Duct types
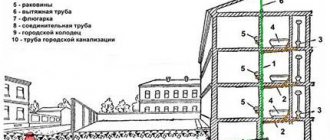
The ventilation system is an important element of any home, apartment or enterprise, which ensures the removal of unpleasant odors from the premises, reduction of humidity, and the flow of clean air from the external environment. All rooms of the house need ventilation, especially the bathroom, where there is always high humidity, as well as the kitchen, where there is a lot of steam, fat fumes, and the smell of cooking food in the air. If a gas boiler is used in the house, then the installation of an air duct is also mandatory for fire safety reasons.
The main element of ventilation is the air duct, the quality, design and size of which directly determine the functioning of ventilation systems. A number of requirements are put forward to it:
— ensure high tightness;
— meet standards for aerodynamic noise levels;
— guarantee the necessary air capacity;
— restrain the calculated pressure of the air mass;
— provide the required thermal insulation.
Another criterion that ventilation ducts must meet is their compact size. It is important that the air ducts do not reduce the usable area of the premises.
General classification
The large number of types of air ducts is due to the variety of their applications in ventilation systems. For ease of classification, air ducts are usually divided according to the following parameters:
- Section shape (rectangular, round, elliptical)
- Size (diameter)
- Structural design (spiral, straight-seam)
- Materials used (galvanized or stainless steel, metal-plastic, plastic)
- Rigidity
- Connection method (flanged, wafer)
- Type of connection (diffusers, tees, bends)
Metal duct design for exhaust hood
The design of some types of exhaust ducts is not so complex that they need to be considered in detail. Plastic air ducts and products made from other synthetic materials can be made of any shape and configuration due to the ease of shaping. Therefore, it is better to consider all possible designs and their features using the example of metal exhaust ducts. Metal exhaust duct is made of various materials: structural steel or aluminum alloys, which allows you to achieve different levels of mechanical strength and resistance to external influences. Structural steel is used to give the exhaust duct mechanical strength and rigidity, which is especially in demand for long routes and installation in the absence of ready-made supports (walls, ceilings, etc.). Aluminum alloys are used to lighten the structure and ensure chemical resistance of the created ventilation system. Also, aluminum exhaust ducts can have special designs (foil or thin aluminum film), which allow the installation of ventilation systems of complex geometry or in conditions where there are many obstacles in the installation area. Solid metal air ducts for exhaust have the best strength and tightness, but the installation of such systems requires highly qualified performers. The design of twisted metal air ducts for exhaust involves the use of a narrow metal strip, which is wound in the form of a cylinder and connected by welding, a rigid fixed or movable lock. In this case, the profile of the metal strip may have special stiffening ribs, which increases the overall mechanical characteristics of the exhaust duct. Metal flexible and corrugated air ducts for exhaust are made of thin material and allow you to change the geometry of the channel while maintaining the shape and size of the cross-section. This feature makes it possible to lay ventilation routes in conditions of many obstacles or when it is necessary to make many turns and turns of the air duct.
Application of air ducts
Air ducts are special ventilation channels that direct air flows in a given direction and have the ability to regulate air pressure and the intensity of its flow. Various types of air ducts are combined into a often complex system, consisting of many branches, channels, shafts and hoses, which is an essential element in the functioning of ventilation as a whole.
When choosing ventilation equipment, it is necessary to take into account what types of air ducts were used when designing the system on a particular section of the ventilation line. In addition, it is necessary to make sure of the methods of connecting ventilation equipment to the air duct network, paying attention to the diameters and capacity of the air ducts in a certain area, and also take into account what material the walls, ceilings and all parts of the building adjacent to the attachment point are made of.
What you need to know to install high-quality ventilation
Ventilation is a complex engineering system, the performance of which is affected by every little thing:
- the length of the air duct should not exceed 3 m - otherwise the performance of the line will decrease by 15% with each additional meter;
- Turns can also reduce performance, each of them by 10%;
- avoid the formation of obtuse angles when turning the line - they disrupt the mechanism of natural outflow of air;
- To eliminate reverse draft, check valves are installed in the air ducts;
- the place where the ventilation riser exits onto the roof is insulated to avoid the formation of condensation during the cold season;
- The ventilation duct in the kitchen is located next to the place for the stove.
It is important! The main thing for installing ventilation is careful calculations and drawing up a detailed design of the engineering system. Preliminary consideration of the design and selection of materials for it will allow you to avoid mistakes.
Section shape
The most common types of air duct cross-sections used when designing a ventilation network are round
and
rectangular
.
If the design features of the ventilation system impose strict restrictions on the size and shape of the section, then air ducts of an elliptical
(flat oval) cross-section are used, which are made from round air ducts by processing them on special machines.
Round air ducts require less material for production and are manufactured using simpler technology than rectangular ones. If metal is used, the production of a rectangular air duct will require, on average, 20-30% more material than for a round one with similar indicators. More complex production is due to the fact that rectangular air ducts are put together from several smaller parts.
The advantage of round air ducts is good tightness, high air flow speed, low noise level, ease of installation, and lighter weight compared to a rectangular counterpart.
The main and important advantage of models with a rectangular cross-section is the possibility of their optimal location in space. They take up less space and adapt to certain features of the layout of the premises, for example, in the case of low suspended ceilings.
As practice shows, the round type of air ducts is most widely used in industry and other production premises, while rectangular ones are more actively used in ordinary buildings, country houses, apartments and other small premises.
Requirements for air ducts
Air ducts perform an important function - they ensure the outflow and inflow of air in a building, so the performance of ventilation directly depends on their parameters. There are a number of requirements for pipes for the engineering system; they must:
- be completely sealed;
- meet sanitary standards for noise levels (aerodynamic hum);
- comply with design calculations (ensure the passage of air masses at a certain speed and maintain the design pressure);
- meet thermal insulation requirements.
Air ducts should be as compact as possible so that the internal engineering system does not take up useful space in the premises.
Structural design
Also, air ducts, in turn, are divided into straight-seam (seam)
,
spiral-wound (spiral-lock)
and
spiral-welded
.
Straight-seam (industrial) air ducts are made of steel sheet metal with a thickness of 0.55-1.2 mm and a length of 1.25 m (on average). For rectangular models, the seam is placed on the fold to give the structure additional rigidity.
Spiral-welded air ducts are made of special steel strips with anti-corrosion coating, thickness 0.8 - 2.2 mm, width 400-750 mm (on average) and without restrictions on length. By welding the joints overlapping, the seam is dense and durable.
Spiral-lock air ducts are made of special steel strips with an anti-corrosion coating, 0.5 - 1 mm thick, 130 mm wide (on average) and without restrictions on length. By welding the joints overlapping, the seam is dense and durable. In the manufacture of spirally wound pipes, two methods are used: in a ring and in a tape. The first production option is considered more expensive and of higher quality.
Features of production and installation of air ducts
The following tools and equipment are commonly used to make steel ventilation ducts:
- roller shears:
- cross cutting machines;
- guillotines for obtaining blanks.
After preliminary production work with the metal, the stage of forming folds using folding machines follows;
- For round pipes, rolling machines are used;
- for rectangular bending equipment.
Seam crimping is performed using a folding machine.
A high-performance method for producing round pipes is the use of specialized spiral-winding machines.
And in the manufacture of rectangular pipes, tunnel assembly machines are used.
To create air-conducting plastic pipes, high-performance extrusion equipment is used.
Nowadays, ready-made air ducts are usually used, a wide range of which are manufactured by specialized enterprises. There you can also purchase fasteners for ventilation air ducts, including a variety of brackets, mounting clamps and punched tape, dowels and anchors, mounting profiles, flanges, and clamps.
Materials used
The materials used to make different types of ductwork depend on the specific application and the features of the existing ventilation system.
Galvanized air ducts
are used to transport air in temperate climates without an aggressive environment (temperatures up to +80 °C). The zinc coating helps protect the steel from corrosion, which significantly extends the service life, but increases the cost of such products. Due to their resistance to humidity, mold will not appear on the walls, which makes them attractive for use in places with high humidity in the ventilation system (residential premises, bathrooms, public catering places).
Stainless steel ducts
used to transport air masses at temperatures up to +500°C. The production uses heat-resistant and fine-fiber steel, up to 1.2 mm thick, which allows this type of air duct to be used in aggressive environments. The main places of application are heavy industrial plants (metallurgy, mining, with increased background radiation).
Metal-plastic type of air ducts
made using two layers of metal, such as corrugated aluminum, with foam plastic sandwiched between them. This design has high strength characteristics with low weight, has an aesthetic appearance and does not require additional thermal insulation. The downside is the high cost of these products.
Also, the plastic type of air ducts has become especially popular in conditions of transferring aggressive air environments .
The main industries in this case include chemical, pharmaceutical and food. Modified polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is used as the main material, which has good resistance to moisture, evaporation of acids and alkalis. Plastic is a light and smooth material that ensures a minimum of pressure losses in the air flow and tightness in connections, due to which a large number of different connecting elements are made from plastic, such as elbows, tees, bends.
Other types of ducts such as polyethylene ducts,
find their application in supply ventilation systems.
Air ducts made of fiberglass
are used to connect the fan to the air distributors.
Air ducts made of vinyl plastic
are used in aggressive environments where the air contains acid vapors that promote corrosion of steel.
These types of air ducts have high corrosion resistance, are lightweight and can be bent in any plane at any angle.
VENTILATION FROM TEXTILE DUCT
Textile air ducts are a new type of air ducts used to create ventilation systems for premises for various purposes. These products provide optimal air distribution; they are actively used to create supply and exhaust ventilation, climate control and air conditioning systems.
Air ducts can be of several types; they differ in the material used and performance characteristics.
- Air-permeable - they are made of polyamide, they are intended for transportation and uniform distribution of air masses throughout the premises. They are also called fabric diffusers. The breathable material serves both as a channel for transporting air and for filtering it from mechanical contaminants.
- With myco-perforation - the presence of micro-holes in the fabric allows you to evenly distribute air in the room at a low speed of its movement along the air duct. Thanks to this method of supplying and distributing air, such air ducts are used in places where many people often gather.
- “Textile nozzle” - this type of air duct is used to provide targeted air supply to a specific area of the workspace. They are also installed to create an air curtain.
There is another type of textile diffuser made using membrane technology. An airtight membrane is installed in the fabric air duct along its entire length, the position of which is controlled by a servo drive. The direction of air movement and the ability to disperse it depend on the position of the membrane. In this way, you can regulate the movement and distribution of air flows directed to different rooms.
In hot air transportation systems, as well as in rooms with increased fire hazard, air ducts made of material that includes fiberglass are used. Air heated to +300°C can be transmitted through such channels.
MAIN CHARACTERISTICS OF TEXTILE MATERIAL
— high strength;
— resistance to ignition and combustion (flammability class G1, flammability class B1);
— can be installed in “clean rooms” (up to class 4);
— antistatic and antibacterial effect;
— ease of maintenance;
— the color of the fabric does not fade over many years.
Rigidity
At the moment, the most widespread type of air ducts on the market is rigid.
Therefore, a significant part of all ventilation equipment is oriented towards rigid ventilation ducts.
As a rule, rigid air ducts are made with a round or rectangular cross-section. The material used is sheet metal (galvanized or stainless steel, aluminum or plastic). Thermal insulating materials (basalt wool) can be used as a laminating coating. Metal pipes are produced on roll forming machines, and plastic analogues are pressed through special extruders.
This type of air duct is used in structures that require high strength ventilation ducts. The advantages of these products include ease of installation and maintenance, as well as good aerodynamic performance. When creating, however, an extensive ventilation network, it is necessary to take into account the total weight of the future air duct system and, if necessary, take care to strengthen the entire structure.
Flexible duct type
appears in the form of a corrugated sleeve, which is why they are sometimes called corrugated or spiral. The base is made of steel wire reinforcement, and the walls are made of metallized polyester (laminated foil). The peculiarity of this product is its exceptional ease of installation, transportation and maintenance. If necessary, new elements can be wound onto an existing structure and bent in any direction. The disadvantages include the corrugated surface of the walls, which negatively affects the speed of air passage through the channel, as well as sound insulation.
Semi-rigid type of air ducts
- an intermediate link that has the strength of rigid and elasticity of flexible models. This type is made of aluminum or steel strips rolled into a tube and having a spiral seam. The main disadvantage, as in the case of flexible models, is the low speed of air passage through the ventilation ducts, which makes it difficult to use these products in an extensive ventilation network.
Installation nuances
The route for laying the air duct should, if possible, have the shortest length and the minimum number of connections. Before assembly begins, the ventilation system is divided into separate blocks no more than 15 meters long.
Each such node is assembled separately, using the following algorithm:
- The fastening points are marked on the structural elements, and holes are drilled if necessary.
- The individual elements are assembled into larger units, and the joints are carefully sealed.
- Fasteners are installed.
- The finished unit is lifted into place and secured.
- The connection is made with the previously installed node.
For semi-rigid and flexible air ducts, certain features are taken into account during installation. Thus, passage through walls is carried out only with the use of auxiliary elements - special sleeves. The bending radius should not exceed two diameters, and the direction of air movement should coincide with the markings on the air duct. Fastening is carried out at a distance of at least 1 meter, and the permissible sagging is no more than 5 cm for each meter of length.
Installation of metal air duct:
Installation of plastic air duct:
Mounting methods
The connection of adjacent air duct elements is made in two ways: flange and wafer (bandage).
In the first option, there are flanges at the edges of the air duct elements, which are connected to each other with self-tapping screws, rivets or clips (the distance between adjacent fastening elements is at least 20 cm). If necessary, the seam can be welded. Tightness is ensured in another way - through sealing gaskets.
A wafer connection involves the use of a metal band. This method is more economical and easier to implement.
Connection using C-rail:
Insulation of air ducts
Insulation of the air duct is not considered a prerequisite for its installation. The main role of the heat-insulating layer is to combat condensation, which negatively affects the performance characteristics of any material. First of all, thermal insulation will be required on the external sections of the air duct, or on sections of the route passing through unheated rooms.
Another advantage of insulated air ducts is sound insulation. The noise level in such areas will be several times lower, which allows them to be used in children's rooms, bedrooms and other rooms where silence must be maintained. A similar effect is achieved by using elements with thick walls.
DIY exhaust ventilation
The easiest way to install exhaust ventilation is in a private house, and you can equip it yourself, without turning to specialists for help. A separate air duct is installed for each room, and it is placed in a strictly vertical position. It is important to remember that each bend, “knee” or turn reduces the traction force in the channel by 10-15%. The speed is reduced by differences in diameter, protrusions or unevenness of the air duct.
Ducted exhaust ventilation ends above the base of the house's roof. The minimum cross-section of air ducts is 100 cm2, the larger the better. Preference is given to round exhaust ducts because they have minimal air resistance.
The design of exhaust ventilation begins at the construction stage of a country house, making it easy to hide ventilation ducts and shafts in the walls. If this is not provided for at the stage of construction of the facility, you will have to make holes of appropriate sizes in the ceilings, lay pipes and equip a brick box for the shaft.
The shaft exit area is formed independently, while the upper part is covered with a special umbrella to protect the channel from debris and precipitation. It is best to place the deflector there. In terms of price, it will cost more than traditional canopies, but it also helps to increase traction inside the shaft.
Calculation of exhaust ventilation
Calculation of exhaust ventilation for large production workshops and enterprises begins with identifying areas of distribution of unsafe substances and emissions. At the next stage, specialists determine the volumes of air masses for removal and supply in order to ensure sanitary standards.
If there are no active sources of unwanted substances in the space, it is advisable to use a simple formula:
O = m*n
- O – the volume of pure oxygen provided for by sanitary standards and regulations;
- m – average value of oxygen consumption for 1 hour of active work;
- n is the constant number of workers working in the premises every day.
As for the value of m, it has specific definitions documented by SNiPs:
- m = 30 m3 – for ventilated rooms;
- m = 60 m3 – for objects without access to clean air.
The above values are adjusted to take into account hazardous volatile substances released during the production process. In this case, their total volume is taken into account, and the calculated data on the influx of fresh oxygen changes upward.
Description of certification of ventilation systems for industrial premises
The peculiarity of harmful substances is that they tend to spread throughout the entire volume of the workspace, pavilion or production workshop. In this case, the main task is to reduce the level of their concentration to values at which a person can stay and work in the room.
Specific threshold values are provided for each harmful substance. Taking this into account, the volume of fresh air inflow is calculated using the formula:
O = Mb/(Ko-Kп);
- Mb is the average weight of an unwanted or potentially hazardous substance entering the workspace per unit of time (1 hour);
- Ko is the value of the remote concentration of a potentially hazardous substance in the surrounding space;
- Kp – concentration of undesirable substances at the inlet of the air handling unit.
Taking into account the volume of clean air required, choosing an engine of optimal power for exhaust ventilation will not be difficult.
Help in creating ventilation systems
By contacting, you can count on assistance in choosing various types of air ducts and their fasteners. The professionalism of our employees and long-term work in the field of ventilation systems (more than 20 years) allows us to provide our customers with only high-quality parts that are sold at an affordable price. We work only with trusted suppliers, whose products are ideal for your purposes and will last for many years. Good discounts are provided for regular customers. After placing your order, the product will be delivered to you in a matter of days. You can also purchase custom parts from us, which will be manufactured in a short time. We value our clients and offer them the most favorable terms of cooperation!
Natural and forced
Each exhaust ventilation system, regardless of type, design, complexity and cost, is aimed at removing waste air masses. To achieve this goal, various technologies, installations and methods are used. The exhaust ventilation system, taking into account the principle of operation, can be forced or natural.
If all processes with the “fifth ocean” are governed by nature and the corresponding laws, then the system works according to the natural principle. For cases where the exhaust ventilation unit operates using special equipment, the system is considered mechanical. These are automatic units that provide air exchange at a predetermined level, in accordance with passport and design standards.
Natural ventilation: pros and cons
The main advantage of natural exhaust ventilation in a house or apartment is its affordability. It does not require serious financial investments, and in terms of operation it is generally beyond competition, because free. Air mass exchange is carried out without additional equipment. The second important advantage is that solutions for this system take up minimal free space.
Natural ventilation works on a simple principle - hot air rises and cold air falls down.
Natural exhaust ventilation also has a serious drawback - its operation cannot be controlled, because it functions unilaterally. Air masses move in the system due to the fact that different pressures are formed at the inlet and outlet of the pipe. But conditions may develop in such a way that there will be no “traction” in principle.
If the temperature inside the house is lower than outside, the exhaust ventilation unit will work like a supply air unit. Air masses from outside are directed into the apartment. Taking this into account, they are equipped mainly within the residential space, but they are not suitable for production workshops and industrial facilities.
At large facilities their productivity is insufficient, which can be dangerous for workers.
General and local (local) ventilation
Experts divide all exhaust ventilation systems, taking into account the area of their design cleaning - local (local) and general.
A general ventilation hood is capable of quickly removing polluted air from all rooms in the building. A striking example is exhaust ventilation in an apartment. Its grilles are traditionally located in the bathroom and kitchen (in the upper part of the room), through which polluted air, small particles of soot and fat are removed.
General exchange systems are actively used in health institutions, warehouse complexes, storage facilities, residential buildings, shopping centers and shops. A characteristic feature of these objects is that the concentration of unwanted contaminants is minimal; they are evenly distributed throughout the volume of the room.
It is recommended to install general-exchange exhaust ventilation in a number of cases:
- the presence in the space of leaky mechanisms and machines that produce hazardous emulsions and substances;
- insufficient power of local solutions;
- absence of outlets for contaminated oxygen and unsafe substances.
Warehouse complex with mixed ventilation system
General exchange ventilation hoods eliminate the concentration of hazardous particles and impurities in the room to the optimal values stipulated by regulations.
Local exhaust ventilation is used to eliminate point releases of hazardous and harmful substances.
Due to their directional impact, they guarantee normal working conditions at the local site. The basis of the structures are exhaust pipes for ventilation, with the help of which smoke, air, dust, and unsafe fumes are removed, thereby preventing their spread.
The best clear example of such a device is mechanical kitchen hoods. The cost of equipment for a local system is an order of magnitude cheaper than a general exchange system. From an economic point of view, they are much more affordable. If the pollution is spread over the entire area of the room, the described solutions are ineffective.