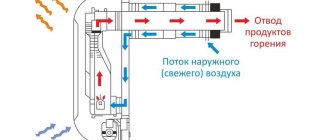
The installation of any heating device or structure operating on solid, liquid or gaseous fuel, a stove, fireplace or boiler, will require the mandatory installation of a waste combustion product removal system.
Stainless steel chimney
Not so long ago there was no particular alternative - it was necessary to erect a brick structure or resort to the use of asbestos-cement pipes, which have many more disadvantages than advantages. Currently, the situation has changed dramatically - a stainless steel chimney shows excellent versatility.
In skillful hands, a set of stainless steel parts turns into a universal tool, making it possible to quickly install a chimney system that fully meets all the requirements of current standards and safety requirements. In addition, the overall cost of installing a chimney, even with the seemingly expensive components, will always be more attractive than other options. With a competent approach and knowledge of the basic principles of installation, assembling such a system is a completely feasible task for any home owner.
Scope of application of tubular metal chimneys
The advantages of using such materials include several points:
- Light weight. For chimneys, electric-welded pipes with a wall thickness of 0.5–1.5 mm are used. The total load of this design allows it to be used for all types of stoves, including metal bath stoves, closed and open brick stoves, slow burning stoves in greenhouses and residential premises, as well as for other types of heat sources.
- Tubular devices do not require special support structures in the form of foundations.
- Long service life. For galvanized pipes it is 10–20 years, and manufacturers of stainless steel products declare durability for 100 years. Of course, there is no factual data on this issue.
- The simplicity of installing a chimney from pipes makes it easy for even a person with minimal DIY skills to cope with this task.
The construction of a steel chimney for a sauna stove is quite simple
The limiting factor in the use of steel pipes is their cost, but this only applies to stainless pipes.
Video: what you need to know about metal chimneys
Stainless steel sandwich chimneys
CHIMNEY COMPANY produces, sells and installs chimneys, gas ducts, stainless steel air ducts for boilers, stoves, fireplaces, baths and saunas in Moscow and the Moscow region.
The production of stainless steel chimneys is located near Moscow in the village. Maydarovo, Solnechnogorsk district. which allows you to make a stainless steel chimney of non-standard sizes in the shortest possible time.
In the production of chimneys, high-quality steel grades AISI 409, 430, 304, 316, 321 are used. The seams of the chimney elements are made using TIG butt welding on stainless steels. The insulation used is IZOVOL basalt insulator, which can withstand temperatures up to 1000°C.
All products are certified.
Types of stainless steel chimneys
| Single-wall chimneys - intended for use inside a heated room, or for lining brick ducts. | Double-walled chimneys (sandwich) - designed for use inside and outside buildings, which minimizes the formation of condensation. |
Chimney " ECONOMY " AISI 430
Types of steel pipes for chimneys
A specialized hardware store offers a wide range of steel pipes, which differ in purpose:
- Single-walled - made of galvanized or stainless steel, cheap, used for repairing existing chimneys.
- Multilayer - consist of an outer shell and an internal conductive pipe, made of stainless steel, galvanized or combined. This allows you to significantly reduce the price. The gap between the two walls is filled with heat-resistant insulation, for which refractory basalt wool is often used.
Sandwich pipe is ideal for chimneys
- Coaxial - the same sandwich pipe, but there are partitions between the walls. Air is supplied inside the furnace through a free channel to improve combustion and increase heat transfer. This is know-how in the field of chimney installation. Coaxial pipes are used for forced draft boilers.
Coaxial pipe went on sale quite recently
Types of chimneys
Based on the components used, these devices can be divided into the following:
- single;
- multilayer.
The materials used for their manufacture are particularly durable and highly resistant to acid condensate. A clean surface helps to completely remove moisture and soot from the smoke duct.
Single pipe structures are very often used. Such technical solutions are used to adapt old chimneys to new heating equipment. Pipes for them are made square, oval or round. Austenitic stainless steel is used for their production. Enameled pipes are also produced, but they are not widely used because they are sensitive to mechanical stress.
Single chimney needs additional protection
When installing a single chimney, you should be guided by the fire safety rule, which requires a distance to the nearest wall made of flammable materials of at least 1 m.
Double-layer structures have their advantages. The thermal insulation layer between the walls of such a chimney reduces the cooling of the inner pipe, resulting in less condensation. The inner pipe is made of high-quality steel, since condensate has an acidic reaction and other materials, including galvanized steel, will not be able to work for a long time in such conditions.
The double-layer chimney is already insulated
Such chimneys are placed at a distance of at least 20 cm from walls made of flammable materials. If this cannot be avoided, then the wall is sheathed with metal with a backing. It is made from fire-resistant material, for example, asbestos sheet.
According to the installation method, chimneys are:
- Internal. This design can rise vertically from the furnace through the internal ceilings and roofing pie. Its main disadvantage is that condensate flows directly into the firebox, increasing its concentration in the flue gases. The result may be an unpleasant pungent odor in the room and accelerated wear and tear of the chimney.
- External. With this design, the chimney is diverted from the stove horizontally through the wall. For this, two elbows are used, which can have a rotation angle of 30, 45, 60 or 90 degrees. In this case, the outer one looks like a tee, and at the bottom there is a container for collecting condensate. The vertical part of the chimney is installed parallel to the wall, the pipe is attached to it using brackets and clamps.
Components
It is impossible to assemble a chimney without using fittings. They are intended for:
- performing contours of engineering systems;
- changes in pipeline direction;
- switching to another diameter;
- traction adjustments;
- condensate collection;
- protecting the upper end from precipitation, leaves, debris and nesting birds.
Additional elements for assembling a chimney from pipes must be used
Using these structural elements, you can assemble a chimney of any configuration with your own hands. The permissible length of horizontal sections is no more than 1 m, otherwise the traction will be greatly weakened.
Chimney "STANDARD" made of steel grade 304
AISI 304 - austenitic stainless steel (0.5 mm and 1 mm thick) is used in the production of high-quality chimneys, which are best suited for gas boilers, water heaters, water heaters, boilers, diesel boilers, as well as solid fuel stoves, boilers, fireplaces
The cost of Standard chimneys can be found here >>>
Chimney "PREMIUM" AISI 321
Calculation of chimney parameters
The basis for calculating the height and diameter of the chimney is the power indicator.
The performance of a boiler or furnace is directly affected by the height of the chimney. For household appliances it is 5 m. This characteristic is provided for by the SNiP requirements for stoves in residential buildings. The measurement is taken from the device's grate to the hood. At a lower altitude, the natural draft in the stove will not ensure efficient combustion of fuel; it will smoke and not produce the optimal amount of heat. However, the ability to increase height is limited. Experiencing the natural resistance of the pipe walls, the air will slow down if the channel is too long, which will also lead to a decrease in draft.
Rules for selecting chimney length
For a private house, calculating the height of the chimney is based on certain rules:
- The pipe must be at least 5 m.
- The excess of the chimney end above a conventionally flat roof is at least 50 cm.
- For a pitched roof, a pipe whose axis is located no further than 1.5 m from the ridge, and if there are superstructures, then from their highest point, the excess is 0.5 m.
- When the distance to the ridge is 1.5–3.0 m, the end of the pipe should be no lower than the level of the ridge.
- When installing a chimney at a distance of more than 3 m from the ridge, in particular for outdoor installation, the angle between the horizon level and the conventional straight line between the ridge and the end of the pipe must be at least 10 degrees.
The height of the pipe depends on its location
When choosing a location for the chimney outlet through the roof, it should be taken into account that it should not be located near roof windows and other similar devices in order to avoid creating fire hazards.
Calculation of the chimney cross-section
The procedure given below for determining the size of the channel is valid for a circular cross-section. It is the optimal form, since the flue gases do not move in a monolithic straight stream, but the flow swirls and they move in a spiral. In rectangular channels, vortices are formed at the corners, inhibiting the movement of gases. To calculate the cross-sectional value, the obtained result should be multiplied by 1.5.
You will need the following initial data:
- Furnace power, that is, the amount of heat generated by the device per unit time when fully loaded.
- The temperature of the flue gases at the outlet of the furnace is usually taken to be within 150–200 degrees.
- The speed of gas movement through the channel (is 2 m/sec).
- Chimney height.
- The value of natural draft (4 MPa per 1 m of smoke channel).
The dependence of the cross-sectional area of the chimney on the volume of fuel burned is obvious.
Smoke doesn't move in a straight line
To perform the calculation, you need to use the converted formula for the area of a circle: D2 = 4 x S * Pi, where D is the diameter of the smoke channel, S is the cross-sectional area, Pi is the number pi equal to 3.14.
To calculate the cross-sectional area, you need to determine the gas volume at the point where they exit from the stove into the chimney. This value is calculated depending on the volume of fuel burned and is determined from the ratio Vgas = B x Vtop x (1 + t / 273)/ 3600, where Vgas is the volume of gases, B is the amount of fuel burned, Vtop is a tabular coefficient that can be found in GOST 2127, t - temperature of gases at the outlet of the furnace, usually a value within 150–200 degrees is accepted.
The cross-sectional area is determined by the ratio of the volume of passing gases to the speed of its movement, that is, by the formula S = Vgas/W. In the final version, the desired value is determined by the relation D2 = Vgasx4/PihW.
Having made the necessary calculations, you will get the result - the diameter of the chimney should be 17 cm. This ratio is valid for a stove in which 10 kg of fuel burns per hour with a humidity of 25%.
The calculation is made for cases where non-standard heating units are used. If the power of the device is known, it is enough to use the chimney parameters recommended by experts:
- for devices with power up to 3.5 kW - 140 x 140 mm;
- at 3.5–5.0 kW - 140 x 200 mm;
- with a power of 5.0–70 kV - 200 x 270 mm.
For chimneys with a round cross-section, its area should not be less than the calculated size of a rectangular one.
Video: how to calculate a chimney for a solid fuel boiler
To calculate the cost of a chimney, send a request or a photo of the object by e-mail:
or on WhatsApp: tel. 8(985)698-15-65
Current prices for components for Economy chimneys made of AISI 409, 430 stainless steel.
Price list 2021, prices in rubles.
Sandwich pipe diameter 110/200 ( 110 - inner pipe diameter / 200 - outer pipe diameter) AISI 409 (1mm) - stainless steel 1 mm thick. AISI 430(0.5mm) - stainless steel 0.5 mm thick. Zinc (0.5mm) - galvanized steel 0.5 mm thick.
| Name | Diameter ø | 409(1mm)/ 430(0.5mm) | 430(0.5mm)/ 430(0.5mm) |
| Sandwich pipe 1 m | 80/160 | 2000 | |
| 110/200 | 3300 | 2650 | |
| 115/200 | 3300 | 2650 | |
| 120/200 | 3300 | 2650 | |
| 130/200 | 3400 | 2750 | |
| 150/230 | 3900 | 3200 | |
| 160/230 | 4200 | 3300 | |
| 180/260 | 4600 | 3750 | |
| 200/280 | 5300 | 4100 | |
| 250/330 | 6900 | 4850 | |
| 300/380 | 7800 | 5600 | |
| 350/430 | 9000 | 6700 | |
| 400/480 | 10200 | 7600 | |
| 500/580 | 13600 | 10100 | |
| Sandwich pipe 0.5 m | 80/160 | 1100 | |
| 110/200 | 2000 | 1550 | |
| 115/200 | 2000 | 1550 | |
| 120/200 | 2000 | 1550 | |
| 130/200 | 2100 | 1650 | |
| 150/230 | 2400 | 1900 | |
| 160/230 | 2900 | 2000 | |
| 180/260 | 3100 | 2300 | |
| 200/280 | 3600 | 2400 | |
| 250/330 | 4200 | 2900 | |
| 300/380 | 4700 | 3300 | |
| 350/430 | 5450 | 4100 | |
| 400/480 | 6200 | 4550 | |
| 500/580 | 8250 | 6100 | |
| Knee sandwich 135 | Diameter ø | 409(1mm)/ 430(0.5mm) | 430(0.5mm)/ 430(0.5mm) |
| 80/160 | 1150 | ||
| 110/200 | 2400 | 2000 | |
| 115/200 | 2400 | 2000 | |
| 120/200 | 2400 | 2000 | |
| 130/200 | 2900 | 2200 | |
| 150/230 | 3300 | 2600 | |
| 160/230 | 3700 | 2750 | |
| 180/260 | 4000 | 3100 | |
| 200/280 | 4700 | 3600 | |
| 250/330 | 6100 | 4300 | |
| 300/380 | 7000 | 5000 | |
| 350/430 | 8250 | 6000 | |
| 400/480 | 9350 | 6900 | |
| 500/580 | 12300 | 9100 | |
| Knee sandwich 90 | 80/160 | 1700 | |
| 110/200 | 3100 | 2400 | |
| 115/200 | 3100 | 2400 | |
| 120/200 | 3100 | 2400 | |
| 130/200 | 3300 | 2500 | |
| 150/230 | 3900 | 3000 | |
| 160/230 | 4100 | 3100 | |
| 180/260 | 4600 | 3600 | |
| 200/280 | 5500 | 4200 | |
| 250/330 | 7200 | 5000 | |
| 300/380 | 8900 | 6500 | |
| 350/430 | 10300 | 7700 | |
| 400/480 | 11700 | 8700 | |
| 500/580 | 16900 | 12250 | |
| Sandwich tee 90 s (plug included) | Diameter ø | 409(1mm)/ 430(0.5mm) | 430(0.5mm)/ 430(0.5mm) |
| 80/160 | 2300 | ||
| 110/200 | 4100 | 3400 | |
| 115/200 | 4100 | 3400 | |
| 120/200 | 4100 | 3400 | |
| 130/200 | 4200 | 3600 | |
| 150/230 | 4900 | 3800 | |
| 160/230 | 5100 | 4000 | |
| 180/260 | 5700 | 4500 | |
| 200/280 | 6650 | 5000 | |
| 250/330 | 9350 | 6300 | |
| 300/380 | 10500 | 7500 | |
| 350/430 | 12000 | 9000 | |
| 400/480 | 14600 | 10900 | |
| 500/580 | 20900 | 15400 | |
| Quad sandwich Cross | 80/160 | 3100 | |
| 110/200 | 5600 | 4600 | |
| 115/200 | 5600 | 4600 | |
| 120/200 | 5600 | 4600 | |
| 130/200 | 5750 | 4700 | |
| 150/230 | 6800 | 5200 | |
| 160/230 | 6950 | 5400 | |
| 180/260 | 7900 | 6100 | |
| 200/280 | 9100 | 6900 | |
| 250/330 | 12700 | 8600 | |
| 300/380 | 14300 | 10250 | |
| 350/430 | 16500 | 12000 | |
| 400/480 | 19950 | 14850 | |
| 500/580 | 28500 | 20900 | |
| Sandwich tee 135 (plug included) | 80/160 | 2900 | |
| 110/200 | 5500 | 4100 | |
| 115/200 | 5500 | 4100 | |
| 120/200 | 5500 | 4100 | |
| 130/200 | 5900 | 4300 | |
| 150/230 | 7000 | 4900 | |
| 160/230 | 7300 | 5100 | |
| 180/260 | 8800 | 6100 | |
| 200/280 | 10200 | 7000 | |
| 250/330 | 11500 | 9100 | |
| 300/380 | 12700 | 10800 | |
| 350/430 | 13900 | 13000 | |
| 400/480 | 16000 | 15300 | |
| 500/580 | 21500 | 19800 | |
| Start sandwich | Diameter ø | 409(1mm)/ 430(0.5mm) | 430(0.5mm)/ 430(0.5mm) |
| 80/160 | 600 | ||
| 110/200 | 1300 | 1000 | |
| 115/200 | 1300 | 1000 | |
| 120/200 | 1300 | 1000 | |
| 130/200 | 1400 | 1100 | |
| 150/230 | 1650 | 1150 | |
| 160/230 | 1750 | 1300 | |
| 180/260 | 2000 | 1400 | |
| 200/280 | 2300 | 1550 | |
| 250/330 | 2500 | 2000 | |
| 300/380 | 2750 | 2300 | |
| 350/430 | 3200 | 2650 | |
| 400/480 | 3800 | 3100 | |
| 500/580 | 5700 | 4200 | |
| Assembly area | 80/160 | 1400 | |
| 110/200 | 1700 | 1550 | |
| 115/200 | 1700 | 1550 | |
| 120/200 | 1700 | 1500 | |
| 130/200 | 1800 | 1550 | |
| 150/230 | 2000 | 1850 | |
| 160/230 | 2200 | 2100 | |
| 180/260 | 2750 | 2600 | |
| 200/280 | 3200 | 3000 | |
| 250/330 | 3800 | 3500 | |
| 300/380 | 4500 | 4100 | |
| 350/430 | 5300 | 4900 | |
| 400/480 | 6000 | 5500 | |
| 500/580 | 7700 | 6800 | |
| Stub | Diameter ø | 430(0.5mm) | |
| 80/160 | 400 | ||
| 110/200 | 450 | ||
| 115/200 | 450 | ||
| 120/200 | 450 | ||
| 130/200 | 450 | ||
| 150/230 | 500 | ||
| 160/230 | 500 | ||
| 180/260 | 650 | ||
| 200/280 | 700 | ||
| 250/330 | 800 | ||
| 300/380 | 950 | ||
| 350/430 | 1150 | ||
| 400/480 | 1300 | ||
| 500/580 | 1700 | ||
| Heading | 80/160 | 1100 | |
| 110/200 | 1200 | ||
| 115/200 | 1200 | ||
| 120/200 | 1200 | ||
| 130/200 | 1200 | ||
| 150/230 | 1300 | ||
| 160/230 | 1300 | ||
| 180/260 | 1550 | ||
| 200/280 | 1800 | ||
| 250/330 | 2200 | ||
| 300/380 | 2750 | ||
| 350/430 | 3300 | ||
| 400/480 | 3800 | ||
| 500/580 | 5000 | ||
| Head with deflector | Diameter ø | 430(0.5mm) | |
| 80/160 | 1600 | ||
| 110/200 | 2200 | ||
| 115/200 | 2200 | ||
| 120/200 | 2200 | ||
| 130/200 | 2200 | ||
| 150/230 | 2500 | ||
| 160/230 | 2500 | ||
| 180/260 | 3000 | ||
| 200/280 | 3300 | ||
| 250/330 | 4000 | ||
| 300/380 | 4500 | ||
| 350/430 | 5000 | ||
| 400/480 | 5700 | ||
| 500/580 | 7500 | ||
| Head cone | 80/160 | 650 | |
| 110/200 | 800 | ||
| 115/200 | 800 | ||
| 120/200 | 800 | ||
| 130/200 | 800 | ||
| 150/230 | 900 | ||
| 160/230 | 950 | ||
| 180/230 | 1000 | ||
| 200/280 | 1100 | ||
| 250/330 | 1400 | ||
| 300/380 | 1750 | ||
| 350/430 | 2200 | ||
| 400/480 | 2500 | ||
| 500/580 | 3300 | ||
| Crimping clamp | 200 | 250 | |
| 230 | 270 | ||
| 260 | 280 | ||
| 280 | 300 | ||
| 330 | 330 | ||
| 380 | 400 | ||
| 480 | 460 | ||
| 580 | 550 | ||
| PPU | Diameter ø | Zinc/stainless | |
| 200 | 1300 | ||
| 230 | 1300 | ||
| 260 | 1300 | ||
| 280 | 1750 | ||
| 330 | 2000 | ||
| 380 | 2200 | ||
| 480 | 3000 | ||
| 580 | 3800 | ||
| Pipe 1 m | Diameter ø | 409(1mm) | 430(0.5mm) |
| 80 | 650 | ||
| 110 | 1400 | 800 | |
| 115 | 1400 | 800 | |
| 120 | 1400 | 800 | |
| 130 | 1500 | 900 | |
| 150 | 1500 | 1000 | |
| 160 | 1600 | 1100 | |
| 180 | 2000 | 1200 | |
| 200 | 2350 | 1400 | |
| 250 | 3000 | 1650 | |
| 300 | 3600 | 2000 | |
| 350 | 4200 | 2400 | |
| Pipe 0.5 m | 80 | 400 | |
| 110 | 850 | 500 | |
| 115 | 850 | 500 | |
| 120 | 850 | 500 | |
| 130 | 900 | 550 | |
| 150 | 1000 | 600 | |
| 160 | 1000 | 650 | |
| 180 | 1200 | 750 | |
| 200 | 1450 | 850 | |
| 250 | 1800 | 1000 | |
| 300 | 2200 | 1200 | |
| 350 | 2550 | 1450 | |
| Tee 90 | 80 | 950 | |
| 110 | 1650 | 1100 | |
| 115 | 1650 | 1100 | |
| 120 | 1650 | 1100 | |
| 130 | 1700 | 1200 | |
| 150 | 2100 | 1400 | |
| 160 | 2200 | 1500 | |
| 180 | 2500 | 1700 | |
| 200 | 3000 | 2000 | |
| 250 | 3800 | 2500 | |
| 300 | 4600 | 2900 | |
| 350 | 5500 | 3300 | |
| Tee 135 | 80 | 1100 | |
| 110 | 2150 | 1400 | |
| 115 | 2150 | 1400 | |
| 120 | 2150 | 1400 | |
| 130 | 2400 | 1500 | |
| 150 | 2900 | 1800 | |
| 160 | 3100 | 1900 | |
| 180 | 3300 | 2200 | |
| 200 | 4000 | 2500 | |
| 250 | 5000 | 3100 | |
| 300 | 6300 | 3900 | |
| 350 | 7500 | 4700 | |
| Knee 135 | Diameter ø | 409(1mm) | 430(0.5mm) |
| 80 | 400 | ||
| 110 | 800 | 500 | |
| 115 | 800 | 500 | |
| 120 | 800 | 500 | |
| 130 | 850 | 550 | |
| 150 | 1050 | 600 | |
| 160 | 1100 | 700 | |
| 180 | 1300 | 850 | |
| 200 | 1500 | 950 | |
| 250 | 1800 | 1200 | |
| 300 | 2500 | 1450 | |
| 350 | 2900 | 1800 | |
| Knee 90 | 80 | 500 | |
| 110 | 1150 | 700 | |
| 115 | 1150 | 700 | |
| 120 | 1150 | 700 | |
| 130 | 1300 | 750 | |
| 150 | 1600 | 850 | |
| 160 | 1750 | 900 | |
| 180 | 2000 | 1100 | |
| 200 | 2200 | 1300 | |
| 250 | 2650 | 1700 | |
| 300 | 3000 | 2200 | |
| 350 | 3800 | 2600 | |
| Gate valve rotary | Diameter ø | 409(1mm) | |
| 110 | 800 | ||
| 115 | 800 | ||
| 120 | 800 | ||
| 130 | 800 | ||
| 150 | 900 | ||
| 160 | 1000 | ||
| 180 | 1100 | ||
| 200 | 1250 | ||
| 250 | 1550 | ||
| 300 | 1700 | ||
| 350 | 1950 | ||
| Gate valve | 110 | 1000 | |
| 115 | 1000 | ||
| 120 | 1000 | ||
| 130 | 1000 | ||
| 150 | 1200 | ||
| 180 | 1650 | ||
| 200 | 1900 | ||
| 250 | 2300 | ||
| 300 | 2650 | ||
| 350 | 3100 | ||
| Telescopic bracket | 115 | 800 | |
| 150 | 800 | ||
| 200 | 900 | ||
| 230 | 1000 | ||
| 260 | 1050 | ||
| 280 | 1100 | ||
| 330 | 1200 | ||
| 380 | 1350 | ||
| Stainless steel consoles (kerchiefs) | 400 | 1500 | |
| 500 | 2200 | ||
| 600 | 2200 | ||
| 750 | 3000 | ||
| 950 | 4000 | ||
| Platform with clamp | 115 | 900 | |
| 150 | 900 | ||
| 200 | 1000 | ||
| 230 | 1000 | ||
| 260 | 1100 | ||
| 280 | 1200 | ||
| 330 | 1300 | ||
| 380 | 1500 | ||
| 430 | 1800 | ||
| Wall fastening | 115 | 650 | |
| 150 | 650 | ||
| 200 | 800 | ||
| 230 | 850 | ||
| 260 | 900 | ||
| 280 | 1000 | ||
| 330 | 1100 | ||
| 380 | 1200 | ||
| 430 | 1350 | ||
| Masterflash (roof penetration) | Color | Diameter 200-280 mm. | Diameter 260-480 mm |
| brown | 2300 | 5000 | |
| red | 2300 | 5000 | |
| grey | 2300 | 5000 | |
| green | 2300 | 5000 | |
| As well as the production of products and components for chimneys of non-standard sizes according to customer drawings (adapters, tanks, heat exchangers, etc.). | |||
Materials and tools for making a chimney
Before you start purchasing parts, fasteners and tools to perform this work, you need to decide on the design of the device and complete a preliminary design, an integral part of which is a material list, which lists all the necessary parts. By adding the cost of materials to this list, you will receive a cost estimate.
Before construction, it is recommended to sketch the chimney
Installation of the device is carried out from the bottom up, that is, from the stove to the top, for which you will need:
- a transition device made of fittings from the furnace to the pipe; depending on the design, a branch may be required;
- multilayer pipe;
- gate;
The gate allows you to adjust the draft
- fireproof material for the passage through the ceiling;
- plates made of galvanized sheet, approximately 500x500 mm in size - to close the passage;
- materials for insulating the intersection of the roofing pie, for example, a probe for protection from the outside;
- chimney head;
- clamps for fixing connections at the rate of 1 pc. for each;
- brackets for attaching chimneys to walls (depending on its design);
- collection for draining condensate;
- high-temperature sealant for sealing joints;
- steel pipes at the rate of 1 pc. per meter of chimney;
- stainless steel wire for guy wires;
- screws, nails.
The list of tools is small and may look like this:
- drill with drill bits for concrete and wood;
- jigsaw;
- screwdriver or wrench for installing fasteners;
- plastic inserts (dowels) for attaching brackets;
- hammer.
Depending on the design of the chimney, other tools may be needed; this will become clear when drawing up a preliminary design.
Preliminary calculation of the chimney system
Schematic diagrams for installing stainless steel chimneys
When planning the installation of a stainless chimney, it is necessary to take into account several important criteria, which are provided for by special fundamental documents of the technical supervision service:
1. The total height of the chimney cannot be less than 5 m - to ensure normal draft.
2. The construction of horizontal sections more than 1000 mm in length is not allowed.
3. In unheated rooms or in open space (on the street), the installation of elements that do not have their own thermal insulation is prohibited.
4. Particular attention to the excess of the chimney cut above the roof:
- If the roof is flat - at least 500 mm.
- The same requirements apply if the distance from the pipe to the ridge of the pitched roof is less than 150 cm.
- At a distance of 150 to 300 cm, the pipe must be at least level with the height of the ridge.
- At large distances, the pipe cut should not be below a line of 10º from the ridge height horizon.
- There are situations when other buildings are attached to the main building. In this case, the height of the pipes must be at least higher than their upper level.
5. If the chimney passes through a roof made of flammable materials, a spark arrester must be installed.
6. The most critical areas are passage through walls, ceilings, and roofs, especially if they are made of flammable materials. If the pipe is uninsulated (single-walled), then the distance between it and the ceiling must be at least 1000 mm. This, in fact, is not practiced, but even with a sandwich thickness of 50 mm, the minimum gap should be 200 mm.
7. Pipe joints in thick walls or ceilings are not allowed. Minimum distance from floor, ceiling, wall – 700 mm
8. When a chimney passes even through a non-combustible roof, the minimum gap between the pipe and the covering cannot be less than 130 mm.
9. Two basic rules must be taken into account:
- On a horizontal or inclined section from a heating device or stove, pipes are installed “along the smoke”, i.e. so that combustion products move freely along the internal channel. In practice, this is a pipe that is put on the previous one from the boiler.
- On the vertical section of the chimney, the opposite is true - installation is carried out “through condensation”, so that the resulting moisture “has no chance” of getting into the insulation. Thus, each subsequent pipe section is inserted into the underlying one.
10. The diameter of the pipe in any of its connections cannot be smaller than the standard outlet pipe of the heating device.
11. The total number of chimney turns, regardless of their angle, is no more than three.
The chimney may have an internal layout, passing through the premises of the house. In this case, either thermally insulated sandwich pipes are used, or the chimney itself can be covered with brickwork.
Indoor chimney diagram
Recently, with the widespread use of double-layer insulated parts, its external placement, with brackets attached to an external wall, has become a more popular scheme.
The location of the chimney outside on brackets...
or with the installation of a special supporting structure made of a metal profile.
...or on a special supporting structure.
The advantages of this arrangement are obvious - there is no need to arrange complex thermally insulated passages through the interfloor ceilings and roof.
Chimney insulation
This operation is only performed if single pipes were used. It is necessary to reduce the intensity of condensation and protect combustible structures from exposure to high temperatures.
The best material for this purpose is basalt wool, since it is absolutely non-flammable and does not emit harmful fumes in fire conditions. It is also used in the manufacture of multilayer pipes.
Insulation of a metal chimney may not always be required
An insulating layer of aluminum foil must be installed on top of the insulation, and its installation begins from the bottom up with an overlap of turns of 10–12 cm. This order ensures that the joints are oriented downward, which does not allow water to penetrate into the heat-insulating layer.
Features of operation
Metal chimneys, having a lot of undoubted advantages, require increased attention both during assembly and during operation:
- They should not be located near other utilities, such as electrical wiring or plumbing.
- Before starting installation work, the internal longitudinal seams of the pipes must be coated with a special sealant, since they are subject to temperature changes, which gradually weakens the joining edges.
- When cleaning stainless steel pipes, it is better not to use traditional metal balls with a wire “hedgehog”. Their influence deteriorates the mirror inner surface, making it difficult to drain condensate into the storage tanks. It is better to choose a brush made of synthetic materials.
Mechanical cleaning method is the most effective
Chimney maintenance
With a properly manufactured chimney, especially if it is made of stainless steel, the main maintenance operation is to clean the internal surface of soot.
Causes of soot formation
Combustion is the reaction of fuel oxidation with atmospheric oxygen. If it is insufficient, soot is released and adheres to the walls of the chimney. In reality, conditions arise under which the smoke duct becomes clogged in just a few months:
- A lack of oxidizer in the firebox can be caused by deliberately reducing draft by manipulating the damper in order to achieve slow burning or even smoldering of the fuel, which can quickly lead to negative consequences.
- Another firebox mistake is the use of damp firewood. Moisture prevents intense combustion of fuel, resulting in the formation of a large amount of soot.
- The use of resinous firewood, the combustion of which is accompanied by the release of soot, should be considered an unfavorable factor. Of course, heating stoves with oak or ash is too expensive, but you should strive to use firewood from non-resinous tree species.
- It is strictly not recommended to burn garbage in the oven, especially plastic bags or bottles for the same reasons.
- It is especially unfavorable to use plywood, particle boards and other materials for the manufacture of which synthetic adhesives are used for burning waste. With such fuel, the chimney becomes clogged with soot most quickly.