suitable tape and then measure the resulting length using a ruler.
- L is the circumference of a circle;
- π is a constant number “pi”, equal to approximately 3.14;
- D is the diameter of the circle's circumference.
It is enough to carry out a simple transformation to calculate the outer diameter of the pipe using this formula:
Calculation of pipe cross-section
This figure clearly shows indicators such as the outer diameter of the pipe and the thickness of its wall. The difference between the outer diameter and thickness allows you to calculate the inner diameter of the pipe
The formula for the area of a circle looks like this:
S=πR², where:
- S is the area of the circle;
- π—pi number;
- R is the radius of the circle, calculated as half the diameter.
If information about the outer diameter and wall thickness of the pipe is used, the formula may look like this:
S=π(D/2-T)², where:
- S—sectional area;
- π—pi number;
- D is the outer diameter of the pipe;
- T is the thickness of the pipe walls.
Let's say there is a pipe whose outer diameter is 1 meter and the wall thickness is 10 mm. First, you need to agree on all units of measurement. The wall thickness will be 0.01 meters. According to the above formula, we calculate the cross-section of such a pipe:
S=3.14Х(1m/2-0.01m)²=0.75m²
Thus, the cross-section of the pipe with the specified parameters will be equal to 0.75 square meters. m.
As you know, the accuracy of calculations with the number “pi” depends on the number of decimal places that are used when applying this constant. However, in construction there is usually no need for ultra-precise calculations, and the number “pi” is taken equal to 3.14. It also makes sense to round the final result to two decimal places.
How to calculate the volume of a pipe?
This diagram clearly shows the use of data such as the cross-sectional radius of the pipe and its length to determine the volume of the pipe
Calculating the volume of a specific pipe section is also not difficult. To do this, you must first find the circumference of the pipe based on its outer diameter using the formula given above:
S=π(D/2)² or S=πR²
In this case, D is the outer diameter of the pipe, and R is the outer radius, i.e. half the diameter. After this, the resulting value must be multiplied by the length of the pipe section, obtaining the volume, which is expressed in cubic meters. The formula for calculating pipe volume may look like this:
- V—pipe volume, cubic meters. m.
- S—external section area, sq.m.;
- H is the length of the pipe section, m.
Let's say there is a pipe with an outer diameter of 50 cm and a length of 2 meters. First, all units of measurement must be agreed upon. D=50 cm=0.5 m. Substitute this value into the formula for the area of a circle:
This table provides reference weight data
of various types, taking into account their sizes and features of production technology
Middle school students are well aware that the mass of an object can be found by multiplying its volume by the density of the substance from which the object consists. Builders are spared from tedious calculations of the mass of a specific pipe section, since various construction reference books contain information on the weight of a linear meter of a wide variety of types of pipes. The easiest way is to calculate the mass of the pipe using the relevant GOSTs, using information about:
- the material from which the pipe is made;
- its outer diameter;
- wall thickness;
- internal diameter, etc.
Having found out the weight of one linear meter of pipe, you should multiply the resulting value by the total number of linear meters. The complexity of the task corresponds to the level of the fourth-fifth grade of a general education school.
The occurrence of problems in the water, gas or sewer system often involves pipe installation - replacing a fragment of an old pipe or installing a new one. When performing such work, you will need the skills to determine the diameter of the pipes of your system using improvised means. When installing a new water supply system, it is also necessary to accurately determine the dimensions of old pipes in order to determine the choice of new plastic or metal-plastic pipes.
Of course, there are special tools for carrying out such measurements, for example, a laser meter, a ruler-circometer and others. But what if you are not a professional specialist, and your home tool kit does not include such high-precision instruments? How to measure the diameter of a pipe in another way?
Before answering this question, it is useful to know in what units these indicators are measured. Pipe diameter is usually measured in inches. One inch is equal to 2.54 centimeters.
When working with a pipe, both its internal and external diameter will be measured. The external diameter of the pipe is important due to the fact that it is its value that is taken into account when applying threads and creating threaded connections. The outer diameter is directly dependent on the thickness of the pipe walls. The wall thickness size is the difference between the outer and inner diameters of the pipe.
Small diameter pipe measurement
Measurements are taken using a caliper without any mathematical calculations. The condition is complete accessibility to the pipe. This method is suitable for measuring accessible pipes of small diameter (no more than 15 cm). To take measurements, the legs of the caliper are applied to the end of the pipe and clamped tightly on the outer walls. The resulting value on the caliper scale, accurate to tenths of a millimeter, will be the outer diameter of the pipe.
Sources
- https://mnogo-trub.ru/razmery-trub/izmerit-diametr-truby-opredelit.html
- https://stroychik.ru/strojmaterialy-i-tehnologii/diametry-stalnyh-trub
- https://m-strana.ru/articles/diametry-trub/
- https://TrubaNet.ru/instrumenty-dlya-trub/kak-zamerit-diametr-truby.html
- https://montagtrub.ru/kak-izmerit-diametr-truby-dostupnye-sposoby/
- https://kakpravilnosdelat.ru/kak-izmerit-diametr-truby/
[collapse]
Similar posts:
- Diameters of steel pipes - table of external and...
- Which pipes are better for plumbing in an apartment: types,…
- The slope of the gutter, the need for calculation and...
- Rating of the best soldering irons for polypropylene pipes
- How to choose a pipe for a heated floor - recommendations...
- Hands are not for boredom or crafts from plastic pipes
How to determine the diameter at home
You will need the following tools and devices:
- any measuring ruler or tape measure;
- calipers;
- If necessary, a camera.
If it is fully available for measurement
Note!
If you need to measure the diameter of pipes, the ends of which are accessible for direct observation and measurement, and provided that the requirements for calculation accuracy are minimal, use a construction tape or ruler.
- Attach your measuring tool to the end of the product, at the level of its widest part.
- Next, count the number of divisions that will correspond to the diameter.
- This method makes it possible to find out the dimensions of products with an accuracy of up to several millimeters.
To measure the outside diameter of small pipes, you can use a caliper.
- Spread the legs of the tool and attach them to the end of the product.
- Then move them so that they are pressed quite tightly against the outer walls.
- Use the instrument's scale to determine the outer diameter. The accuracy of this method is down to tenths of a millimeter.
If the pipe is already installed
When the end part of the product is not accessible for measurement, for example, if it is an element of an existing gas or water supply system, this must be done.
- A caliper is applied to the side surface for measurements.
- Using this method, you can measure a pipe when the length of the tool legs exceeds half its diameter.
How to measure a large item
This is very easy to do, knowing the length of its circumference and the number π, approximately equal to 3.14.
- First, use a tape measure or cord to measure the pipe around its circumference to determine the circumference.
- Next, substitute the values you know into a simple formula: d=l:π, where the symbols mean: d is the diameter you are looking for, l is the found circumference.
For example: l is 31.4 cm. In this case, d=31.4:3.14. We get 10 cm, which corresponds to 100 mm.
What to do if the pipe is completely inaccessible
When it is impossible to take direct measurements of the pipe for some reason, you can use the copying method.
- For this purpose, attach a ruler or a small object to the pipe, the linear parameters of which are known in advance. For example, a matchbox whose length is 5 cm.
- Next, take a photo of this area.
- Make further calculations and measurements using the photo.
- To do this, you need to measure the visible thickness (in mm) of the pipe in the picture.
- Then convert the data you received into the actual dimensions of the product, taking into account the scale of the photograph.