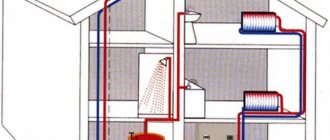
If you plan to repair pipes or radiators yourself, then you need to understand which taps to install on heating radiators. The presence of properly selected and efficiently operating shut-off valves makes it possible not only to disconnect heating devices for repair and maintenance, but also to regulate the amount of coolant entering the batteries.
In our article we will talk about which cranes can be installed, and also describe their key features.
A variety of valves and valves are used to control the operation of the heating system.
Stop valve
This category of equipment is suitable for connecting heating radiators in a system with two pipes. Due to their design, these valves allow you to quickly shut off the flow of coolant to the radiator, without requiring a complete shutdown of the heating system. Shut-off valves are also very convenient for draining water from the heat exchanger. As for the advisability of purchasing and installing this particular solution, from the technical side there is not much difference between such a valve and a ball valve. If the simplest thermostat is installed on the pipe that supplies the coolant, then both options will work exactly the same. However, shut-off valves have differences in design. The ball valve can only be opened or closed. And the valve allows you to regulate the flow of hot water in the system. Also, the device does not have a valve for turning. The cost of a shut-off valve is slightly higher than that of a ball valve.
Using valves with thermal heads
These are the best taps that can be installed on radiators in the heating system of a private home. Tuned to a certain air temperature, the thermal head acts on the valve stem, forcing it to open or close its flow area. In this way, automatic quantitative regulation of the coolant passing through the heating device occurs.
The thermostatic valve is installed on the supply line to the battery, and a balancing valve is installed on the return line. It is a mistake to assume that the system will be automatically balanced by thermal heads; valves are needed in any case. Installation of conventional ball valves instead of them is allowed for centralized heating or in systems with associated coolant movement (Tichelman loop). But it is unacceptable to regulate the coolant flow using a ball valve, and it will not work.
Advice. Most models of thermal valves have a mechanical blocking mode for the flow area. If you received products without such a mode, then to service the battery you will have to install an additional cut-off device, as shown in the diagram:
What is it and what is it for?
A thermal valve is a type of pipeline fitting. It allows you to maintain a given temperature in the room by optimizing the heat transfer of a separate heating device.
Purpose and scope
The thermal valve is designed for manual or automatic regulation of coolant flow through a radiator or distribution manifold.
Installation of such devices is recommended:
- In autonomous heating systems, where the medium is heated by a solid fuel boiler.
- On hot water pipelines. Water for domestic needs may be supplied too hot (up to 95 ºС) and, in the absence of a mixing tap, causes burns to users.
- In front of the plastic elements of the piping system. The thermal valve will protect the material from which the pipes are made from overheating.
Characteristics
For your information, here are a number of basic technical characteristics of thermostatic valves:
- The maximum operating pressure level is 1.0 MPa.
- Pressure testing before commissioning is 1.5 MPa.
- The maximum operating temperature is +110 ºС.
- The maximum permissible ambient temperature is +50 ºС.
- The valve capacity is from 1.6 to 2.5 m³/h.
- Temperature control range - +20…+60 ºС.
- Response time: 25 min.
- MTBF with manual control - 8000 cycles.
What materials are they made from?
Corrosion-resistant metals are used to make the thermostatic valve body:
- Brass.
- Bronze.
- Stainless steel.
Features of the ball product
integrity violations
If the water pressure is insufficient, then the reason should be sought in the valve, which is most likely clogged. To prevent similar situations in the future, you should take care to install a hard filter.
Most often, control ball valves for heating radiators are used in heating, ventilation and cooling systems. This element acts as a regulator of the water flow circulating in the heating and cooling system.
The advantages of ball valves include increased operational reliability. Thanks to them, it is possible to protect a certain section of the heating network, which reduces consumers’ costs for servicing these systems.
Locking devices
The taps used for installation in the room heating system should be divided into two groups - shut-off and control. This division is largely arbitrary, since shut-off valves also allow you to regulate the movement of the coolant. Naturally, in this case the adjustment accuracy is quite low, but it is possible to cut off the battery from the water source.
Ball design diagram
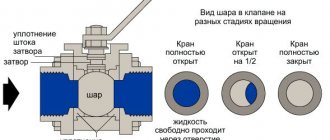
The simplest and most commonly used type of valves are ball valves:
The ball valve is designed to shut off the radiator. Its design allows the device to be installed in either an open or closed position, so that the adjustment is carried out quite according to the principle “there is heat - there is no heat.”
Ball valves for heating radiators provide two-position adjustment
Please note! In principle, you can fix the valve in an intermediate position, but then the rate of its wear will increase many times due to the friction of particles suspended in water against the shut-off element. So it is better not to do this unless absolutely necessary
- The coolant flow is blocked by the movement of a metal ball with a hole coaxial with the pipe clearance. When you turn the faucet handle, the rod comes into action, which rotates the sphere inside the body, aligning the hole in it with the lumen of the pipe.
- As a rule, faucet parts are made of steel, bronze or brass. PTFE gaskets are responsible for sealing the connections and the locking part, which, if necessary, can be replaced with your own hands.
- Connection to the radiator is carried out either using a regular nut or using an “American” one.
Ball design with American
Unlike ball valves, cone valves make it possible to regulate the coolant flow more smoothly. This is ensured by the features of their design:
Sectional view of the device
- The locking element is a conical rod, on the surface of which a thread is applied.
- When we rotate the flywheel, the rod moves along the thread, moving in a vertical plane.
- In the lowest position, the pipe lumen is completely blocked. The tightness of the overlap is ensured by elastic gaskets that fit onto the annular grooves of the rod.
- By lifting the locking part, we open the gap slightly, and the coolant begins to flow into the radiator.
Please note! The indoor microclimate can only be adjusted approximately by decreasing or increasing the amount of hot water in each battery
Model in polypropylene case
In practice, bronze or brass cone valves for heating radiators are most often used: only systems are equipped with polypropylene, some of the pipes in which are also made of plastic. This is explained by the relatively low strength and wear resistance of polymers compared to sanitary alloys.
On the other hand, polypropylene taps for heating radiators are somewhat cheaper, so in conditions of budget deficit they can be used.
Mayevsky crane
When you pour coolant into the heating system, air gets inside along with water or antifreeze.
To remove it, special devices are used - the so-called Mayevsky taps:
Air release device
- The design of such a product is quite simple: it is based on a shut-off rod installed in a housing with a thread for the radiator plug.
- The rod is driven either by a screwdriver or a special wrench, opening the lumen of the pipe in the saddle.
Please note! If possible, buy valves for a screwdriver, since you will regularly lose the key, which is not surprising - you will have to use it once or twice a year. You need to keep in mind that the throughput of such a faucet is small, so, for example, you shouldn’t install it on an expansion tank: it will take about an hour to bleed off excess air. In such a situation, a regular valve or a water tap installed with the spout facing up is more suitable.
In such a situation, a regular valve or a water tap installed with the spout facing up is more suitable.
You need to keep in mind that the throughput of such a faucet is small, so, for example, you shouldn’t install it on an expansion tank: it will take about an hour to bleed off excess air. In such a situation, a regular valve or a water tap installed with the spout facing up is more suitable.
Photo of the installed valve
Radiator insertion
What are the possible ways to connect heating radiators to bottlings and risers?
| Name | Description | Peculiarities |
| Lateral one-sided | The connections are connected to the upper and lower collectors on one side of the heater | With a small number of sections it ensures maximum heat transfer. If the number of sections is more than ten, the edge of the radiator farthest from the connections will cool down. Silt accumulates in the outer sections over time |
| From bottom to bottom | The connections are connected to both plugs of the lower manifold | The heat transfer of the device is slightly reduced due to slow circulation through the upper collector. The radiator does not require flushing: sections do not silt |
| Diagonal | The connections are connected to the top plug on one side of the radiator and the bottom plug on the other side | Heat transfer is maximum at any radiator length. The bottom of the sections from the side of the blind bottom plug is silted |
Please note: in a closed autonomous heating system, you can forget about the problem of silting of batteries. A small amount of suspended matter contained in the coolant quickly collects in the mud pan and does not create problems in the future. Accordingly, it makes sense to choose those types of heating radiator connections that will ensure maximum heat transfer.
Mayevsky cranes
Heating systems are a closed circuit in which coolant constantly circulates. If an air lock appears in it, then the heat transfer of the system is significantly reduced. And this is the best thing that can happen. In such situations there are risks of system freezing. To eliminate such plugs in heating systems, a Mayevsky tap is used. The price of the device starts from 100 rubles. This is an inexpensive, but at the same time necessary and very effective device. If you turn the valve on the tap all the way, you can hear air coming out, if there is any. Once the entire plug has come out, the mechanism can be closed. Air is released from a hole with a diameter of 2 mm. This hole is located in a plastic gasket or in a brass housing. There is a simple or automatic Mayevsky crane on sale.
The price for automatic solutions is higher and starts from 350 rubles. But such devices are much more convenient.
Air valves and radiator fittings
Almost all modern radiators provide the possibility of installing Mayevsky manual valves for air discharge. Some manufacturers even complete their products with them. If desired, instead of a manual air vent, you can install an automatic one, but in practice it does not look very presentable.
Recently, laying heating lines below floor level and using radiators with bottom connections has become increasingly popular. Then there remains a small gap between the battery and the floor, where it is not always possible to place any fittings. For this case, there is a special connection headset with built-in taps, shown in the picture (left):
On the right is a headset for the bottom connection of a conventional radiator with side plugs; it also has valves plus the ability to connect a thermal head. Such solutions look very aesthetically pleasing, but will require maximum financial costs. More information about the headset is shown in the video:
Ball Valves
Valves are cheap, but at the same time ineffective control devices. Ball valves are often installed at the entrance to the radiator, with the help of which they regulate the flow of water.
But this equipment also has another functionality - shut-off valves. Valves are used to completely shut off the flow of coolant into the system. For example, in the event of a leak in a heating device, ball valves located at the inlet and outlet of the radiator allow repairs to be made without stopping the heat supply and draining the liquid.
Heating radiators in the apartment cannot be adjusted using ball valves. They have only two positions - completely closed and open. An intermediate position only brings harm.
The fact is that inside such a faucet there is a ball with a hole, which in its normal position is not in danger, but in all other situations the solid particles present in the coolant grind it down and pieces break off from it. As a result, the tap will not be sealed and in the “closed” position, water will continue to flow into the battery, which can lead to big troubles if the device leaks.
If one of the property owners decides to control the radiators using ball valves, you must remember that they should be installed correctly.
This method is usually used in apartment buildings. If the wiring is single-pipe vertical, then the hot water pipe enters the room through the ceiling and a radiator is connected to it (read: “Correct adjustment of heating radiators in an apartment - comfort in the home and saving money”). The pipeline departs from the second entrance to the device and is directed through the floor to the room below.
In this case, it is necessary to install the taps correctly, since the installation of a bypass is mandatory. The bypass pipe is needed so that when the liquid flow to the radiator is closed, the coolant continues to circulate in the general house system.
In some situations, the tap is placed on the bypass to change the amount of water passing through it and thereby adjust the heat transfer of the battery. To ensure greater reliability of the heating system, at least three valves are installed: two will be shut-off valves on the radiator and function normally, and the third will become a regulating valve.
But here we must not forget what position the devices are in. Otherwise, you can completely block the riser and you will not be able to avoid the cold in the apartment, as well as unpleasant showdowns with neighbors and representatives of the management company.
How to properly install a thermal head on a battery
Intermediate positions when adjusting the water flow can lead to rapid wear of the locking mechanism and its leakage.
A cone valve is a more suitable candidate, since this valve does not need to be fully opened/closed.
Important. The tap must be returned to its original position after a while. Adjustment is done manually
Adjustment is carried out manually.
Adjustment of batteries using an automatic regulator, otherwise known as a thermostat, is carried out according to several schemes, depending on the type of heating system.
Thermostats for single-pipe heating systems
The principle of such adjustment
They are installed only if there is a connecting part between the pipes (bypass), which ensures constant movement of water in the battery to the radiator from the coolant.
Read more about the purpose and design of the bypass here: https://kvarremontnik.ru/bajjpas-dlya-otopleniya/
For any type of heating system, the thermostat is installed in front of the radiator/battery, strictly in a horizontal position. This compensates for the heating of the pipe and thermostat.
When installing a control valve, you need to take into account the direction of movement of the heat flow: with vertical pipelines, the movement is installed along them. Arrows on the valve indicate the direction of movement of the coolant.
When installing the regulator on a two-pipe system, the general requirements are met:
- installation takes place at the site of the jumper (plug) between the batteries and the coolant supply pipe;
- connection is made with the heating system turned off and the water drained from the system;
- The thermostat must be installed strictly horizontally.
Special conditions for installing a thermostat
Example of a thermostat
The thermostat operates on the principle that when a certain temperature is reached, the gas inside the regulator expands, shutting off or reducing the supply of hot water.
Therefore, special installation conditions are required so that the heating radiators are adjusted correctly:
- The thermostat should not be exposed to direct sunlight.
- It should not be covered by curtains or radiator screens.
- The air in the room must be ventilated, especially around the device itself.
In addition, its operation is influenced by the temperature outside the room and sources of cold and heat.
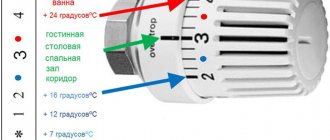
Advice. First of all, it is better to install thermostats in rooms with strong temperature fluctuations (kitchens, living rooms), as well as in the upper floors of private houses.
Read more about thermostats and working with them. And here is detailed material about the installation of equipment.
Home comfort
Expert advice
The diagonal connection scheme for radiators has already proven its best efficiency. The greatest heat loss is allowed when installing the bottom connection.
The thermoregulatory valve head should be placed perpendicular to the radiator screen so that the flow of warm air does not have a corrective effect on its readings.
Do not install the tap on the pipe connecting the expansion tank to the boiler. Unexpected overlap can lead to an explosion.
Why do you need to make adjustments?
The main factors explaining the need to change the heating level of batteries using locking mechanisms and electronics:
- Free movement of hot water through pipes and inside radiators. Air pockets may form in the heating system. For this reason, the coolant stops heating the batteries, as it gradually cools. As a result, the indoor microclimate becomes less comfortable, and over time the room cools down. To maintain heat in the pipes, shut-off mechanisms installed on radiators are used.
- Adjusting the temperature of the batteries makes it possible to reduce the cost of heating your home. If the rooms are too hot, by changing the position of the valves on the radiators you can reduce costs by 25%. Moreover, reducing the heating temperature of the batteries by 1°C provides savings of 6%.
- In cases where radiators heat up the air in the apartment very much, you have to open the windows often. It is not advisable to do this in winter, because you can catch a cold. To avoid having to constantly open windows in order to normalize the microclimate in the room, regulators should be installed on the batteries.
- It becomes possible to change the heating temperature of radiators at your discretion, and individual parameters are set in each room.
Crane installation
It is best to install the valve on the battery - with a bypass or emergency jumper. It is located between the coolant supply and discharge pipes. You need to cut 2 tees into them, which are connected with a piece of the same diameter. Install your own ball-type valve on the bypass, which will shut off the flow of hot liquid and release it into the radiator.
Install shut-off valves on the radiator after the bypass. When the valve is closed, the coolant does not flow into the radiator, but must pass through the jumper so as not to deprive the remaining apartments or rooms of heat supply. When installing a system with a bypass, you must follow the rule: the jumper valve is always in the opposite position with respect to the radiator valves.
The balancing valve is placed on the inflow pipe after the ball shut-off device. After connecting the circuit to the system, it automatically regulates the flow of water into the battery. A needle valve is placed on the upper end of the radiator farthest from the pipeline.
To properly design the outline you will need:
- 3 identical ball valves;
- 2 tee fittings;
- 1-2 pipe sections, the total length of which is equal to the distance between the inflow and return flow;
- 1 thermostat or balancing valve;
- 1 device for bleeding air;
- related materials, plumbing tools.
When installing devices, use sealant or FUM tape to prevent leaks at the junction of the pipe and the coupling of taps and fittings.
Differences between a faucet and a valve
Radiator shut-off devices differ from valves in their compactness and ease of use. In them, just turn the handle and the valve will be closed.
In addition, valves break quickly and constantly require maintenance and replacement of seals.
It is difficult to imagine their use in a home heating network. Due to their low cost, they are used in central heating pipelines where the pipe cross-section is greater than 100 mm.
Types of thermostats and principles of operation
Thermostats are divided into three types:
- mechanical, with manual adjustment of coolant supply;
- electronic, controlled by an external temperature sensor;
- semi-electronic, controlled by a thermal head with a bellows device.
The main advantage of mechanical devices is low cost, ease of operation, clarity and consistency in work. During their operation there is no need to use additional energy sources.
The modification allows you to manually regulate the amount of coolant entering the radiator, thereby controlling the heat transfer of the batteries. The device is distinguished by high precision in adjusting the degree of heating.
A significant drawback of the design is that it does not have markings for adjustment, so setting up the unit will have to be done exclusively by experience. We will look at one of the balancing methods below.
The main elements of a mechanical type regulator are a thermostat and a thermostatic valve
A mechanical thermostat consists of the following elements:
- regulator;
- drive;
- bellows filled with gas or liquid;
The substance contained in the bellows plays a key role. As soon as the position of the thermostat lever changes, the substance moves into the spool, thereby adjusting the position of the rod. The rod, under the action of the element, partially blocks the passage, limiting the entry of coolant into the battery.
Electronic thermostats are more complex designs, which are based on a programmable microprocessor. With it, you can set a certain temperature in the room by pressing several buttons on the controller. Some models are multifunctional, suitable for controlling a boiler, pump, or mixer.
The structure and operating principle of an electronic device are practically no different from its mechanical counterpart. Here the thermostatic element (bellows) has the shape of a cylinder, its walls are corrugated. It is filled with a substance that reacts to fluctuations in air temperature in the home.
As the temperature rises, the substance expands, resulting in pressure being generated on the walls, which promotes the movement of the rod, which automatically closes the valve. As the stem moves, the conductivity of the valve increases or decreases. If the temperature decreases, the working substance is compressed, as a result the bellows does not stretch, but the valve opens, and vice versa.
Bellows have high strength, long service life, and can withstand hundreds of thousands of compressions over several decades.
The main element of the electronic regulator is a temperature sensor. Its functions include transmitting information about the ambient temperature, as a result of which the system generates the required amount of heat
Electronic thermostats are conventionally divided into:
- Closed thermostats for heating radiators do not have an automatic temperature detection function, so they are adjusted manually. It is possible to adjust the temperature that will be maintained in the room and the permissible temperature fluctuations.
- Open thermostats can be programmed. For example, if the temperature drops by several degrees, the operating mode may change. It is also possible to set the response time of a particular mode and adjust the timer. Such devices are used mainly in industry.
Electronic regulators are powered by batteries or a special battery that comes with a charger. Semi-electronic regulators are ideal for domestic purposes. They come with a digital display that shows the room temperature.
The operating principle of semi-electronic devices for adjusting heat transfer by a radiator is borrowed from mechanical models, so its adjustment is carried out manually
Purpose and scope
Today's installation technologies require that each heating device be equipped with a locking element. This allows in emergency situations to cut off the flow of coolant into the battery, dismantle it and carry out repairs without draining water from the system.
Along with shut-off valves, heating devices are equipped with temperature control devices. A Mayevsky bleed valve is mounted in the upper radiator plug.
These types of fittings have become a mandatory attribute of a “smart home”; they are used both in residential premises and in administrative buildings, institutions, shopping centers, and everywhere where people live and work.
Thermal valve for heating radiator classification
Now let's talk about the lower part of the thermostat - the valve (valve). First of all, you need to know that the industry produces control devices for different systems. And you only need to use devices for your system.
Devices for two-pipe systems have at least twice the hydraulic resistance than for single-pipe systems. This was done on purpose, since balancing in this case occurs due to the pressure drop across the valves. That is why devices with a small flow area are installed. By placing such a device in a one-pipe system. you will probably be cold. Therefore, be careful.
There are thermal valves for radiators in one-pipe and two-pipe systems. And you cannot use devices for a two-pipe system in a one-pipe system.
Sometimes modifications for single-pipe systems are positioned as devices for natural circulation systems. They have reduced hydraulic resistance and can be used in single-tubes.
In a one-pipe system, install thermostats with a flow capacity of at least 3 (Kvs=3 and higher).
Depending on the method of pipe installation, radiator temperature regulators are either angular or straight (through). There are also axial models. In this case, they are chosen depending on the type of connection of the heating device. If the pipe approaches from the side, it is more convenient to install a straight valve, if from below - one of the corner ones.
According to the type of connection, thermostatic valves for radiators are straight and angular
Thermal valves also differ in the material from which they are made. Metals that have good corrosion resistance are used. Some of them also have an additional protective coating applied (usually nickel or chrome plating). So, thermostatic valves are made from:
- bronze, nickel-plated and chrome-plated;
- brass, nickel plated;
- stainless steel
It is clear that stainless steel is better, but such valves cost a lot and are rarely found on sale.
Why are there taps on radiators?
Each heating device is a separate element of the system that requires adjustment and periodic maintenance. If you control the coolant flow through the batteries depending on the heat demand, you can achieve good results in terms of energy savings. That is, radiator valves and heating taps are designed to solve the following problems:
- Complete isolation of the heating device from the system.
- Restriction of coolant flow through the battery.
- Change in coolant flow depending on external conditions.
- Bleeding air from the radiator and piping network.
There are many situations in which it is difficult to do without disconnecting the battery. For example, properly working central heating in the middle of spring, when it’s already warm outside, but it’s just hot in the apartment. Another case is the need to remove a heating device for the purpose of replacement, flushing or repair. In the absence of shut-off valves, carrying out any action with the radiator becomes problematic.
Valves are also installed on batteries in retro style
Restriction of the flowing coolant is carried out in order to balance individual heating in a private house or apartment
No matter what type of heating system you have, without balancing with valves, the first radiators will always receive more water than the last ones. Limiting the coolant flow at the beginning of the network and thereby balancing all devices with each other is the task of the control radiator fittings
Automatic control of the flow of incoming coolant is a way to save energy used to heat the house. If each tap on the heating radiator maintains the set air temperature in the room by controlling the flow of water through the radiator, then in general the system will consume only the required amount of heat, no more. And this is a considerable saving.
Well, the problem of air release when filling the system or during operation is also solved by special air valves installed on all modern radiators. Below is a list of types of shut-off and control valves, listed in the same order as the tasks they solve:
- Half-turn ball valves in straight and angle versions. Made from brass, bronze or polypropylene with a metal insert.
- Balancing valves for radiators – straight and angular.
- Regulating valves with thermal heads (thermostatic valves).
- Air drain valves – automatic and manual.
For reference. Some home craftsmen use three-way mixing valves to connect heating appliances. But such a solution is unreasonably expensive and is rarely used in practice.
Now we should consider in detail which taps are best installed on radiators in various conditions and circumstances. Some options are clearly shown in the video:
Circuit diagrams
If in a city apartment the layout of the heating system as a whole or its individual loop does not depend on our efforts, then in a private house the circuit is designed from scratch.
Two fundamentally different schemes can be distinguished:
- Single-pipe , which is the only bottling around the perimeter of the heated building. Heating devices are installed parallel to the filling.
Note: sequential installation of batteries is also practiced; it is inconvenient because it does not allow independent adjustment of the devices.
- Two-pipe - independent supply and return bottling. Each radiator acts as a jumper between them.
The advantages of a single-pipe scheme are low cost, ease of installation and exceptional fault tolerance. Disadvantages are a significant temperature difference between the first and last heating device, as well as the difficulty of laying around the perimeter of the house in the presence of high openings and panoramic windows.
The two-pipe scheme is devoid of these disadvantages, but under certain conditions it can create much more serious problems for the owner. The batteries closest to the boiler dampen the difference between pours, which slows down the circulation in distant devices. That is why a two-pipe system requires mandatory balancing - throttling the connections and adjusting their throughput to equalize temperatures.
This problem is elegantly avoided in a passing two-pipe system - the Tichelman circuit, all of whose loops are of equal length.
Purpose. Characteristic
Taps ensure efficient operation of water pipes. The heating system cannot operate without these devices, and in some situations, using it without them becomes downright dangerous.
When the riser leaks, it is the shut-off valves that shut off the water, which makes it possible to make repairs without stopping the entire system
An important function will also be managing the heat dissipation of the battery.
The minimum set for the normal functioning of a conventional heating system consists of several types of shut-off and control valves. When connecting to the radiator, shut-off ball valves are mounted on the supply pipes, on the outlet and on the bypass. A mechanism is installed on the supply to adjust the coolant pressure. The radiator itself must be equipped with a Mayevsky tap. to bleed air. As you can see, the number of such products is significant and this is by no means an excessive option.
Taken together, this system allows:
- turn off the radiator without shutting off the entire circuit for repair, replacement, or maintenance;
- direct all coolant through the heater with the bypass turned off;
- control the pressure power through the radiator to reduce or increase the temperature;
- drain water, bleed air;
- protect the system from hydraulic shocks and breakdowns;
- regulate the efficiency and level of heat supply, which saves heating costs.
Requirements
The criteria for the variety of types of taps placed on heating radiators are: design, principle of operation and material
It is important to know that mechanisms of this type are divided into shut-off and control valves. What are the best taps to install? It must be taken into account that they have a rather complex structure and must meet a number of requirements in order to function in difficult conditions
- coolant temperature up to 200°C;
- must withstand pressure of 16–40 bar;
- high corrosion resistance;
- resistance to mechanical loads.
For heating systems, such mechanisms are made more stable. Conventional taps and valves for cold water cannot be installed in heating radiators.
Each connection has its own characteristics: there are regular and corner (for the bottom connection) taps. This division allows you to maximize the distribution of pipes when installing a heating system. The design features of the valves allow you to hide the pipes behind the decor, in a screed, or to mount radiators in a small space under a window opening.
In everyday life, the general name is used - “faucets”. But from a technical point of view it is correct to distinguish:
Heating systems also use thermostats; it is not recommended to use dampers or valves in radiators - they quickly become inoperable. If shut-off valves are needed, then ball valves are the best for this. They have only two positions - closed/open. Valves with a cone are designed to control the pressure manually. There are also mechanisms for automatic adjustment - these are thermostats with valves or cones.
Tips for choosing
For home wiring without adjustment, it is enough to install ball valves on the devices. If used correctly, they will last a long time and be effective.
In apartments with central heating, it is recommended to install control valves with thermal heads. They do not clog so quickly and are capable of performing both shut-off and regulating functions.
The technical characteristics of the fittings can be determined by the markings stamped on the body of each product.
Balancing valve
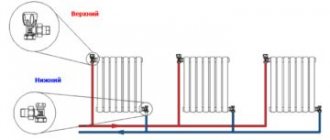
The design of a valve for regulating heating differs from a conventional ball valve in that it can smoothly close the flow area in a few turns. Moreover, after balancing, the position of the valve can be fixed so that no one accidentally violates the settings. This type of control valves is installed at the outlet of the radiator, as shown in the diagram:
Shown here is the connection to a two-pipe horizontal system, most common in private houses and apartments with individual heating. By the way, the principle of installing fittings with a single-pipe scheme remains the same. A regular ball valve is installed on the supply line, and an adjustment valve is installed on the return line. In the case when a two-story house has a system with vertical risers, the installation diagram of the accompanying fittings looks like this:
The principle of product selection is the same as in the previous section
Straight or angular design is accepted depending on the layout of equipment and pipelines; it is also important to use American designs during assembly
Pay special attention to the quality of casting and the thickness of the brass walls of the fittings. If you have networks made of polypropylene pipes, do not rush to buy PPR taps; it is better to install adapters and reliable metal products
Advice. Balancing valves are installed on all radiators, except for the very last one, located at the dead end of the branch. It is enough to install simple ball valves on the connections to it.
How to choose a ball valve
If we imagine the mechanics and physics of closing a pipe with a ball valve ball, then a logical question arises: how will a ball valve work if it is installed not vertically, but horizontally or at an angle.
Practitioners recommend using a cast iron valve “Tech-Pol” (Poland). It works in both horizontal and vertical positions.
Functionality
A tap for heating radiators will be extremely useful when it is necessary to dismantle the battery to clean it from blockages without draining the coolant. Radiators are also removed to eliminate leaks. Mayevsky-type taps allow you to get rid of air pockets that have formed in the system. Air often forms in the upper parts of heat exchangers. There is a fundamentally different shut-off valve - these are taps for heating radiators with a thermostat. They are equipped with thermostatic heads, with the help of which the heating of the radiators is regulated. This complex allows you to reliably protect the heat exchanger and heating system from any damage, and allows you to control the efficiency of the heat supply to the premises. Shut-off valves are much cheaper than any repairs due to radiator leaks.