Why do you need a collector, principle of operation
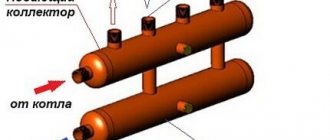
The design of this plumbing fixture is very simple. Essentially, this is a piece of large diameter pipe equipped with threaded fittings for connecting the circuits of the water system. The length of the heating comb depends on the number of connections; the main line is usually connected to the end.
Reference. As a rule, collectors are equipped with outlet pipes of the same diameter, which is 0.5...0.75 from the cross-section of the main chamber. The distance between the fittings varies depending on the coolant flow in the circuits and the purpose of the comb.
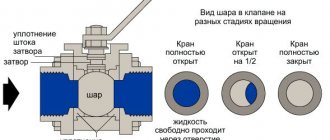
What happens in the collector, where water flows from 2...10 parallel branches:
- From several lines, a coolant with various parameters - temperature, flow rate, flow rate per unit of time - enters the collection pipeline.
- In a large flow section of the comb, the speed of water movement decreases and the hydraulic resistance decreases.
- Mixing in the main chamber, different flows acquire the same temperature and speed at the outlet.
Scheme of operation of a collector pipe for collecting coolant
So, the task of the collector is to collect coolant, equalize its parameters and send it back to the boiler along the main line. You cannot do without a comb when you need to combine several lines with different water flow rates, hydraulic resistance and length into one pipeline. Try to connect such branches on tees - 2-3 circuits will immediately stop working normally.
The heating distribution manifold operates in a similar way, only in the opposite direction. Water from the boiler, flowing slowly through the main chamber, is distributed in the required quantity through secondary lines.
One bare pipe with branches is of little use without accompanying fittings - taps, valves and other elements. The assembled collector unit helps solve several important problems:
- regulate the amount of coolant in each branch, balance them among themselves;
- by mixing, reduce the temperature of the supplied water and maintain it at a given level;
- empty the system, bleed air;
- automatically control the microclimate of each room using room thermostats.
Advantages and disadvantages
The collector heating system has the following advantages:
- Saving fuel consumption for heating large areas - the coolant, in the process of passing to the radiators, performs the function of heat exchange with less losses, which allows you to save money during the heating season.
- The ability to independently determine the desired temperature in different rooms - a person himself regulates the desired temperature by disconnecting individual parts from the overall system.
- The pipes are ideally hidden in the floor screed, which will rid the room of outdated decor in the form of pipes.
- Convenient repairs - just turn off a separate section, and in other rooms the heating will continue to function as before.
Despite the apparent savings, this system also has some disadvantages:
- High pipe consumption, which will lead to additional expenses.
- Full operation depends on the availability of electricity in the network. If the lights are turned off, the pump will not be able to pump water, accordingly, the heat exchanger circulation process will be absent and the radiators will quickly cool down.
- The relatively high cost of all elements of the system, the payback of which will be more than 2-3 years.
When laying pipes in a concrete screed, it is important to take into account the nuance that the place of any coupling is a potential leak, and if it occurs, you will have to remove the floor and spend money on quite expensive repairs.
Types of collector units
Before considering the types of combs, we will indicate ways of their use in water heating systems of private houses and apartments:
- distribution and regulation of water temperature in underfloor heating circuits, abbreviated as TP;
- distribution of coolant to radiators using a radial (collector) circuit;
- general heat distribution in a large residential building with a complex heat supply system.
On the left in the photo is a coplanar manifold for distributing the coolant among the branches, on the right is a ready-made collector module with a hydraulic switch.
In country cottages with branched heating, the collector group includes a so-called hydraulic switch (otherwise known as a thermo-hydraulic separator). Essentially, this is a vertical manifold with 6 terminals: 2 from the boiler, two to the comb, one on the top to remove air, and water is discharged from the bottom.
Addition. There are cascade water guns with a large number of fittings where the heating circuits are connected directly. Then the manifold type distributor is not used.
Now about the types of distribution combs:
- To limit water temperature, regulate flow and balance heating floor circuits, special collector blocks made of brass, stainless steel or plastic are used. The size of the connecting hole of the main heating main (at the end of the pipe) is ¾ or 1 inch (DN 20–25), the branches are ½ or ¾, respectively (DN 15–20).
- In radiator beam circuits, the same combs of underfloor heating systems are used, but with reduced functionality. We will explain the difference below.
- For general house distribution of coolant, large steel collectors are used, the connection diameter is over 1” (DN 25).
Factory manifold groups are not cheap. To save money, homeowners often use hand-soldered polypropylene combs or buy cheap distributors for water supply systems. Next we will indicate the problems associated with the installation of homemade and plumbing manifolds.
Combs for radiator and floor systems – made of stainless steel, brass and plastic
FAQ
How to position the pump correctly in this system: horizontally or vertically?
The circulation pump shaft must be positioned horizontally. If you change this position to the opposite, the pump will periodically overheat and will soon fail.
Is it possible to connect a heated floor to the collector system?
It is possible, such a system is installed according to all requirements, after which it is thrown onto the dedicated comb nozzles. The main condition is that the individual circuits do not communicate with each other.
Is it possible to make a comb with your own hands?
You can, to do this you need to use the necessary material and tools, having previously calculated the number of pipes. This is only appropriate if you have the skill to use a welding machine. It is best to purchase combs from the manufacturer, giving preference to stainless steel.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that the collector heating system works well in large heated areas and is ideal for a private home. In an apartment, parallel connections are usually not used due to the short duration of the circulation circle.
For an apartment, sequential installation of radiators is better suited. The collector system allows you to regulate the temperature in individual rooms, and if repairs are necessary, you can easily turn off the required element, while in other rooms you do not have to turn off the heating.
Comb device for heated floors
The temperature of the coolant supplied to the underfloor heating circuits should not exceed 50 °C, the optimal temperature schedule is 40/30 °C. If the floor surface heats up above 30 degrees, the room will become stuffy and uncomfortable.
Only gas boilers are capable of maintaining a supply of 40–50 °C, and even then with a loss of efficiency. To effectively consume gas or other energy carriers, water must be heated to 60 degrees, and then the temperature at the entrance to the transformer loops must be reduced. This is one of the main tasks of the collector block, consisting of the following elements:
- the collector itself – 2 separate tubes (supply and return) with wall mounting brackets;
- thermostatic pressure valves with connection for Eurocone pipes;
- flow meters (rotameters) with a scale of 0.5…5 l/min;
- end blocks with automatic air valves and drain valves;
- dial thermometer blocks;
- shut-off ball valves;
- bypass line with bypass valve.
Distributor design for underfloor heating systems
Rotameters and pressure valves are screwed into special sockets on the comb, the latter are closed with plastic caps. Air vents with drain valves are screwed into the ends of the collector tubes on one side, and blocks of thermometers and taps on the other. The bypass is installed depending on the design of the comb.
Note. Typically, flow meters are located on the supply line, thermal valves are on the “return” line. But there are also other models of collectors with rotameters on the return line. If you mix up the distributor tubes, you won’t be able to twist the valves instead of the flow meters - the internal shape of the bushings is different.
The thermometers are followed by ball valves, followed by a circulation pump and a mixing unit. Let's consider each element of the collector group separately.
Design and purpose of flow meters
Rotameters are designed to monitor and regulate the maximum fluid flow through loops. The elements are screwed into special pipes on the manifold without winding materials - the seal is an EPDM rubber gasket.
The flow meter body contains a spring-loaded rod with a working plate at one end and a control washer at the other. How does a rotameter work:
- The coolant flows through the side hole in the housing, then moves down, presses on the plate and goes into the pipe.
To adjust the maximum flow on the flow meter using the adjusting washer, you need to remove the protective plastic cap - The more water flows through the flow meter, the greater the pressure on the plate. The spring is compressed, the rod with the control washer is lowered. The flow rate in l/min can be observed on the scale marked on the transparent bulb of the element.
- The amount of flow is regulated by rotating the upper part of the housing. When twisting, the passage hole is partially or completely closed by the piston.
Reference. Some manufacturers' collectors are equipped with unregulated rotameters. To limit flow, separate valves built into the pipe body are used. See the video below to see how such elements look.
Flow meters installed on the return line are designed similarly, only the spring is on the other side of the control washer. The coolant enters from below and pushes the plate upward, the rod and washer rise. How to distinguish between different types of rotameters:
- if, in the absence of flow, the washer is at the top of the flask, then the flow meter is placed on the supply;
- if at zero water flow the washer is at the bottom of the scale, the element is intended for “return”;
- the scale on the flask is graduated in the appropriate direction, in the first case the counting is from top to bottom, in the second – from bottom to top.
During operation, rotameters must be maintained - cleaned when dirty. A transparent bulb serves as an indicator; when it becomes coated from the inside, the element should be unscrewed, disassembled and dirt removed from the working surfaces.
How does a thermostatic valve work?
Structurally, the product is no different from other similar thermal valves - radiator or two-way. When you press the spring-loaded rod, the plate lowers into the seat, blocking the passage of the coolant. It is possible to preset: the maximum flow rate is limited by rotating the valve core using a hex key.
Clarification. There are 2 types of valves - normally open and normally closed. The first ones are described above - when you press the rod, the passage closes. The latter are used less frequently, where the channel is initially closed, and when the rod is lowered, the hole opens.
The purpose of the thermostatic valve is to regulate coolant flow during operation (not balancing!). Management is implemented in 3 ways:
- Manual. The position of the rod is adjusted by a plastic handle, which is screwed onto the valve from above.
- Automatic RTL thermal heads that press the rod when the return flow temperature increases. Do not confuse them with conventional radiator heads that respond to air temperature.
- Electric servos connected to room thermostats or weather-dependent automation.
Manual control requires constant attention from the user - when the ambient temperature changes, you will have to press or release the rod. Thermal heads of the RTL type automate the process, but work well only on short loops - up to 60 m. Servo drives plus thermostats are applicable everywhere.
Other comb accessories
At the beginning of the publication, we listed the tasks that the underfloor heating collector group must solve. With balancing and flow control it is clear - these functions are performed by rotameters and valves. Let's move on to the remaining accessories:
- Terminal unit for emptying and automatically removing air bubbles. The element consists of a housing with a drain valve and a float air vent. The fitting is closed with a plug, which at the same time serves as a thumb for opening the valve.
- Blocks of dial thermometers marked up to 80–90 °C. The purpose is clear - measuring the temperature at the inlet and outlet of the comb.
- Ball shut-off valves. Depending on the method of connecting the collector to the heating, straight, angular, American and internal/external threaded taps are used.
- A bypass jumper with a bypass valve is used in systems with automatic control. If, due to warm weather, all circuits are closed, the coolant will flow through the bypass in a circle, the pump will not work on its own. In normal mode, the valve will not allow water to circulate directly and will force it to move in loops.
From left to right: drain end fitting with manual air valve, block with automatic air vent, ball valves and thermometers
Note. Through the terminal unit, you can not only drain the coolant, but also pump it in in case of repairs. The collector is cut off from the main line by taps, and the TP circuits are emptied or recharged through a side fitting.
The number and variety of additional fittings depends on the comb manufacturer. These accessories are the main ones; in addition to them, various plugs, adapters and valves are also used.
A mixing unit is located in front of the collector block; its composition depends on the method of preparing the coolant for the TP. There are 3 methods of bringing water in heated floors to the desired temperature:
- Mixing into hot water circuits with a two-way thermostatic valve. The element launches portions of the coolant at the command of a thermal head with an external temperature sensor in the form of a copper flask. The latter is attached to the metal wall of the manifold and connected to the head through a capillary tube.
- Mixing cooled and heated coolant using a three-way valve. The principle is as follows: the pump drives water through the bypass along the circuits; when it does not cool down, the valve opens the supply of heated water from the boiler line. The difference from the previous method is a smoother flow and mixing quality.
- Restriction of reverse flow by RTL thermal heads installed on the comb thermal valves. Here a pump module is not needed at all.
You can control a two- or three-way valve in three ways: manually, using a thermal head with a remote flask and an electric actuator. The latter is controlled by a controller that receives signals from room or weather sensors.
What types of solar collectors are there?
There are two types of such systems: flat and vacuum. But, at their core, their operating principles are similar. They use the sun's heat to heat water. They differ only in the device. Let's look at the operating principles of these types of solar systems in more detail.
Flat
This is the simplest and cheapest type of collector. It works as follows: The metal body, which is internally treated with a highly efficient feather absorber to absorb heat, contains copper tubes. A coolant (water or antifreeze) circulates through them, which absorbs heat. Next, this coolant passes through a heat exchanger in a storage tank, where it transfers heat directly to the water that we can use, for example, to heat a house.
The upper part of the system is covered with high-strength glass. All other sides of the body are insulated with insulation to reduce heat loss.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Low cost panels | Low efficiency, approximately 20% lower than vacuum |
| Simple design | Large amount of heat loss through the body |
Because of their ease of manufacture, such systems are often made even with their own hands. You can purchase the necessary materials at construction stores.
Vacuum
These systems work a little differently, this is due to their design. The panel consists of double tubes. The outer tube plays a protective role. They are made of high-strength glass. The inner tube has a smaller diameter and is covered with an absorber that accumulates solar heat.
This heat is then transferred to pullers or rods made of copper (they come in several types and have different efficiencies, we’ll look at them a little later). Heat extractors transfer heat using a coolant to a storage tank.
There is a vacuum between the tubes, which reduces heat loss to zero and increases the efficiency of the system.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| High efficiency | Higher price relative to flat |
| Minimum heat loss | Impossibility of repairing the tubes themselves |
| Easy to repair, tubes can be changed one unit at a time | |
| Large selection of species |
Types of heat removable elements (absorbers), out of a total of 5
- Feather absorber with direct-flow heat channel.
- Feather absorber with heat pipe.
- U-shaped direct-flow vacuum manifold with coaxial flask and reflector.
- System with a coaxial bulb and a heat pipe.
- The fifth system is flat-plate collectors.
Let's look at the operating efficiency of different absorbers, and also compare them with flat-plate collectors. Calculations are given for 1 m2 of panel.
This formula uses the following values:
- η is the efficiency of the collector, which we calculate;
- η₀ - optical efficiency;
- k₁ - heat loss coefficient W/(m²·K);
- k₂ - heat loss coefficient W/(m²·K²);
- ∆T - temperature difference between the collector and air K;
- E – total intensity of solar radiation.
Using this formula, using the data given above, you can do the calculations yourself.
Without delving into the variables, to put it simply, efficiency depends on the amount of heat absorbed by the copper heat sinks and the amount of loss by the system.
But these are only theoretical calculations “on the bench”. The final result depends on many factors: climate zone, correct choice of installation location, etc.
Systems with flow-through heaters or thermosiphon
According to their structure, they can be either flat or vacuum. They use the same operating principles. However, they have one significant difference in technical design.
This system can operate without an additional backup storage tank and pump group.
The operating principle is as follows. The heated coolant is accumulated in the base tank, which is located at the top of the system, usually 300 liters. A coil passes through it, through which water circulates from the pressure of the house’s plumbing system itself. It warms up and is supplied to the consumer.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Low cost due to the absence of some equipment. | Low system efficiency in the winter season and at night |
| Easy to install, requires minimal effort, as the system is equipped with everything necessary |
Distributor for radiant heating system
Let us remind you: radial wiring provides for an individual two-pipe connection of each radiator to a common distribution manifold located in a convenient location (usually closer to the center of the building).
An example of radiant heating distribution in a one-story house
To install the collector unit, the following combs are used:
- factory for TP (described above), made of stainless steel, brass or plastic;
- factory for water supply with built-in shut-off valves, made of polypropylene or metal;
- homemade manifolds twisted from brass fittings and polypropylene tees.
The type of comb you choose depends on your budget and radiator system requirements. If each battery is equipped with its own balancing valve and thermal head, then a clean manifold without valves and flow meters is sufficient. Leave the air and water discharge module.
Advice. If you have a limited budget, you can choose an inexpensive water supply manifold with taps, shown in the photo. Many homeowners do this and balance the system with radiator valves.
If you want to automate the heating operation and place all adjustments in a manifold cabinet, buy a comb for underfloor heating. Install all accessories - rotameters, valves with servo drives, air vents, room regulators. A mixer is still not needed; the coolant is supplied to the batteries directly from the boiler room.
The video below shows a combined heating manifold that distributes heat to radiator wiring and floor circuits. Both parts of the comb are installed in parallel. Please note that the master used water distributors to distribute the coolant.
How to install the collector correctly?
The heating collector is connected by a specialist with experience, knowledge and tools. The place and method of installing the collector must be chosen by the master. Any room with normal humidity levels is suitable for installing the distribution block. Suitable for this:
- storage room;
- dressing room;
- corridor.
All communications of the collector can be hidden in a special cabinet with a locking mechanism, this will help protect the device from children, and the attractive design of the cabinet will complement the interior of the room. It is dangerous to install complex communications without experience and knowledge in this area, because if the installation is incorrect, or the automatic air vent or expansion tank is incorrectly connected, failures in the heat supply to your apartment and to your neighbors may occur.
The selection of pipes for a manifold heating circuit also requires a professional approach:
— the pipe must be in a coil;
— made of especially durable materials that can withstand a coolant pressure of 1.5-2 atmospheres, a temperature of 60-75 degrees (for radiators), 30-40 degrees (for the floor);
— pipes must be resistant to moisture.
Common house collector group
The main comb performs the same functions as the TP collector - it distributes the coolant among the branches of the heating network of various loads and lengths. The element is made of steel - stainless or black, the profile of the main chamber is round or square.
Reference. Factory-made main manifolds are called coplanar. This buzzword means that all the parts of the comb lie in the same plane - the vertical supply pipes completely intersect the “return” chamber and vice versa. The goal is to reduce the weight and dimensions of the structure.
There are compact models of distributors for 3–5 circuits, made in the form of one pipe. Here's the trick: the return manifold is placed inside the feed chamber. As a result, we get 1 common housing with 2 cameras of equal capacity.
In the vast majority of country houses with an area of up to 300 m², distribution manifolds are not needed. For several heat consumers, a piping scheme using the primary-secondary ring method is used, described in a separate article. When should you think about buying a communal heating comb:
- the number of floors of the cottage is at least two, the total area is over 300 square meters;
- for heating, at least 2 heat sources are used - gas, solid fuel, electric, and so on;
- the number of individual radiator heating branches is 3 or more;
- The boiler room diagram contains an indirect heating boiler, heating circuits for auxiliary buildings, and heating of the pool.
The listed factors must be considered separately and together, and to select a model of specific sizes, the load on each branch must be calculated. Hence the conclusion: it is better not to buy a collector without consulting an expert.
Drawing of a coplanar manifold and photo of the finished product with pumping groups
What methods can be used against a debtor under the law?
Changes in legislation have narrowed the capabilities of such specialists and established limits. But here the situation is twofold. After all, 90% of the population are simpletons and do not know their own rights.
In reality, if you look at the law, collectors can only:
· communicate with identified debtors as long as they agree to listen to them;
· remind politely of the debt, tell the “client” about the possible consequences;
· call a maximum of once a day, 2 times a week or 8 times a month, during the daytime, maximum in the evening;
· Personal meetings once a week.
That is, no late-night calls, unauthorized visits to home or work. It is also illegal to touch the debtor's relatives if they are not listed as co-borrowers.
When they call about a relative’s debt , and you are not a spouse, heir or guarantor, you must demand that the calls be stopped and that the phone number be removed from the database. They begin to threaten - turn on the recording and inform the collector. It works. After all, with a printout you can contact the police or prosecutor’s office. When you get hold of banking institutions, write to the Central Bank or Rospotreb.
It's another matter when you are a guarantor . And by law you are responsible for the loan. Banks can demand repayment of the debt from both the debtor and you. Then all that remains is to convince the debtor not to hide and repay the debt.
If you are simply a relative of the debtor, then by law you do not bear any responsibility for the debts of your loved one. Even spouses are responsible only through the courts. Reporting to law enforcement helps stop this practice.
Sometimes they call a complete stranger, the number someone provided when applying for a loan. You need to find out what the debt is, who issued it and get a certificate that there is no debt. Report that this error and the collector violates the law on personal data.
Installation nuances
The technology for attaching the collector to the wall is quite simple: the TC and radial distribution comb are suspended on mounting brackets, the loops are connected with Eurocone fittings. Pipes going to the top of the collector (usually the “return”) are passed under the bottom.
Advice. No one is forcing you to mount the distributor on brackets. If necessary, the tubes can be spread apart and mounted separately on the wall. The collector box is used in residential areas; when installing the collector in the boiler room, the cabinet is not needed.
Let's briefly list the main points:
- The size of the comb is selected according to the diameter of the pipes used in the heating loops - Ø16 or Ø20 mm. Accordingly, we take a ¾ or 1 inch distributor. The material of the product does not matter; in terms of price/quality ratio, stainless steel wins.
- If the number of comb outlets exceeds 12, assemble a collector assembly of 2 sections. When installing accessories, winding materials are not used, since the parts are equipped with rubber seals.
- A heavier common house collector is suspended on hooks, reinforced brackets, or installed on the floor. Pumps, pipes and other piping elements must not load the distributor with their own weight.
- The hottest coolant receives an indirect heating boiler. The coil and circulation pump of the water heater are connected to the comb directly, usually from the end.
- The radiator heating and TP branches are connected to the manifold through mixing units with three-way valves. A separate pump is installed on each line, selected for pressure and performance.
A heavy coplanar comb can be installed on the floor - weld metal supports
Important point. The mixing unit for heated floors can be installed in the boiler room, near the main comb. Then water at the required temperature will flow to the TP distributor.
Collectors: installation rules, functional features
The complexity of the design of an important element of the heating system is noticeable upon first inspection: the device can be mounted from several collectors, supplemented with drain and air release valves, and a heat meter can also be mounted on the collector. Correctly connecting several collectors into one block is not an easy task; collector heating wiring is created by craftsmen in accordance with the requirements of SNiP, which guarantees uninterrupted functionality of the system.
Did you know that two collectors are installed on communications to heat a room? One is for the pipeline supplying cold water to the system, the second is for supplying coolant. The purpose of this device is to supply hot water to a separate radiator, ensuring good heating of the room and saving energy costs. There is a small disadvantage of installing the collector - the high price, since all the constituent elements are made of special strength steel, and installation requires special fittings for installation.
Finally about homemade collectors
Above in the text we mentioned budget options for combs - tap, polypropylene and homemade. Such distributors can be used without problems in radiator beam circuits. To balance and regulate the flow, a balance valve and a faucet with a thermal head are installed on each battery. The collector is equipped with “air vents” + drain taps.
If you put the indicated combs on the TP, you will encounter the following nuances:
- the distributor cannot be equipped with rotameters;
- without flow meters it is difficult to balance circuits of different lengths;
- Factory plastic manifolds have shut-off valves, which means there is nothing to regulate the flow;
- combs assembled from polypropylene or brass tees have many joints;
- It's worth noting that homemade distributors don't look too good.
A self-made underfloor heating manifold can still be brought to perfection. We assemble the distributor from tees, and on the return connections we mount thermostatic radiator valves with RTL-type thermal heads, as shown in the photo.
A skilled owner can easily make a coplanar common house collector - weld it from a round or profile pipe. But there’s a catch in the calculations: you need to know the cross-section of the chambers and pipes for a specific heating system. If a specialist calculates these parameters, use the experience of the master from the video:
Areas of use of collectors
Horizontal wiring of a heating system is the installation of a two-pipe communication with a special radial collector circuit. Used when installing heating systems in multi-storey buildings. The main advantage is the ability to connect/disconnect the heat supply on each floor. A very convenient CO system, with which you can install individual heat meters.
The two-pipe collector floor scheme is considered one of the most complex heating systems, requiring a competent approach, design, and correct calculations when installing communications. Manifold wiring is considered an expensive pleasure, since metal-plastic pipes are used during installation, plus the mandatory connection of a heating collector is required. Moreover, this type of CO is the most economical and efficient to use. The service life of two-pipe collector systems is at least 25 years, which fully compensates for installation costs.
Horizontal heating distribution is used in multi-storey and individual construction, and it is important that the work, from planning and drawing up drawings to commissioning of the facility, is carried out by specialists.
Current changes for 2021, question and answer
Expert opinion
Galina Yarina, private financial (bills) observer
A bill of amendments to the Code of Administrative Offenses has been prepared - credit organizations that threaten debtors offer fines from 50 thousand to half a million; the FSSP will deal with such cases.
Last year, there were 4 main bills on collectors discussed. This is a ban on debt collectors' offices, digital pseudonyms and housing and communal services debts. Let's describe each one.
Bill to ban collection agencies
Recently introduced to the State Duma. The bottom line is that debt collectors often act in violation of the law and exceed what is permitted. They bother both the debtor himself in a rude manner and his relatives and friends. It is proposed to ban their activities on the territory of the Russian Federation. Debt collection should be handled by banks and microfinance organizations themselves, without transferring data and debts to third parties. It's a completely sound idea, but it's unlikely to be approved. Since financial market experts believe that pre-trial debt collection cannot be removed from the recovery stages. Banks will not be closely involved in this, so there will always be commercial or government organizations such as collection firms or private bailiffs.
Digital aliases
The Ministry of Justice is preparing an initiative according to which bank employees for the return of overdue debts and debt collectors will be able to introduce numbers or pseudonyms during conversations rather than their real data. This will protect them from overly aggressive debtors who could harm them. But it is unclear who to complain to if moral damage is caused by an annoying debt collector. The project is at the discussion stage.
Do not involve relatives and friends in debt relationships
From 2021, it is possible that the rules of communication with debtors, namely their loved ones, will become stricter. Nowadays, communication with third parties occurs initially on the basis of consent and stops after refusal. According to the new rules, written consent will be required
Debts for housing and communal services
This topic has been discussed for a long time, then collectors are prohibited from collecting debts for housing and communal services and utilities, then they decide to allow it again so that housing services do not have a staff of employees who deal exclusively with debt. So far they are not doing this closely. And the debts are piling up.
Requirements from January 1, 2021 for equipment and software of collection companies
The equipment used must ensure: - registration of outgoing/incoming correspondence sent and received in the course of debt collection activities, with registration number and date - recording of information about debtors, including the amount of overdue debt, the presence of written agreements, statements, notifications, judicial acts - recording information about interaction with the debtor, his representative - listening to an audio recording of a telephone conversation - listening to a conversation in a personal meeting. - storage of audio recordings of all conversations with the debtor or his representative, for at least three years - storage of records of text, voice and other messages for at least three years - storage of electronic copies of paper documents received for the return of overdue debt, for at least three years - database reservation data on a separate tangible medium.
To communicate with the debtor’s relatives, you will have to ask for consent
The State Duma has passed amendments that relate to the interaction of a creditor or collector with members of the debtor’s family, relatives, neighbors and other persons. In order to contact them, you must first obtain written consent from them in the form of a separate document
. And not, as is customary now, consent is given by the debtor himself. This amendment was adopted to reduce and, in an amicable way, eliminate cases when relatives or neighbors of the debtor are forced to justify themselves to debt collectors.
Yuryev I.
Credit consultant
Question to the expert
Do banking institutions always have the right to transfer a debt to a collector?
Absolutely not. According to the explanations of the Supreme Court, this point must be expressly stipulated in the contract or additional agreement before receiving a loan. Another thing is that it is often not read and banks do not explicitly stipulate it, but it seems that it is not prohibited. And this is precisely the situation that can be appealed, since there was no your consent. That is, if you did not give consent (read everything you signed), but the debt was transferred, then you can safely challenge it and most likely win in court.
Do I have the right not to sign a loan agreement if it contains a clause on the transfer of debt to third parties?
At the familiarization stage, if you encounter this provision, you have the right to demand changes, but they will tell you that this is a standard agreement and are unlikely to change it. Then you can simply find another bank and not get hung up on one with obviously unfavorable conditions.
What other methods of protection exist?
Although the authorities have tightened the requirements, in practice they still remain. Constant calls, night visits, property damage. And the painted walls in a person’s own entrance are not surprising.
It’s difficult to deal with such pressure, but you can:
A. Install an answering machine and a voice recorder on your phone. Home and cell phone to record every call from the collector. His threats, insults. The main thing here is to speak calmly and with restraint.
B. Each time ask to name yourself and your company. To get this on the record.
C. If personal visits become regular, install cameras. Record the time of day and people's behavior.
D. Contact third-party organizations involved in protecting the rights of victims of debt collectors.
E. Hire a lawyer to file a claim for misconduct if the situation has gone really far.
F. Call or visit the lender. Start a constructive dialogue with him about solving the debt problem.
This is what most creditors achieve when they turn to debt collectors.