Culverts are man-made structures that are laid under a highway or railroad bed and are used to carry wastewater. Water can pass through such pipes continuously or at certain intervals. Also, such pipes can serve as a passage tunnel for people.
Culverts are most often installed under roads and railways to drain water and prevent embankment erosion.
Features and benefits of culverts
The culvert allows you to organize drainage under a road or railway. Most often, such a structure is installed to divert a stream or the bed of a small river. Such a pipeline is also used in cases where drainage of rain and melt water is necessary.
Important! If the height of the road embankment is small, it is not possible to organize a full-fledged bridge, so a culvert pipeline in this case is the only way out of the situation.
Let's look at the main advantages of using a culvert:
- the use of such pipes in the road surface not only solves the problem of water drainage, but also makes it possible to strengthen the road embankment. This increases the strength of the road and reduces the risk of embankment failure.
- The cost-effectiveness of installing a culvert, compared to a bridge, allows you to save on road construction.
- the possibility of installing a culvert after the construction of the embankment is completed. Installing a bridge in this case is most often simply impossible or much more expensive.
- increased speed of installation work.
The positive aspects of installing these structures largely depend on the specific case and on the material from which the culvert is made.
MGK teams
Prefabricated corrugated metal structures (abbreviated SMGC), used in the construction of culverts, have a lower cost compared to reinforced concrete products.
They have a number of advantages:
- Due to the presence of a variety of cross sections, you can easily select products for specific construction work.
- Their low weight makes it possible to easily transport SMGK sheets, and the ability to pack them in pallets reduces the space they fill.
- Simple installation allows you to lay pipes from SMGK sheets without special qualifications or special skills.
- The flexibility and strength of the resulting structure is ensured when used together with backfill soil. Thanks to this, the erected structure has greater seismic resistance compared to structures made of concrete.
- Long service life, which can reach 80-100 years, confirmed by many years of experience in using structures.
- The low price allows you to reduce the amount of costs due to the use of SMGK by approximately 30-50%, when compared with the use of other materials.
- It is possible to carry out work on laying pipes from SMGK in various climatic conditions.
Corrugated metal culvert pipes, according to experts, are the most resistant to loads. This advantage is explained by the fact that iron as a material copes better with external influences compared to concrete and plastic.
A significant drawback that prevents the widespread distribution of pipes made of this material is that they are highly susceptible to corrosion processes, and therefore are afraid of moisture.
Types of Culverts
All culverts are classified according to several basic criteria.
Pipes for culverts can be made of different materials, including polymers
Culverts can be made of the following materials:
- metal;
- concrete;
- reinforced concrete (precast concrete products);
- made of polymer material.
According to cross sections, depending on their shape, culverts are:
- rectangular;
- round;
- oval.
By the number of points in sections:
- one-pointers;
- two-pointers;
- multi-point.
In addition, there is a division of culverts for cross-section work. However, this parameter is taken into account only if hydraulic calculations of pipes are carried out.
Let's consider the types of culverts according to the cross-section:
- non-pressure;
- semi-pressure;
- pressure
Pressure products operate across their entire cross-sectional area, thereby creating maximum flow rates. Semi-pressure ones operate with the entire cross-section only in the area of the pipe head. Gravity pumps constantly operate only part of their cross-section.
Gravity pipes allow a small amount of waste to pass through and are installed where water volumes are small
Work on the construction of road structures with drainage pipes
The road construction project does not simply take into account the presence of reinforced concrete pipes under the roadbed for drainage. The designer must indicate these places both in documents and directly on the ground (the position is indicated by pegs, including the direction of the pipes along the longitudinal axis).
The first part of the work is planning the construction site. It is necessary to prepare a place for parking and movement of construction equipment, an area for storing reinforced concrete parts. Since construction work is carried out directly near a reservoir or water stream, the channel must be cleared on one side and blocked on the other in order to eliminate contact with surface water during work. Usually it is necessary to install a bypass ditch or protect the construction site with an earthen rampart.
Then they begin to dig a pit for the pipe. The foundation of the pit is continuous excavation, carried out using a bulldozer or excavator. The edges of the trench are then finished with an excavator and finalized by hand. The trench is sized according to the width of the foundation with an additional space of 0.5 meters in each direction.
Next, a 10-centimeter cushion of crushed stone is laid at the bottom of the trench - this is the base for a foundation made of patterned blocks. The crushed stone is compacted, but the planned slope should not be disrupted. The foundation block is flat at the bottom and has a semicircular recess where the pipes are laid, so assembling the structure requires a minimum of time. Culverts with a flat base, which is securely installed on a flat foundation surface, are also easy to use.
Direct installation begins from the side of the outlet head. First, the portal block is installed, then the openings, then the foundation blocks and on top - the elements of the prefabricated pipe. The clear order of laying the elements of the culvert is indicated in the construction flow chart. At the junctions of reinforced concrete elements, tow impregnated with bitumen is laid. The parts are fastened using cement mortar, and then a moving concrete mixture is tapped on the sides.
Upon completion of installation work, waterproofing of the culvert begins. This applies to seams, joints, and weak areas, which are treated with waterproof compounds - for example, bitumen mastic. This is done strictly in dry weather at a temperature of at least +5 degrees.
The finished culvert is filled with soil to the level of the road under construction, after which construction of the roadway continues. The thickness of the earthen layer with which the structure is filled should be from 0.5 meters (the distance between the top of the pipe and the bottom layer of asphalt).
Dimensions
Culvert structures with a circular cross-section, mounted under a roadway or railway, can have the following diameters:
- 500 mm - the length of such pipes depends on the specific case and is calculated based on the width of the road;
- 750 mm - such pipes can have a length of up to 15 m;
- 1000 mm - a structure with such a diameter should not have a length higher than 30 m.
The design for on-farm roads can have a cross-section of 500 mm and a length of up to 10 m.
TVEL-PEKS-1 pipes
Installation of heating mains
Flexible pipeline TVEL-PEKS-1 in single-pipe design, polyurethane foam insulation.
Pressure P = 6 bar (SDR 11), 10 bar (SDR 7.4) for heating networks with a temperature curve of +95 ... +70 (peak temperature t = 110°C) Installation of heating mains
Types of heating main TVEL-PEKS-1, pressure 6 bar
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 6 bar, 20×1.9/90 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 6 bar, 25×2.3/90 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 6 bar, 32×2.9/90 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 6 bar, 40×3.7/90 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 6 bar, 50×4.6/110 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 6 bar, 63×5.8/125 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 6 bar, 75×6.8/140 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 6 bar, 90×8.2/160 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 6 bar, 110×10.0/160 mm
Types of heating main TVEL-PEKS-1, pressure 10 bar
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 10 bar, 20×2.8/90 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 10 bar, 25×3.5/90 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 10 bar, 32×4.4/90 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 10 bar, 40×5.5/90 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 10 bar, 50×6.9/110 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 10 bar, 63×8.7/125 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 10 bar, 75×10.3/140 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 10 bar, 90×12.3/160 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-1, 10 bar, 110×15.1/160 mm
Features of reinforced concrete pipes
Today, the cost of concrete and reinforced concrete structures is considered the most budgetary of all possible options. The low price of these materials is a determining factor for many construction companies. In addition, such structures have excellent strength and tightness.
Reinforced concrete culverts are more durable compared to concrete products. The main advantage of reinforced concrete pipes is the possibility of organizing their production at the installation site (near the road). Otherwise, their transportation is carried out using special lifting machines.
As mentioned above, a culvert can serve not only to drain water, but also serve as a pedestrian crossing. The channel diameter can be from 500 to 4000 mm. In addition, it is worth noting the fact that reinforced concrete culverts can also be used in seismically active areas. Studies have shown that, regardless of the diameter, the drainage canal can withstand even strong earthquakes (up to 9 points on the Richter scale).
Reinforced concrete pipes are highly durable and can be used in seismically active regions
Such pipes are produced in the form of separate segments. Links of reinforced concrete culverts can have a length from 1 to 4 m. Reinforced concrete products are regulated by GOST 24547–81.
TVEL-PEKS-2 pipes
Installation of heating mains
Flexible pipeline TVEL-PEKS-2 in two-pipe design, polyurethane foam insulation.
Pressure P = 6 bar (SDR 11), 10 bar (SDR 7.4) for heating networks with a temperature curve of +95 ... +70 (peak temperature t = 110°C) Installation of heating mains
Types of heating main TVEL-PEKS-2, pressure 6 bar
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 6 bar, 2x20x1.9/110 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 6 bar, 2x25x2.3/110 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 6 bar, 2x32x2.9/125 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 6 bar, 2x40x3.7/140 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 6 bar, 2x50x4.6/160 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 6 bar, 32×2.9+20×1.9/125 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 6 bar, 40×3.7+32×2.9/140 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 6 bar, 50×4.6+32×2.9/140 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 6 bar, 50×4.6+40×3.7/160 mm
Types of heating main TVEL-PEKS-2, pressure 10 bar
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 10 bar, 2x20x2.8/110 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 10 bar, 2x25x3.5/110 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 10 bar, 2x32x4.4/125 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 10 bar, 2x40x5.5/140 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 10 bar, 2x50x6.9/160 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 10 bar, 32×4.4+20x2.8/125 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 10 bar, 40×5.5+32×4.4/140 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 10 bar, 50×6.9+32×4.4/140 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-2, 10 bar, 50×6.9+40×5.5/160 mm
Polymer pipes
Today, products made from polymers are becoming increasingly popular. In addition, the capabilities of modern production make it possible to produce polymer pipes that have high strength characteristics and can replace pipes made of reinforced concrete or metal. At the same time, the weight of polymer products is much lower compared to other materials, which facilitates transportation and installation work.
However, despite the high strength characteristics, plastic culvert pipelines are mounted in iron arches. Metal structures make it possible to protect the structure from collapse.
In some cases, a special stone arch or box - a gabion - is built around the plastic channel. The result is a durable structure that can withstand heavy loads and has a corrosion-resistant polymer core. The service life of such a design under normal conditions can reach several decades.
Metal culverts
Metal structures have a corrugated body and are the most durable. Such culverts can withstand enormous loads, however, such pipes have one big drawback - they are susceptible to corrosion.
Metal pipes are susceptible to corrosion, so they are used as temporary structures
Helpful information! Due to rusting, metal culverts are typically used as temporary structures.
The most popular use of such pipes is a temporary passage under a highway. Passages are made to drain water from one side of the road to the other. This need often arises in the event of a blockage or collapse of the main culvert. In addition, a metal pipe can be used as a protective case for a polymer pipeline that is resistant to corrosion.
Corrugated iron culverts are also used to reinforce the walls of boreholes. Sometimes a permanent structure is still installed from such pipes, however, this happens extremely rarely.
Metal drainage channels are assembled from individual segments. Assembly is usually carried out at the installation site. It is also worth noting that such pipes can have almost any finished shape. This is due to the fact that they have corrugated walls that can bend. If the metal sheets have a protective anti-corrosion layer, this design can last up to 50 years. The cost of installing a metal drainage channel is 20–30% lower than a reinforced concrete one.
Corrugated metal structures
Recently, corrugated culverts have become widespread. They are used not only to drain excess water under road surfaces, but also to strengthen or change the course of small rivers. With their help, multi-span bridges are installed.
Corrugated products have the main advantage of lower cost. In addition, they demonstrate the following advantages:
- High degree of adaptability thanks to a wide range of products with different cross-sections.
- Light weight and the ability to deliver products on pallets.
- Simplicity of installation, accessible to specialists without experience in installing culverts.
- The strength and flexibility of the pipe, which, in combination with the optimal thickness of soil backfill, demonstrates seismological performance higher than that of concrete structures.
- Long service life. Corrugated products can last up to 100 years.
- Affordable price for products, which allows you to save up to 30% of the cost of drainage construction.
- Possibility of operation in all climatic zones.
Corrugated pipes are produced from galvanized rolled steel. They are characterized by a diameter from 1.0 to 15.0 m.
The section can take several forms:
- round (from 1.5 to 7.0 m);
- square (from 3.0 to 8.0 m);
- pear-shaped (from 1.5 to 8.0);
- arched (structure height from 2.0 to 13.0 m);
- ellipsoidal (from 1.5 to 6.5 m).
Elements of culverts: heads and links
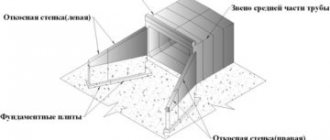
Extension with caps is used to interface the pipe body with the soil embankment, as well as to provide optimal conditions for water flow.
Polymer Corrugated Culvert
There are the following types of headers:
- portal;
- bell-shaped;
- collar;
- streamlined.
The portal head is easy to manufacture, however, its design does not ensure smooth water flow. Because of this, it is used in places with small volumes of water and slow flow for pipes with a diameter of 0.5-0.75 m.
The bell-shaped head consists of a portal wall and flaps. Two flaps are rotated relative to the longitudinal axis of the pipelines at an angle of 20-30˚. The product demonstrates good throughput, so it can be used in pressure and non-pressure pipes. To increase the efficiency of its operation, conical or elevated links are mounted at the input head.
The collar head is arranged in such a way that its edging is put on the outermost link of the pipe, which is cut to the slope cavity. The streamlined head design provides high throughput but is difficult to manufacture. It is made in the form of a truncated cone.
The links are used when laying embankments under road surfaces, as well as in the construction of roads for industrial or provincial purposes. The links are made from concrete and reinforcement.
Due to the strength of the material, the links can withstand seismic activity up to 9 points and have no temperature restrictions. There are round, rectangular and flat-supported links.
Since reinforced concrete pipes have a prefabricated structure, the links ensure the extension of the culvert to the required distance. Such links are effective on unstable soils.
Installation and dismantling of corrugated culverts (video)
Installation of culvert systems under the road
The culvert is installed in accordance with the following steps:
- Development of the pit.
- Foundation construction.
- Pipe installation.
- Construction of the embankment.
The choice of pit size depends on the size of the culvert. Also, to calculate it, the type of soil structure is taken, since it is designed to support a fairly heavy structure. The process of developing a pit includes traditional stages: removal of the fertile soil layer, excavation of the first stage, excavation of the second stage, and the like.
To avoid deformation of the structure due to soil heaving, you need to dig a pit below the freezing level of the soil.
Since the installation of culvert structures occurs in highly moist areas, care should be taken about drainage. It is constructed using a drainage trench around the structure or using a pump. Gabions are used to strengthen the walls of the excavation. Waterproofing is installed underneath them to protect the structure.
Whatever type of pipe is chosen, it is mounted on a special foundation laid on a sand and gravel bed. The cushion protects the base device from deformation. The foundation can be block or monolithic.
Laying a block foundation begins with the head. The first block is installed to a depth of up to 30 cm. Then the height differences are compensated for by sand and gravel backfill. The monolithic base is poured onto a reinforced frame. Its device is characterized by maximum strength.
Installing an earthen edge is the initial stage of pipe installation. First, the output heads are installed. Then arched structural elements are laid on top of the foundation. At the end, the input head is installed. On connections of a concrete structure, adhesion is performed using cement mortar, and on corrugated ones - using latches.
The final stage of installation of the culvert structure is the construction of the road embankment. Its thickness can reach two, four or six meters.
Production technology
Enterprises that produce such pipes adhere to a number of important rules:
- Each component element (link) of the pipe must undergo the necessary testing for compliance with GOST standards. According to GOST, the length of the link can have a deviation from 0 to 10 mm. The wall thickness can also vary slightly - from 5 to 10 mm. Other indicators may have an error of up to 10 mm;
- The joints of all elements must be cleared of sagging and splashes of concrete that could have formed during the production process. The cleanliness of the joints is a necessary parameter that affects the tightness of the connection of the links;
- The sorting of individual elements must be carried out in accordance with the brand. After this, all sorted elements must be moved to one place.
Manufactured reinforced concrete pipes are checked according to many parameters, which must comply with GOST standards
In this way, production finishing and sorting of individual products for culverts is carried out.
Note! Transportation of these elements to the place where installation work will take place is carried out in accordance with the necessary standards to prevent damage to the product. All products are delivered to the installation site in the same form in which they were delivered to the warehouse after sorting.
Before installation, preparatory measures are required.
TVEL-PEKS-4 pipes
Installation of heating mains
Flexible pipeline TVEL-PEKS-4 in four-pipe design, polyurethane foam insulation.
Pressure P = 6 bar (SDR 11), 10 bar (SDR 7.4) for heating networks with a temperature curve of +95 ... +70 (peak temperature t = 110°C) Installation of heating mains
Types of heating mains TVEL-PEKS-4, pressure 6-10 bar
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-4, 6 bar, 2x25x2.3+2x20x1.9/140 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-4, 6 bar, 4x25x2.3/140 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-4, 6 bar, 2x32x2.9+2x25x2.3/140 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-4, 2x32x2.9+32x4.4+25x3.5/140 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-4, 6 bar, 2x40x3.7+2x32x2.9/160 mm
- Pipe TVEL-PEKS-4, 2x40x3.7+40x5.5+32x4.4/160 mm
Preparatory work before installation
At the very beginning, before installing the culvert, a site is selected where construction will subsequently begin. After the required location has been selected, it is cleared of foreign objects (grass, branches, debris, etc.).
Next, all components of the future culvert pipeline are laid out in the correct sequence for subsequent assembly. Before assembly, it is necessary to carry out appropriate markings and determine the axis of the product, as well as the contour of the pit. In addition, before preparatory work, all necessary calculations (including hydraulic calculations) are performed. All this is necessary to ensure that no unforeseen situations arise during the installation process; the normal operation of the culvert pipeline in the future also depends on it.
Concrete quality
Even during the preparatory work and creation of the project drawing, engineers must ensure that the concrete or reinforced concrete products they use meet the maximum quality standard established by GOST.
This will help them. Our Mikabet brand concrete meets all quality criteria and is suitable for the construction of projects of maximum complexity. With our concrete you can lay a culvert even under the highest external pressure.
Check out the catalog of products offered on our website, and our managers will help you with preliminary calculations and placing an order. Prices for our products remain the most reasonable in the entire Belarusian concrete market. So the choice becomes obvious.
Installation nuances
Work on digging a pit is carried out using special equipment, however, leveling the walls of the pit is done manually (using shovels). If the soil at the bottom of the pit is unstable and soft, it is paved with cobblestones. It is laid over the entire area of the bottom of the pit using special tools.
Preparing a pit for pipes is carried out using equipment
Digging a pit is carried out without installing special fences, but in some cases fences are still necessary. For example, if water runoff can get into the pit. Quite often, workers are faced with the need to strengthen the walls of a pit. Such strengthening is carried out taking into account building codes and safety rules in cases where there are residential or industrial buildings near the pit being developed.
The dimensions of the pit, as a rule, depend on the specific case and are determined taking into account the diameter and cross-sectional shape of the culvert. The slope angles of such a design are directly dependent on the properties of the specific soil under which installation work is carried out.
Important! When constructing a pit for a culvert, it is necessary to foresee and conveniently plan the location of the pipe in advance, so that in the event of a breakdown, the culvert is available for repair work.
To carry out work on installing a waterproofing coating or anti-corrosion protection, you need to remember one important rule - the distance between the walls of the foundation and the walls of the pit should not be less than 70 cm. This is necessary for the convenience of performing the work, because these procedures are carried out by workers. If the use of people is not mandatory, this figure is reduced to 10 cm. It is also worth noting that if there is no need to arrange a foundation, the pit for the culvert is dug exactly according to the dimensions of the pipe.
General concept
Culverts are used to pass water from the upper part of roads to the lower part. These include culverts, bridges, and drainage systems. The latter are used to pass various channels under the road surface.
Culverts are used in cases where it is necessary to pass small drainage systems under the road (streams, drainage of water after rain or melting snow, and so on). The passage of water through pipes can be carried out continuously or periodically. The passage of livestock or the passage of vehicles is sometimes organized through such structures.
The installation of culverts does not require narrowing the roadway or changing the type of road surface. A backfill is placed over the structure. The thickness of the layer of poured soil reduces the pressure on the structure from cars and softens their impact.
Using pipes to pass water has its advantages:
- The pipes are installed without damaging the subgrade.
- Installing pipes is cheaper than building a bridge.
- When the thickness of the backfill layer is more than 2 m, the influence of temporary loads from passing vehicles on the structure is minimized.
Foundation installation
If the foundation consists of prefabricated reinforced concrete slabs, then the first step is to install the links that will form the head of the future culvert. The blocks are laid down to the level of the sole, and then work is done to fill the sinuses to the same level.
Concrete blocks or slabs are used to install the foundation
Let's consider the main stages of arranging a monolithic foundation:
- First of all, you need to make or purchase ready-made formwork.
- Next, the concrete solution required for pouring is prepared.
- At the third stage, the concrete solution prepared in advance is poured into the formwork.
- When the solution hardens, it is necessary to dismantle the formwork and fill the formed sinuses.
Design and construction of the foundation
Scheme of the construction of a cathedral-monolithic foundation.
There is a small-block and large-block foundation.
When installing a foundation using prefabricated elements, you first need to lay the head blocks to the bottom level. Then the cavities of the foundation heads are filled to the same level. Subsequently, they are covered with local soil on three sides, and in places where foundations of different depths meet, with sand-gravel or sand-crushed stone mixtures, which must be compacted layer by layer and filled with cement mortar.
Then the foundation masonry and caps must be carried out taking into account the sectional installation of pipes. Consecutive construction is required, from the exit heads to the entrance ones. Multi-row masonry is performed using suture dressing. To install a monolithic foundation you need:
- manufacture and install formwork;
- deliver ready-mixed concrete or prepare it on site;
- lay down the mixture;
- provide the necessary care, remove the formwork, fill the sinuses.
The simplicity of the foundation outlines makes it possible to produce formwork in the form of an inventory panel, which is used on many construction sites. The surfaces of such shields must be smooth. Before concreting, it is recommended to lubricate them with grease. This will make it easier to separate the panels from the concrete structure in the future.
In order to load concrete mixture into sectional formwork, it is necessary to use inventory trays or buckets, which are loaded on site or delivered from a concrete mixing station. Concrete compaction occurs using deep or surface vibrators.
The construction of a prefabricated monolithic foundation occurs in the following sequence: it is necessary to install formwork between sections on the prepared base or cushion, and pour concrete mixture into the available space.
The requirements for concrete work are the same as for constructing a monolithic foundation. Mechanisms and equipment for foundation devices must be selected taking into account all technological processes for pipe construction.
An approximate list of equipment is: crane, mortar mixer, concrete mixer, vibrator, electric rammer, welding unit, mobile power station.
You can increase efficiency when installing pipes if you organize the manufacturing processes, delivery of structures and installation of pipes on site, observing a single comprehensive schedule.
A prerequisite for these events is good access and developed construction bases. The foundation and the number of pipe heads in this situation are mounted “on wheels”. The necessary elements are removed from the vehicle by crane and placed in the structure.
The construction of a pile foundation is very common where there is weak soil. The driving of piles occurs mainly with units that include driving equipment on the bases of tractors, truck cranes or excavators.
Culvert installation
Before carrying out installation work, it is necessary to clean all structural elements (links, blocks, etc.) from dirt. If installation is carried out in winter, then all products must be cleared of snow and ice. After this, you can proceed directly to installation. Installation is carried out in three stages:
- Structural elements that have flat edges are mounted on cement mortar. The cylindrical parts of the culvert are installed on special wooden supports. After this, the solution is poured under the cylindrical links.
- The solution is poured from one side until it appears on the other side. Thanks to this, alignment and complete filling of all seams in the structure is achieved. If concreting is carried out for each link separately, a solution with mobility along a reference cone of 12 cm is used.
- After the concreting of the culvert is completed, it is waterproofed. It is carried out using mastic.
Comments
April 28, 2017
Vlad
What is SMGK and what kind of structures are they?
0 0 Reply
April 28, 2017
Mikhail (o-trubah.ru)
SMGC (Prefabricated metal corrugated structures) – metal load-bearing structures in the form of pipes. They are formed from corrugated metal sheets and connected using bolts. An example of such a design is in the photo:
0 0 Reply
Culvert repair
Today, there are several basic options for repairing culverts. As a rule, repair of culverts is carried out using the pitless method. That is, repair work is carried out without digging out the pipe from the pit. The pit method is used much less frequently - in cases where a complete replacement of the pipeline is necessary.
Restoring the functions of the canal can be carried out using a new pipe, which is simply inserted into the old one
Let's consider the main options for repairing culverts:
- rehabilitation;
- SPR technology;
- relining;
In addition, there is another method of repairing such pipes - microtunneling, however, it is used extremely rarely due to the high costs of equipment. In addition, one set of equipment is suitable only for a certain diameter of a pipe with a round cross-section.
Sanitation
Rehabilitation is a method based on pulling a plastic sleeve inside the culvert being repaired. After the hose is pulled through, air is pumped into it to create excess pressure. The sleeve, inflated with air, repeats the shape of the pipe from the inside. It is then irradiated with ultraviolet rays. As a result of this, the sleeve hardens and a kind of additional frame is formed, which not only repairs the pipe, but also enhances the strength characteristics of the structure as a whole. The thickness of the walls of such a sleeve is approximately 8 mm.
Note ! All repair work takes only a few hours, so this method of repairing a culvert is very popular.
SPR
SPR technology is a method of repairing culvert structures that have large diameters. In addition, this technology is used to repair pipes not only with a round cross-section, but also for others.
The repair process using this technology takes place in 2 stages:
- A profile is wound inside the channel being repaired. The profile is usually made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and reinforced with special inserts.
- The solution is poured into the gap between the pipe being repaired and the body.
After repair using SPR technology, the load-bearing performance of the structure increases by 2–3 times.