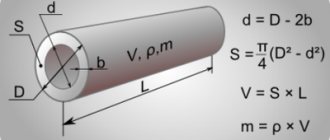
Automated calculation of the volume of insulation of round surfaces, such as pipes, air ducts and pipelines, by outer diameter. The calculator calculates the volume of insulation in cubic meters, as well as the insulation area in square meters. According to the technical part of the collection FER26:2. Rules for calculating the volume of work 2.1 The volume of insulation “in use” (Oi) m3 per 1 m of length of pipelines or cylindrical equipment is calculated using the formula: Oi = 3.14 × (D + T) × T, where T is the thickness of the insulating layer, m; D - outer diameter of the pipeline or equipment, m.2.2. Length of insulated pipelines, as well as equipment of cylindrical and rectangular sections, etc.
determined along the center line for each section, and fittings and flanges, fittings, etc. are not excluded from the length.2.3. The perimeter of a polygonal and similar section is determined as the arithmetic mean of the perimeters of the internal and external surfaces of the insulation.2.4. The volume of insulation of individual places near instrumentation and fittings, as well as near all kinds of hatches, fittings, openings on equipment is taken into account in prices, while the length of insulated pipelines is measured without deducting the indicated places.
To get the result, enter values in the form fields.
Did you like the calculator? Share with your friends
Find the angle ABC of an isosceles trapezoid ABCD if the diagonal AC forms with the base AD and * Trapezium Mathematics / Russian language 9th grade.
Calculation of insulation volume, area of anti-corrosion coating and covering material
Calculation of the volume of insulation, the area of covering material and anti-corrosion coating often has to be done when drawing up estimates and closing completed volumes. We are all used to using reference books or a calculator to calculate actual volumes, but if it can be automated, then let's use this opportunity.
To calculate the volume of insulation and the area of covering material, select the type of surface to be insulated and enter the values in the appropriate fields.
Why you need to know this
Below we will consider situations where these parameters usually always need to be taken into account in work:
- Knowledge of the area formula will be useful when calculating the heat transfer of a heated floor or heating register. Data can be obtained based on the total area that transfers heat to the air in the room from a working fluid of a certain temperature.
- The second option is the opposite situation, which also occurs often. Especially if it is necessary to calculate heat losses along the entire length of the pipeline to the heating device. When calculating the number and size of convectors, radiators and other devices, the instructions require you to know exactly how many calories they can produce. The data is determined taking into account the surface area of the pipeline transporting water.
The photo shows heating calculations for 1 sq. m of area, based on the diameter of the pipeline
- Knowing how to calculate the surface area of a pipe will help you purchase the correct amount of insulation. Very often, the length of the heating main is tens of kilometers, so accurate data will help companies save significant funds.
Steel pipe surface area calculator for painting
- Another point is the cost of painting or anti-corrosion coating, the price of which is sometimes impressive. In this case, knowledge will allow you to accurately calculate the required volume of material. In addition, it is possible to use indirect methods to determine the negligence of the work performers if the costs per 1 m2 of surface increase significantly.
- Calculating the pipe area (section) will allow you to find out the maximum permeability of the product. Of course, you can simply immediately install a obviously larger diameter, however, with large investments in construction projects, this indicator plays a significant role in cost overruns.
Do not also forget that when the hot water supply tap is opened, the volume of liquid in the water supply cools down aimlessly. The large diameter of the pipe accumulates a large amount of water that will stand in it, so you will spend more heat to heat the room.
How to calculate the cross section
- It is necessary to calculate the area of the circle and subtract the thickness of the walls.
- The formula is as follows: S = π(D/2-N)2.D – diameter, N – wall thickness.
For hydraulic calculations of the latter, the concept of live section was introduced.
The diameter of the water supply must correspond to its tasks
Surface calculation
A geometric problem that you have encountered more than once in class, when you needed to find out the surface area of a cylinder, and, well, a pipe is what it is. To find out the required figure, you need to know the circumference and height of the cylinder (in our case, the length of the pipeline).
The formula for the circumference is Lcirc = πD, for the surface – S = πDL, where L is the length of the pipeline, and D is its diameter.
For painting, you can use this formula directly, but if you need to carry out thermal insulation work, you will need a little more material, since it is thick. In addition, during the process, mineral wool is laid with some overlap of the sheets.
Do-it-yourself insulation of steel products
Calculating the inner surface
Non-experts will definitely ask the question - why do you need to know this parameter? Experts will answer - for hydrodynamic calculations, in order to know what area has contact with water while moving through pipes.
The inner surface of plastic products is not overgrown with mineral deposits
There are several associated nuances with this parameter:
| Diameter | The larger it is, the less the wall roughness affects the movement of the working fluid. If the diameter of the pipeline is large and its length is small, the resistance of the pipe can be neglected. |
| Roughness | This parameter is of great importance for hydrodynamic calculations. For example, a steel water pipe, rusty inside, and a smooth polypropylene pipe have different effects on the speed of the working fluid. |
| Consistency of internal diameter | Steel and cast iron products change their internal area over time due to corrosion and mineral deposits. Because of this, the passage for flow is reduced. |
Corrosion on the inner surface reduces the passage for working fluid
The calculation formula will be as follows: S=π(D-2N)L, where N is the wall thickness, L is the length of the pipeline, D is its diameter.
Calculation of insulation volume, area of anti-corrosion coating and covering material
Calculation of the volume of insulation, the area of covering material and anti-corrosion coating often has to be done when drawing up estimates and closing completed volumes. We are all used to using reference books or a calculator to calculate actual volumes, but if it can be automated, then let's use this opportunity.
To calculate the volume of insulation and the area of covering material, select the type of surface to be insulated and enter the values in the appropriate fields.
Method for determining the surface temperature of an insulating layer based on a given temperature
This requirement is relevant in industrial enterprises where various pipelines run inside rooms and workshops where people work. In this case, the temperature of any heated surface is normalized in accordance with labor protection rules in order to avoid burns. Calculation of the thickness of the thermal insulation structure for pipes with a diameter over 2 m is carried out in accordance with the formula:
Formula for determining the thickness of thermal insulation.
δ = λ (tп – tп) / ɑ (tп – t0), here:
- ɑ – heat transfer coefficient, taken from reference tables, W/(m2 ⁰C);
- tп – normalized temperature of the surface of the heat-insulating layer, ⁰C;
- other parameters are as in the previous formulas.
The thickness of the insulation on a cylindrical surface is calculated using the equation:
ln B =(dout + 2δ) / dtr = 2πλ Rн (tt – tp) / (tp – t0)
Designations of all parameters are as in the previous formulas. According to the algorithm, this calculation is similar to calculating the thickness of insulation based on a given heat flow. Therefore, it is then carried out in exactly the same way; the final value of the thickness of the heat-insulating layer δ is found as follows:
δ = diz (B – 1) / 2
The proposed method has some error, although it is quite acceptable for preliminary determination of the parameters of the insulating layer. A more accurate calculation is performed by the method of successive approximations using a personal computer and specialized software.
Calculation of the volume of pipeline insulation and laying of material
- Types of insulation materials Laying insulation Calculation of pipeline insulation materials Elimination of insulation defects
Insulation of pipelines is necessary in order to significantly reduce heat loss.
First you need to calculate the volume of pipeline insulation. This will not only optimize costs, but also ensure competent execution of work and maintenance of pipes in proper condition. The right material can prevent corrosion and improve thermal insulation.
Pipe insulation diagram.
Today, different types of coatings can be used to protect highways. But it is necessary to consider exactly how and where communications will take place.
For water pipes, two types of protection can be used at once - internal coating and external. It is recommended to use mineral wool or glass wool for heating routes, and to purchase polyurethane foam for industrial ones. Calculations are performed using different methods, it all depends on the type of coating chosen.
Calculations
Let's delve into mathematics and count.
Conventional cylindrical
Here the basis of the calculation is the formula from the school curriculum - calculating a cylinder:
S = 2 x Pi x R x L, where
- R is the outer radius, and
- L – length.
Thus, the table of the pipe painting area in this case will take the form, given that the length of our section is 10 meters:
Now it will not be difficult to calculate the approximate consumption of the selected paint, knowing its hiding power.
Sewer cylindrical
We take into account diameters from 70 to 200 in increments of 20 cm, our manual pipe painting area calculator will give the following results:
- 70 – 1.99 sq.m;
- 100 – 2,83;
- 120 – 3,39;
- 140 – 3,96;
- 160 – 4,52;
- 180 – 5,09;
- 200 – 5.65 sq.m.
Profile
The formula for the area to paint a pipe of this type will consist of the sum of four rectangles - sides:
S = 2 x hx L + 2 xwx L, where
- h – height of the rectangle on one side;
- w – height of the rectangle of the second side;
- L – length.
If we assume that L is still the same - 10 meters, and the heights are 10 and 5 cm, then the result is 3 square meters.
Conical
Let us take into account that the pipes are in the shape of a truncated cone. Its area is calculated by the formula:
S = 2 x Pi x R1 x L + Pi x (R1 x R1 + R2 x R2), where
- R1 – smaller diameter;
- R2 – larger diameter;
- L – length.
If we take into account L of 10 meters, with R1 - 3 cm, and R2 - 6, then the result is 1.90 sq.m.
Corrugated
When considering this option, you need to carefully consider its geometry:
- A – rounding radius;
- B – projection of the straight section along the length;
- C – corrugation pitch;
- D – projection of the straight section onto the diameter;
- E – bevel angle of the straight section;
- F – corrugation height;
- G is the middle line of the corrugation along which it can stretch.
Means:
- We take the rounding radius to be 3 mm;
- this means the rounded part is (2 x Pi x R) – 18.84 mm;
- take the total double D to be 20 mm;
- it turns out that in extended form we have 38.84 mm;
- if we neglect the bevel angle, then the pitch of the corrugation E will be equal to double the diameter - 12 mm.
- we take a length of 10 meters;
- from here we get that there will be 10,000/12 folds or – 866;
- from here, the elongated length will be 866 c 38.84 - 33.64 meters (as we can see, more than 3 times longer);
- if we take the diameter of the elongated version - 52 mm, then we get the final area of our corrugation, neither more nor less - 54.92 sq.m.
Types of insulating materials
Various materials are used to insulate pipelines. They differ in the type of application, layer thickness and their characteristics.
The choice should be taken carefully. Bituminous coatings were considered the most popular not so long ago. In some cases, the pipe can be additionally protected by fiberglass.
Bituminous materials are used for thermal insulation of underground lines. They prevent corrosion. Operating conditions are as follows: for normal outdoor installation -40/+65°C, for deep underground use -5/+30°C.
Copper and steel pipe insulation chart.
To save money, polymer-bitumen compositions can be used. Installation is quick, and the quality of pipeline insulation is high. PPU is a reliable and durable material that can be used during channelless or channel installation of communications, for overhead pipelines.
The result is a “pipe-in-pipe” gasket. The work process is simple, even a beginner can handle it. Polyurethane foam is applied in liquid form to the surface, after which it hardens, forming a durable and strong shell.
Anti-corrosion polyethylene insulation is a multi-layer coating that is applied only in industrial conditions.
Such pipes are used for transporting petroleum products and gas mixtures. Glass wool is also often used today. This is a simple and reliable material that is easy to apply.
Calculating the area is carried out without any particular difficulties, but it is necessary to take into account the thickness of the layer. Mineral wool is also great for heating pipes. The material can be used to insulate pipes of different diameters.
Choosing insulation
The main reason for pipeline freezing is insufficient energy circulation speed.
In this case, at sub-zero air temperatures, the process of crystallization of the liquid may begin. So high-quality thermal insulation of pipes is vital. Fortunately, our generation is incredibly lucky. In the recent past, insulation of pipelines was carried out using only one technology, since there was only one insulation - glass wool. Modern manufacturers of thermal insulation materials simply offer the widest selection of pipe insulation materials, differing in composition, characteristics and method of application.
It is not entirely correct to compare them with each other, much less to say that one of them is the best. So let's just look at the types of pipe insulation materials.
By scope:
- for cold and hot water supply pipelines, steam pipelines for central heating systems, various technical equipment;
- for sewer and drainage systems;
- for pipes of ventilation systems and freezing equipment.
In appearance, which, in principle, immediately explains the technology for using insulation:
- roll;
- leafy;
- casing;
- filling;
- combined (this rather refers to the method of pipeline insulation).
The main requirements for the materials from which pipe insulation is made are low thermal conductivity and good fire resistance.
The following materials meet these important criteria:
Mineral wool. Most often sold in roll form. Suitable for insulating pipelines with high temperature coolant. However, if you use mineral wool to insulate pipes in large volumes, then this option will not be very profitable in terms of economy. Thermal insulation using mineral wool is produced by the winding method, followed by its fastening with synthetic twine or stainless wire.
The photo shows a pipeline insulated with mineral wool
It can be used at both low and high temperatures. Suitable for steel, metal-plastic and other polymer pipes. Another positive feature is that polystyrene foam has a cylindrical shape, and its internal diameter can be adjusted to the size of any pipe.
Penoizol. According to its characteristics, it is closely related to the previous material. However, the method of installing penoizol is completely different - its application requires a special spraying installation, since it is a component liquid mixture. After the penoizol hardens, a sealed shell is formed around the pipe, almost impervious to heat. Another advantage here is the lack of additional fastening.
Penoizol in action
Foiled penofol. The latest development in the field of insulation materials, but it has already won its fans among Russian citizens. Penofol consists of polished aluminum foil and a layer of foamed polyethylene.
This two-layer design not only retains heat, but even acts as a kind of heater! As you know, foil has heat-reflecting properties, which allows it to accumulate and reflect heat to the insulated surface (in our case, a pipeline).
In addition, foil penofol is environmentally friendly, low-flammable, resistant to temperature changes and high humidity.
As you can see, there are plenty of materials! There is plenty to choose from to insulate pipes. But when choosing, do not forget to take into account the characteristics of the environment, the characteristics of the insulation and its ease of installation. Well, it wouldn’t hurt to calculate the thermal insulation of the pipes in order to do everything correctly and reliably.
Laying insulation
The calculation of insulation depends on what kind of installation is used. It can be external or internal.
External insulation is recommended for the protection of heating systems. It is applied along the outer diameter and provides protection against heat loss and the appearance of traces of corrosion. To determine the volume of material, it is enough to calculate the surface area of the pipe.
Thermal insulation maintains the temperature in the pipeline regardless of the influence of environmental conditions.
Internal laying is used for plumbing.
It perfectly protects against chemical corrosion and prevents heat loss through hot water routes. Usually this is a coating material in the form of varnishes and special cement-sand mortars. The choice of material can also be made depending on what kind of gasket will be used.
Channel laying is most often in demand. For this purpose, special channels are preliminarily arranged, and the routes are placed in them. The channelless installation method is used less frequently, since the work requires special equipment and experience. The method is used in cases where it is not possible to carry out trenching work.
Why paint pipes?
Making a pipe look aesthetically pleasing is the most obvious function of painting. But she is far from the only one. First of all, pipes are painted to make them corrosion resistant. Previously, water pipes were made of steel without a special protective coating. This approach allowed for significant savings.
At the end of the last century, the situation was complicated by the fact that there was no control over construction companies as such. And difficult financial conditions have forced companies to resort to austerity.
Therefore, to set up utilities, the cheapest steel pipes with thin walls, which were designed for the installation of gas pipeline systems, were most often used. Such water pipelines literally fell into disrepair within ten years. Painting in this case could extend their service life.
At the moment the situation has improved, but not much. And now steel pipes are most often used in household heating and water supply systems. You can extend the service life of such structures if you carry out painting work (read: “Which paint to choose for heating pipes - possible options, characteristics”). First you need to calculate the paint for the pipe.
Recommendation: galvanized pipes do not require full painting with an anti-corrosion compound. But the threaded area needs protection, since the zinc layer on it is often destroyed. Therefore, the threads in galvanized pipes must be painted.
Calculation of pipeline insulation materials
It is not difficult to carry out insulation calculations for pipelines; for convenience, it is recommended to use special calculators.
There are a number of actions that allow you to preliminarily determine the volume of materials. Before starting calculations, you should immediately decide what type of insulation will be used. Insulators differ not only in appearance, but also in installation conditions and properties.
Painting agents can be used to insulate pipelines.
The quality of the materials is high, the layer is thin but durable, fully performing all functions. The calculation is done as follows:
The formula for calculating the area of the cylinder is S=2πr(h+r), where r is the radius of the base of the pipe, h is the pipe length parameter, π is a constant, the approximate value for this case is 3.14. The resulting value is the coloring area. Next, according to the manufacturer’s instructions, determine the material consumption.
Scheme for calculating thermal insulation for a pipe.
When using conventional insulating materials, calculations are much simpler. It is necessary to determine the volume for the inside and outside of the pipe. To do this, use the formula V=πr2h, where:
- V – pipeline volume; r – radius value (external or internal); h – pipe length; π is equal to 3.14.
The value of the internal and external radius is calculated separately, the resulting difference will be equal to the volume of the entire pipeline insulation material. Wrapping is an option for external insulation. In this case, the calculation is performed similarly using the first formula indicated, but it is necessary to take into account the thickness of the material, since it affects the quantity.
Cylindrical pipes
Specific pipeline pressure loss calculator
To calculate their area, a fairly simple technology is used. Calculation formula:
S = 2 * 3.14159 * R * L
, where R is the radius of the externally directed pipe, measured in mm;
L is the immediate length of the object being painted.
Well, the number 3.14159 - this number “pi” has been known since school.
Thanks to this approach, it is possible to obtain significant benefits. After all, you won’t need to purchase extra cans of paint. In addition, cylindrical pipes have their own variety, which is used for sewers. The same formula is used as for conventional cylindrical pipes. There is an important nuance: cylindrical sewer pipes are large.
To simplify measurements, it is important to understand the factor: the base of all measurements is considered to be a height of 90 cm. In the vast majority of cases, rings of this exact size are used
Well, the external diameter can vary from 70 to 200 cm. Let's give an example. If the diameter is 70 cm, then the area will be 1.99 square meters.
Elimination of insulation defects
Over time, repairs will be required to insulate the pipeline.
Of course, proper operation allows you to extend the service life of not only the pipes, but also the finishing. Periodically it is necessary to carry out an inspection, and then carry out partial repairs so as not to lead to a major one, i.e.
replacing the insulation layer itself or, in the worst case, pipes. How to avoid repairs? It is necessary to install special sensors that monitor the state of the system.
The repair itself may consist of the following actions:
The condition of the insulation surface should be inspected regularly. If there is damage, then it is necessary to patch the defective area and inspect the surface of the pipe.
Further repairs depend on the condition of the pipes. Usually you just need to clean off traces of corrosion, but in more complex cases, individual sections need to be replaced. A new layer of pipeline insulation is then applied.
When repairing the coating, you should choose the same material that was used before. If for some reason it does not meet the requirements, then the entire insulation should be replaced so that there is no heat loss and no areas susceptible to corrosion arise.
Various materials can be used to insulate pipes and protect them from corrosion. Before purchasing them, you should choose the right coating.
Anton Mikhailovich Dergachev
No problem. We take the perf and perforate)
Interesting info, I didn’t know that it was necessary to reinforce foam and gas blocks
I'll add it to my bookmarks. I’m just planning to install a frame.
Lately, I’ve been thinking more and more often about building a house, and I find a lot of similar useful articles. I will definitely do a vapor barrier, especially since Va.
Thank you. Very detailed and understandable, and in my case, relevant.
We offer you a calculator for automated calculation of the volume of insulation for pipelines for various purposes - sewerage, air ducts, heating or gas pipelines. We recommend that you read the instructions first.
In the conditions of our country with its vast expanses, pipeline transport is the most effective means of transporting liquid products. The dimensions of the pipes reach three meters in diameter, which makes it possible to transport large volumes of products through them. Naturally, such highways require certain protection from various factors:
- corrosion of all types; freezing; physical impact of natural phenomena; from unauthorized intervention by unauthorized persons.
All highways, including gas and oil pipelines, not to mention water systems, are subject to insulation for operation in the temperature range of -45 + 60 degrees. Mass application of such a technological operation requires careful calculation of the need for materials for covering the surface of pipes, so that the costs for it are optimal; calculating the insulation of pipelines using various calculators is a necessity.
Basic points of calculations
Bathroom tile calculator and calculation method
If we consider the pipe from the point of view of geometry, then it is nothing more than a simple cylinder. Therefore, the calculation is carried out using the appropriate formulas.
First of all, these calculations can be useful if it is necessary to calculate the heat transfer of any heat exchanger. As a result, it is possible to determine the dimensions of the surface that transfers heat from the coolant. In fact, this value will be the area of the steel pipe to be painted.
It is often necessary to calculate heat loss along the way to an installed heating device. To determine how many radiators or other heating elements will be required for installation, you need to find out how many calories each device that is being considered for installation has. In some cases, a table may be required to make calculating surface area much easier. Thus, it is possible to determine the exact number of heating radiators to ensure adequate heat supply. And if the length of the heating main is several kilometers, then by making an accurate calculation, you can thereby reduce the financial costs of the enterprise.
In this case, everything possible must be done to reduce heat transfer to minimum values. To find out how much heat-saving material to purchase for pipes, you need to calculate the surface area that you need to protect from unwanted heat loss. This is exactly what a table can come in handy for. These calculations allow you to find out the painting area of the profile pipe.
The table below shows the painting area of 1 square meter. m of pipe, depending on the dimensions of the insulating layer:
The surface area to be painted along with the cost of paint consumption per 1 sq. m. allows you to determine a fairly accurate volume of required purchases. In addition, in this case, you can independently determine whether the craftsmen correctly and “honestly” calculated the amount of material required for the repair. For example, if twice as much paint or bitumen varnish is used than was calculated, it means that the remaining amount of material is being used “for other purposes.”
Insulation materials
The range of means for installing insulation is very extensive.
Their difference lies both in the method of application on the surface and in the thickness of the thermal insulation layer. The application features of each type are taken into account by calculators for calculating pipeline insulation. The use of various bitumen-based materials with the use of additional reinforcing products, such as fiberglass or fiberglass, is still relevant.
Polymer-bitumen compositions are more economical and durable.
They allow for quick installation and the quality of the coating is durable and effective. The material, called polyurethane foam, is reliable and durable, which allows its use for both channel and non-channel methods of laying highways. Liquid polyurethane foam is also used, applied to the surface during installation, as well as other materials:
- polyethylene as a multilayer shell, applied in industrial production for waterproofing; glass wool of various thicknesses, an effective insulation due to its low cost with sufficient strength; for heating mains, mineral wool of the calculated thickness is effectively used to insulate pipes of various diameters.
Characteristics of network laying and standard calculation methods
Carrying out calculations to determine the thickness of the heat-insulating layer of cylindrical surfaces is a rather labor-intensive and complex process
If you are not ready to entrust it to specialists, you should be careful and patient to get the right result. The most common way to calculate the thermal insulation of pipes is to calculate using standardized heat loss indicators
The fact is that SNiP establishes the values of heat loss by pipelines of different diameters and with different methods of laying them:
Pipe insulation diagram.
- open method on the street;
- open in a room or tunnel;
- channelless method;
- in impassable channels.
The essence of the calculation is to select the heat-insulating material and its thickness in such a way that the amount of heat loss does not exceed the values prescribed in SNiP. The calculation methodology is also regulated by regulatory documents, namely the relevant Code of Rules. The latter offers a slightly more simplified methodology than most existing technical reference books. Simplifications include the following points:
Heat losses when the pipe walls are heated by the medium transported in it are negligible compared to the losses that are lost in the layer of external insulation. For this reason, they can be ignored. The vast majority of all process and network pipelines are made of steel; its heat transfer resistance is extremely low. Especially when compared with the same insulation indicator
Therefore, it is recommended not to take into account the heat transfer resistance of the metal pipe wall.
Installation of insulation
Calculation of the amount of insulation largely depends on the method of its application. It depends on the place of application - for the internal or external insulating layer.
You can do it yourself or use a calculator program to calculate the thermal insulation of pipelines. Coating on the outer surface is used for water pipelines for hot water supply at high temperatures to protect it from corrosion. Calculation with this method comes down to determining the area of the outer surface of the water supply system to determine the need per linear meter of pipe.
Internal insulation is used for water main pipes. Its main purpose is to protect metal from corrosion. It is used in the form of special varnishes or a cement-sand composition with a layer several mm thick.
The choice of material depends on the installation method - channel or non-channel. In the first case, concrete trays are placed at the bottom of an open trench for placement. The resulting gutters are closed with concrete lids, after which the channel is filled with previously excavated soil.
Ductless installation is used when digging a heating main is not possible.
This requires special engineering equipment. Calculating the volume of thermal insulation of pipelines in online calculators is a fairly accurate tool that allows you to calculate the amount of materials without fiddling with complex formulas. Material consumption rates are given in the relevant SNiP.
Related posts:
Published: December 29, 2017
( 4 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)Loading…
- Date: 04/15/2015 Comments: Rating: 26
Correctly calculated pipeline thermal insulation can significantly increase the service life of pipes and reduce their heat loss. However, in order not to make mistakes in the calculations, it is important to take into account even minor nuances.
Thermal insulation of pipelines prevents the formation of condensate, reduces the heat exchange of pipes with the environment, and ensures the operability of communications.
Methodology for calculating a single-layer thermal insulation structure
The basic formula for calculating the thermal insulation of pipelines shows the relationship between the amount of heat flow from an existing pipe covered with a layer of insulation and its thickness. The formula applies if the pipe diameter is less than 2 m:
Formula for calculating thermal insulation of pipes.
ln B = 2πλ [K(tт - to) / qL - Rн]
In this formula:
- λ — thermal conductivity coefficient of insulation, W/(m ⁰C);
- K is the dimensionless coefficient of additional heat loss through fasteners or supports, some values of K can be taken from Table 1;
- tt is the temperature in degrees of the transported medium or coolant;
- to—outside air temperature, ⁰C;
- qL—heat flow value, W/m2;
- Rн - heat transfer resistance on the outer surface of the insulation, (m2 ⁰C) / W.
Table 1
| Pipe laying conditions | K coefficient value |
| Steel pipelines are open along the street, through channels, tunnels, open indoors on sliding supports with a nominal diameter of up to 150 mm. | 1.2 |
| Steel pipelines are open along the street, through channels, tunnels, open indoors on sliding supports with a nominal diameter of 150 mm or more. | 1.15 |
| Steel pipelines are open along the street, through canals, tunnels, and open indoors on suspended supports. | 1.05 |
| Non-metallic pipelines laid on suspended or sliding supports. | 1.7 |
| Channelless installation method. | 1.15 |
The thermal conductivity value of the insulation λ is a reference value, depending on the selected thermal insulation material. It is recommended to take the temperature of the transported medium tt as the average throughout the year, and the temperature of the outside air tto as the average annual temperature. If the insulated pipeline runs indoors, then the ambient temperature is set by the technical specifications for the design, and in its absence it is taken equal to +20°C. The indicator of heat transfer resistance on the surface of a heat-insulating structure Rн for outdoor installation conditions can be taken from Table 2.
table 2
| Rн,(m2 ⁰C) /W | DN32 | DN40 | DN50 | DN100 | DN125 | DN150 | DN200 | DN250 | DN300 | DN350 | DN400 | DN500 | DN600 | DN700 |
| tt = 100 ⁰C | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.017 | 0.015 |
| tt = 300 ⁰C | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.015 | 0.013 |
| tt = 500 ⁰C | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.012 |
Note: the value of Rн at intermediate values of coolant temperature is calculated by interpolation. If the temperature is below 100 ⁰C, the value of Rн is taken as for 100 ⁰C.
Indicator B should be calculated separately:
Table of heat losses for different pipe thicknesses and thermal insulation.
B = (diz + 2δ) / dtr, here:
- diz - outer diameter of the heat-insulating structure, m;
- dtr — outer diameter of the protected pipe, m;
- δ—thickness of the thermal insulation structure, m.
Calculation of the thickness of pipeline insulation begins with determining the indicator ln B, substituting into the formula the values of the outer diameters of the pipe and thermal insulation structure, as well as the thickness of the layer, after which the parameter ln B is found using the table of natural logarithms. It is substituted into the main formula along with the indicator of the normalized heat flow qL and make a calculation. That is, the thickness of the pipeline insulation must be such that the right and left sides of the equation become identical. This thickness value should be taken for further development.
The considered calculation method applied to pipelines with a diameter of less than 2 m. For pipes of larger diameter, the calculation of insulation is somewhat simpler and is carried out both for a flat surface and using a different formula:
δ = [K(tт - to) / qF - Rн]
In this formula:
- δ—thickness of the thermal insulation structure, m;
- qF is the value of the normalized heat flow, W/m2;
- other parameters are the same as in the calculation formula for a cylindrical surface.