Purpose of the die
The tool in question is quite simple, characterized by the following features:
- The main purpose is to form a threaded surface on various external surfaces. In most cases, a threading die is used to produce grooves on pipes or shafts, and various rods.
- Mechanical processing is achieved through the complex surface of the inner surface. It is represented by a combination of several cutting edges located in a certain sequence. As they rotate, they remove metal to form coils.
- The design has a hole for the workpiece and a knob through which force will be transmitted.
Lerka
The distinctive features of the inch blade are the location of the cutting edges. To ensure removal of chips from the cutting zone, the hole has a rather complex shape, by which the tool can be recognized almost immediately.
Pipe threading
| Author | Share | Rate |
| Victor Samolin |
Interesting on the topic:
Purpose and correct choice of clamp
Designations and classification of pipe threads
Fitting is an indispensable part of engineering systems and communications
Comments on this article
Andrey There is one more nuance in pipe threads that you forgot to mention.
This is a seam on an electric-welded pipe that “throws” the die into the trash, or rather paints the cutting part. 03.11.2015 at 18:36Ruslan One inch, by the way, is not 2.54 mm, but 25.4 mm. 10″ pipe has a diameter of 254 mm + two wall thicknesses 01/19/2016 at 18:44
Types of dies
There are simply a huge number of different versions of the tool, which is associated with the variety of threaded connections. They all have their own specific advantages and disadvantages.
Types of dies are taken into account to select the most suitable version for thread cutting. The main characteristics of the classification are as follows:
- Form.
- Housing design.
- Method of cutting turns.
In addition, do not forget that there are metric and inch dies. Metric threads are more common, but inch threads are used to create various mechanisms.
Metric thread cutting die
The classification of thread cutting dies by shape is as follows:
- In the form of a hexagon.
- Tubular.
- Round.
- In the form of a square.
There are also several types of tools based on design characteristics:
- The one-piece die is left-handed, the thread can be with different pitches, it is represented by a non-separable cast body, which has several holes. This version is the most widely used, as it is characterized by reliability, ease of use, and long service life. However, if you frequently work with different diameters, you have to have a whole set of this tool with you.
- Split ones significantly simplify the process of cutting turns, which is also related to the design features of the body.
- Sliding versions have the most complex body, which can be adjusted within a certain range of diameters. Having one similar tool available, you can cut threaded surfaces on workpieces of various diameters.
Inch thread cutting die
Left-handed threads can be used with all common tool options. By purpose, the following classification can be distinguished:
- For round threads.
- For conical shape.
- For cylindrical.
Manufacturing is carried out in accordance with established standards in GOST.
The design of the die, its difference from the die
A thread cutting die is a nut with axial holes that form the cutting edges, as well as chip holes for removing the generated chips during operation. The working part is, as a rule, an internal cone with 8-10 turns, of which 2-3 turns are the intake part. They can have a solid, sliding or split design. Split and sliding dies have the ability to change the diameter of the thread being cut.
The die material is alloy steel 9ХС, ХВСГВ. High-speed steels are widely used - R18, R6M5K8, R5M5 and others, as well as hard alloys. The steel grade, along with the designation and degree of accuracy, is indicated on the die body (with the exception of 9ХС steel).
The question often arises - what is a lerka and what is its difference from a die. Previously, there was a division - dies were called set-up, adjustable tools for preparing large-diameter threads. Ledgers are solid plates with holes and grooves, usually of small diameter. Now both types of tools are most often called dies.
Rules for cutting threads using dies
Only if the established rules of work are observed, it is possible to obtain a surface with high precision and quality. A die for cutting external threads must be used in conjunction with a special driver, through which force is transmitted.
Options for cutting with round and sliding dies
When considering how to cut a thread with a die, you should pay attention to the following points:
- To determine the exact parameters of the tool, you should pay attention to the markings that are applied to the body. Labeling is carried out in accordance with established standards. Some experts can determine the parameters of a product “by eye”.
- The whole process begins with preparing the workpiece. You can ensure an easy start by chamfering, for which you can use a file. The chamfer is made at an angle of 45 degrees and should not be large. It is necessary to ensure that the metal is removed evenly.
- Cutting turns should not be carried out on a dry surface, as this leads to rapid wear of the cutting edge. A special lubricant is added to the cutting zone, which significantly simplifies the operation by reducing friction. Lubrication can be represented by motor oil or grease.
- The cutting process involves making two turns, followed by one turn in the opposite direction. Due to the movement of the tool in the opposite direction, chips are removed from the cutting zone, which leads to a simplified stroke and an increase in the quality of the work performed. For the first few turns, you need to ensure that the tool is in a strictly vertical position, otherwise the quality of the resulting surface will be poor.
- In the future, every two revolutions during cutting should be about a half-turn. This ensures a smoother ride. If the housing heats up during processing, you should take breaks. Too high a temperature causes plasticity of the metal, which leads to a decrease in wear resistance.
The quality of the resulting turns is checked when using a nut with the required diameter and thread parameters. The first pass may occur with slight difficulties, but within normal limits. The second and subsequent checks should be carried out effortlessly.
Some technical characteristics
To begin with, we note that the type of tool in question can only be used in conjunction with special holders. This is due to the fact that a lot of force must be transferred to the die during machining. One holder can be used to work simultaneously with different types of lechers.
The following information should also be taken into account:
- Left-handed dies are used to produce left-handed threads. Today they are used extremely rarely. To identify the tool, the designation “LH” is applied. Such a thread is required when the element is constantly in rotation during operation.
- Pipe versions differ from metric ones; for identification, the symbol “G” is applied to the surface of the body.
- To obtain a cone thread, a conical pipe tool is used. Most often used on production lines for the production of machine tools or fuel pipelines. Indicated by applying the letter “K” to the surface of the body.
When choosing a tool, you should pay attention to the concept of pitch - the distance formed between two adjacent turns. It is worth considering that the die has a main and an additional step.
Tips for choosing a tool
The cutting die can last for a long period. In its manufacture, as a rule, tool steel is used, which is characterized by high wear resistance.
The tool is selected according to the following parameters:
- Outer diameter of the workpiece.
- Accuracy class.
- Pitch and other thread parameters.
- According to the type of material being processed.
Die threading
Cutting threads using a die
The highest quality and most accurate cutting, as a rule, is carried out when using the split version. The design is characterized by the presence of a locking ring. In addition, there are simply a huge number of different sets on sale, which are represented by products with different diameters and parameters. All the necessary information can be determined by deciphering the markings. All designations, as a rule, are applied to the body of the product.
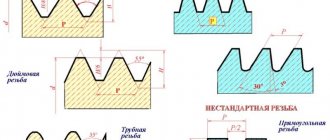
Profile
According to the profile, there are metric, pipe inch dies, and trapezoidal threading tools. Each variety has its own characteristics:
Metric. As the name suggests, they cut metric threads. They are designated by the letter “M”, followed by a number indicating the thread diameter in millimeters. The standards provide for sizes up to 68 mm, each corresponding to a small or large step. Dimensions, designation examples, acceptance rules for such dies according to GOST 9740.
Read here: Review of modern pipe wrenches: characteristics, types, sizes and application advantages
Pipe cylindrical. Visually easy to identify by the letter “G” on the body. This type of thread is measured using the English inch unit, which is 25.4 mm.
So, the designation G 1/2” means that we have a half-inch pipe thread. They are widely used for pipes of heating equipment and water supply systems. Size range from G 1/8” to G 2”.
Pipe conical. In order not to confuse them with other varieties, they are marked with the symbol “K”. They are used when it is necessary to obtain a conical threaded surface - in critical connections operating under pressure or machine components.
Trapezoidal. The cross-section of the threads is an equilateral trapezoid. They are common in power pairs that convert rotation into translational motion. The simplest example is the lead screw and nut of a machine and bench vice.