Sometimes it is very important to accurately calculate the volume of water passing through the pipe. For example, when you need to design a new heating system. This raises the question: how to calculate the volume of a pipe? This indicator helps to choose the right equipment, for example, the size of the expansion tank. In addition, this indicator is very important when antifreeze is used. It is usually sold in several forms:
- Diluted;
- Undiluted.
The first type can withstand temperatures of 65 degrees. The second one will freeze at -30 degrees. To buy the right amount of antifreeze, you need to know the volume of coolant. In other words, if the volume of liquid is 70 liters, then you can purchase 35 liters of undiluted liquid. It is enough to dilute them, maintaining a proportion of 50–50, and you will get the same 70 liters.
What formula is used to calculate
To get accurate data, you need to prepare:
- Calculator;
- Calipers;
- Ruler.
First, the radius is measured, designated by the letter R. It can be:
- Internal;
- External.
The first allows you to calculate how much liquid can fit in the cylinder, that is, the internal volume of the pipe, its cubic capacity.
The outer radius is necessary to determine the size of the space it will occupy.
To calculate, you need to know the pipe diameter data. It is denoted by the letter D and is calculated using the formula R x 2. The circumference is also determined. Denoted by the letter L.
To calculate the volume of a pipe, measured in cubic meters (m3), you must first calculate its area.
To obtain an accurate value, you must first calculate the cross-sectional area. To do this, use the formula:
- S = R x Pi.
- The required area is S;
- Pipe radius – R;
- Pi number is 3.14159265.
The resulting value must be multiplied by the length of the pipeline.
How to find the volume of a pipe using the formula? You only need to know 2 values. The calculation formula itself has the following form:
- V = S x L
- Pipe volume – V;
- Sectional area – S;
- Length – L
For example, we have a metal pipe with a diameter of 0.5 meters and a length of two meters. To carry out the calculation, the size of the external cross member of the stainless metal is inserted into the formula for calculating the area of the circle. The pipe area will be equal to;
S= (D/2) = 3.14 x (0.5/2) = 0.0625 sq. meters.
The final calculation formula will take the following form:
V = HS = 2 x 0.0625 = 0.125 cu. meters.
This formula calculates the volume of absolutely any pipe. And it doesn’t matter at all what material it is made of. If the pipeline has many components, using this formula, you can calculate separately the volume of each section.
When performing calculations, it is very important that the dimensions are expressed in the same units of measurement. The easiest way to calculate is if all values are converted to square centimeters.
If you use different units of measurement, you can get very questionable results. They will be very far from the real values. When performing constant daily calculations, you can use the calculator's memory by setting a constant value. For example, Pi multiplied by two. This will help to calculate the volume of pipes of different diameters much faster.
Today, for calculations you can use ready-made computer programs, in which standard parameters are specified in advance. To perform the calculation, you will only need to enter additional variable values. Download the program https://yadi.sk/d/_1ZA9Mmf3AJKXy
Formula for a single pipe
From a geometry standpoint, the pipe is a straight circular cylinder.
The volume of such an object is equal to the cross-sectional area multiplied by the length:
The cross-sectional area of a pipe shaped like a circle with a known diameter is calculated using the formula:
S = π * d 2 / 4
The final formula for the volume of a pipe with a known internal diameter and length will be as follows:
V = π * l * d 2 / 4
If the unit of measurement for the length and diameter of the pipe is another value (dm, cm or mm), then the volume will be expressed in dm 3, cm 3 or mm 3, respectively.
Also, I wanted to show you a simple way to measure the outer diameter of a pipe (D) without a caliper. D = L / π , where L is the circumference:
How to calculate cross-sectional area
If the pipe is round, the cross-sectional area should be calculated using the formula for the area of a circle: S = π*R2. Where R is the radius (internal), π is 3.14. In total, you need to square the radius and multiply it by 3.14. For example, the cross-sectional area of a pipe with a diameter of 90 mm. We find the radius - 90 mm / 2 = 45 mm. In centimeters this is 4.5 cm. We square it: 4.5 * 4.5 = 2.025 cm2, substitute it into the formula S = 2 * 20.25 cm2 = 40.5 cm2.
The cross-sectional area of a profiled product is calculated using the formula for the area of a rectangle: S = a * b, where a and b are the lengths of the sides of the rectangle. If we consider the cross-section of the profile to be 40 x 50 mm, we get S = 40 mm * 50 mm = 2000 mm2 or 20 cm2 or 0.002 m2.
Polypropylene pipe - what is it?
Polypropylene is a type of thermoplastic polymer. It is produced by combining (polymerizing) molecules of a derivative of ethylene gas. The international designation of polypropylene is “PP”. Next, we will take a closer look at polypropylene pipes: technical characteristics, properties and manufacturing technology of this new generation material.
Having unique resistance to the effects of alkaline solvents and aggressive substances, the material is widely used in the installation of heating systems, water supply systems and sanitary facilities. Can withstand low temperatures (up to -10 degrees) or high temperatures (up to +110 degrees).
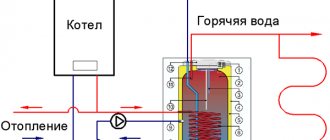
Calculation of the volume of water in the entire system
To determine such a parameter, it is necessary to substitute the value of the internal radius into the formula. However, a problem immediately appears. How to calculate the total volume of water in the pipe of the entire heating system, which includes:
- Radiators;
- Expansion tank;
- Heating boiler.
First, the volume of the radiator is calculated. To do this, its technical passport is opened and the volume values of one section are written down. This parameter is multiplied by the number of sections in a particular battery. For example, one section of a cast iron radiator is equal to 1.5 liters.
When a bimetallic radiator is installed, this value is much lower. The amount of water in the boiler can be found in the device data sheet.
To determine the volume of the expansion tank, it is filled with the amount of liquid measured in advance.
The volume of pipes is determined very simply. The available data for one meter of a certain diameter simply needs to be multiplied by the length of the entire pipeline.
Note that in the global network and reference literature, you can see special tables. They show approximate product data. The error in the given data is quite small, so the values given in the table can be safely used to calculate the volume of water.
It must be said that when calculating values, you need to take into account some characteristic differences. Metal pipes with a large diameter allow the amount of water to pass through, much less than the same polypropylene pipes.
The reason lies in the smoothness of the surface of the pipes. For steel products it is made with great roughness. PPR pipes do not have roughness on the inner walls. However, steel products have a larger volume of water than other pipes of the same cross-section. Therefore, to make sure that the calculation of the volume of water in the pipes is correct, you need to double-check all the data several times and confirm the result with an online calculator.
Formula for determining the cross-sectional area of incompletely filled pipes:
Existing materials for creating water supply networks
Before you calculate the diameter of a pipe for a water supply system, you need to select a material for it. It could be:
- metal (steel, copper, cast iron, their various compounds);
- polymeric materials - plastic, polyethylene, metal-plastic, PVC;
- combinations of metal and plastic structures.
Whatever the characteristics of the materials, the dimensions will also be important. In particular, the diameter of plastic pipes for water supply (metal and metal-plastic too) is divided into external and internal, and the permeability of the pipeline depends on it and the thickness of the walls.
The level of working pressure is also influenced by certain characteristics of the material. In particular, steel is characterized by reliability and strength, but is susceptible to corrosion and is also heavy, making installation of the system difficult. Also, limescale may accumulate inside the steel pipeline - consequently, the diameter will decrease and the permeability of the system will decrease.
Plastic is characterized by low weight, simple and easy installation. Such pipes do not accumulate plaque inside and do not rust; they are inexpensive and flexible. If the pipes are plastic, without a metal layer, then they can expand due to heating, but in metal-plastic products this drawback is eliminated.
Internal volume of a linear meter of pipe in liters - table
The table shows the internal volume of a linear meter of pipe in liters. That is, how much water, antifreeze or other liquid (coolant) is needed to fill the pipeline. The internal diameter of pipes is taken from 4 to 1000 mm.
| Inner diameter, mm | Internal volume of 1 m running pipe, liters | Internal volume of 10 m linear pipes, liters |
| 4 | 0.0126 | 0.1257 |
| 5 | 0.0196 | 0.1963 |
| 6 | 0.0283 | 0.2827 |
| 7 | 0.0385 | 0.3848 |
| 8 | 0.0503 | 0.5027 |
| 9 | 0.0636 | 0.6362 |
| 10 | 0.0785 | 0.7854 |
| 11 | 0.095 | 0.9503 |
| 12 | 0.1131 | 1.131 |
| 13 | 0.1327 | 1.3273 |
| 14 | 0.1539 | 1.5394 |
| 15 | 0.1767 | 1.7671 |
| 16 | 0.2011 | 2.0106 |
| 17 | 0.227 | 2.2698 |
| 18 | 0.2545 | 2.5447 |
| 19 | 0.2835 | 2.8353 |
| 20 | 0.3142 | 3.1416 |
| 21 | 0.3464 | 3.4636 |
| 22 | 0.3801 | 3.8013 |
| 23 | 0.4155 | 4.1548 |
| 24 | 0.4524 | 4.5239 |
| 26 | 0.5309 | 5.3093 |
| 28 | 0.6158 | 6.1575 |
| 30 | 0.7069 | 7.0686 |
| 32 | 0.8042 | 8.0425 |
| 34 | 0.9079 | 9.0792 |
| 36 | 1.0179 | 10.1788 |
| 38 | 1.1341 | 11.3411 |
| 40 | 1.2566 | 12.5664 |
| 42 | 1.3854 | 13.8544 |
| 44 | 1.5205 | 15.2053 |
| 46 | 1.6619 | 16.619 |
| 48 | 1.8096 | 18.0956 |
| 50 | 1.9635 | 19.635 |
| 52 | 2.1237 | 21.2372 |
| 54 | 2.2902 | 22.9022 |
| 56 | 2.463 | 24.6301 |
| 58 | 2.6421 | 26.4208 |
| 60 | 2.8274 | 28.2743 |
| 62 | 3.0191 | 30.1907 |
| 64 | 3.217 | 32.1699 |
| 66 | 3.4212 | 34.2119 |
| 68 | 3.6317 | 36.3168 |
| 70 | 3.8485 | 38.4845 |
| 72 | 4.0715 | 40.715 |
| 74 | 4.3008 | 43.0084 |
| 76 | 4.5365 | 45.3646 |
| 78 | 4.7784 | 47.7836 |
| 80 | 5.0265 | 50.2655 |
| 82 | 5.281 | 52.8102 |
| 84 | 5.5418 | 55.4177 |
| 86 | 5.8088 | 58.088 |
| 88 | 6.0821 | 60.8212 |
| 90 | 6.3617 | 63.6173 |
| 92 | 6.6476 | 66.4761 |
| 94 | 6.9398 | 69.3978 |
| 96 | 7.2382 | 72.3823 |
| 98 | 7.543 | 75.4296 |
| 100 | 7.854 | 78.5398 |
| 105 | 8.659 | 86.5901 |
| 110 | 9.5033 | 95.0332 |
| 115 | 10.3869 | 103.8689 |
| 120 | 11.3097 | 113.0973 |
| 125 | 12.2718 | 122.7185 |
| 130 | 13.2732 | 132.7323 |
| 135 | 14.3139 | 143.1388 |
| 140 | 15.3938 | 153.938 |
| 145 | 16.513 | 165.13 |
| 150 | 17.6715 | 176.7146 |
| 160 | 20.1062 | 201.0619 |
| 170 | 22.698 | 226.9801 |
| 180 | 25.4469 | 254.469 |
| 190 | 28.3529 | 283.5287 |
| 200 | 31.4159 | 314.1593 |
| 210 | 34.6361 | 346.3606 |
| 220 | 38.0133 | 380.1327 |
| 230 | 41.5476 | 415.4756 |
| 240 | 45.2389 | 452.3893 |
| 250 | 49.0874 | 490.8739 |
| 260 | 53.0929 | 530.9292 |
| 270 | 57.2555 | 572.5553 |
| 280 | 61.5752 | 615.7522 |
| 290 | 66.052 | 660.5199 |
| 300 | 70.6858 | 706.8583 |
| 320 | 80.4248 | 804.2477 |
| 340 | 90.792 | 907.9203 |
| 360 | 101.7876 | 1017.876 |
| 380 | 113.4115 | 1134.1149 |
| 400 | 125.6637 | 1256.6371 |
| 420 | 138.5442 | 1385.4424 |
| 440 | 152.0531 | 1520.5308 |
| 460 | 166.1903 | 1661.9025 |
| 480 | 180.9557 | 1809.5574 |
| 500 | 196.3495 | 1963.4954 |
| 520 | 212.3717 | 2123.7166 |
| 540 | 229.0221 | 2290.221 |
| 560 | 246.3009 | 2463.0086 |
| 580 | 264.2079 | 2642.0794 |
| 600 | 282.7433 | 2827.4334 |
| 620 | 301.9071 | 3019.0705 |
| 640 | 321.6991 | 3216.9909 |
| 660 | 342.1194 | 3421.1944 |
| 680 | 363.1681 | 3631.6811 |
| 700 | 384.8451 | 3848.451 |
| 720 | 407.1504 | 4071.5041 |
| 740 | 430.084 | 4300.8403 |
| 760 | 453.646 | 4536.4598 |
| 780 | 477.8362 | 4778.3624 |
| 800 | 502.6548 | 5026.5482 |
| 820 | 528.1017 | 5281.0173 |
| 840 | 554.1769 | 5541.7694 |
| 860 | 580.8805 | 5808.8048 |
| 880 | 608.2123 | 6082.1234 |
| 900 | 636.1725 | 6361.7251 |
| 920 | 664.761 | 6647.6101 |
| 940 | 693.9778 | 6939.7782 |
| 960 | 723.8229 | 7238.2295 |
| 980 | 754.2964 | 7542.964 |
| 1000 | 785.3982 | 7853.9816 |
If you have a specific design or pipe, then the formula above shows how to calculate the exact data for the correct flow of water or other coolant.
Online calculation
https://mozgan.ru/Geometry/VolumeCylinder
What is the displacement of one meter of 16 mm MP pipe?
elmix . The volume of the cylinder is calculated by multiplying S of the circle (base) by H (pipe length), i.e.
User Goryn 68 wrote:
User Peterjela wrote:
I think the TS was just thinking about how many kilos will be put on the ceiling after running water into the warm floor.
I read it again, but didn’t find anything about warm floors.
The volume of water or coolant in various pipelines, such as low-density polyethylene (HDPE pipe), polypropylene pipes, metal-plastic pipes, steel pipes, must be known when selecting any equipment, in particular an expansion tank.
For example, in a metal-plastic pipe with a diameter of 16, a meter of pipe is 0.115 g. coolant.
Did you know? Most likely no. And why do you actually need to know this until you are faced with the selection of, for example, an expansion tank. Knowing the volume of coolant in the heating system is necessary not only for selecting an expansion tank, but also for purchasing antifreeze. Antifreeze is sold undiluted to -65 degrees and diluted to -30 degrees. Once you know the volume of coolant in the heating system, you can buy an even amount of antifreeze. For example, undiluted antifreeze must be diluted 50*50 (water*antifreeze), which means that with a coolant volume of 50 liters, you will need to buy only 25 liters of antifreeze.
What is the displacement of one meter of 16 mm MP pipe?
elmix . The volume of the cylinder is calculated by multiplying S of the circle (base) by H (pipe length), i.e.
User Goryn 68 wrote:
User Peterjela wrote:
I think the TS was just thinking about how many kilos will be put on the ceiling after running water into the warm floor.
I read it again, but didn’t find anything about warm floors.