Heating systems with water coolant very often become airy. Air penetrates massively into the liquid medium when heating networks are fed, and in addition is released from the water in different temperature conditions. In high areas of the network sections, air also collects, forming air plugs, which, depending on their size, can either completely block the circulation of water movement, or significantly limit it, thereby reducing the level of heat transfer, and therefore the efficiency of the system as a whole.
Air pockets can also be located in the heating source, which is especially dangerous and leads to serious accidents on boiler units. In this connection, there is a need for timely discharge of air from the internal circuit of the network using air vents. This is one of the main tasks of safe operation of heat supply systems.
Design and operating principle of manual air valve
The needle manual air valve is also called a Mayevsky valve. His device:
- Brass body (plug) with external thread 1/2 // or 3/4 // for connection to the radiator. The case has two holes for air release Ø 2 mm - one at the end of the case, the second on the side wall;
- Brass locking screw. On one side of the screw there is a groove for a slotted screwdriver, on the other side the screw is machined into a cone that closes the air hole (the “closed” position);
- Plastic casing.
On sale you can find the so-called “faucet at hand”. To use it, you don’t need a key or a screwdriver—the plug can be easily unscrewed by hand.
To remove air from the housing, you need to unscrew the screw. To do this, you can, of course, use a screwdriver, but there are special keys that are most often included. After several revolutions, the screw cone comes out of the end hole and air enters the housing cavity, which is immediately released through the second side hole. The main thing is not to rush to turn off the tap. About 30 - 40% of the air should come out with water, so you need to stock up on time, a basin and rags. After the air has been released, the lost water must be added to the system.
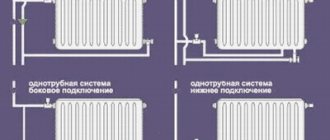
Modern aluminum or bimetallic heating radiators already have a hole for installing a Mayevsky tap. It can be found on the side opposite the coolant supply, from above. Most likely, there is already a nut for installation there. There is a plastic plug screwed into it. After its removal, an air valve is installed in this place. Before this, the tap threads must be sealed with a rubber or silicone gasket.
Installing a Mayevsky crane on a cast iron battery is much more difficult. Let's start with the fact that these valves are much more powerful than those on aluminum radiators - they can withstand pressures of up to 16 atmospheres and temperatures of 150 C°. Sequencing:
- 1 Drain the water from the radiator;
- 2 Cut a hole in the top plug of the cast iron battery and cut a thread that matches the external thread of the air vent;
- 3 Screw in the Mayevsky tap;
- 4 Add water to the system.
Malfunctions and ways to eliminate them
If the faucet malfunctions, a leak appears. There may be several reasons for this:
- Manufacturing defects. One in fifty taps does not hold pressure at all. The only way out is replacement;
- The screw is too short. In this case, its conical part cannot completely block the hole, so you need to apply a certain force to screw the screw in until it stops;
- Solid particles of debris falling between the screw and the housing can damage the internal threads. Fum tape can help here once, but later you will still have to change the tap.
Modernization of the circulation system
Instant access to hot water in the circulation system is only possible if it is constantly heated, which is certainly associated with certain energy costs. However, these costs are less than when we simply flush the cooled water down the drain. However, it is possible to make the circulation system even more economical.
Recently, experts have begun to use new thermostatic balancing valves
(photo on the right), which calibrate the flow of such a cross-section that will ensure minimal water circulation, but while maintaining the specified temperature in the circuit. As the water cools, the valve increases flow capacity. If the temperature increases above a predetermined level, the valve closes, thus ensuring optimal circulation.
Such valves allow you to set the water temperature in the system within 40-60°C. Previously, throttle flanges or pre-set control valves were used for this. These devices are not automatic and therefore require regular adjustment. New thermostatic valves themselves determine the required distribution of water depending on the prevailing conditions, for example, when actively dispensing water from several taps. This makes it possible to ensure optimal water distribution and slightly reduce energy costs. In addition, thermostatic valves allow you to maintain different water temperatures in the circuits. So, with their help, you can make sure that hotter water flows into the kitchen than into the bathroom, where there is no need to supply water hotter than 45°C.
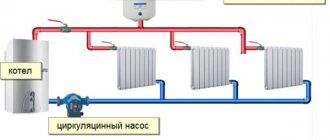
DHW with circulation and thermostatic valve
. A simple circulation circuit with a new generation thermostatic valve consists of a hot water source (boiler, storage water heater), a circulation pump, a thermostatic valve, pipes and tapping points. Hot water from the boiler enters the circulation circuit. The thermostatic valve is installed on the return pipe after the last water draw-off point, but before the circulation pump, which is located immediately before the “return” entrance to the boiler. If the system consists of several hot water circuits, then they are connected in parallel, i.e. depart from the supply pipe and return through thermostatic valves to a common return pipe, which, passing through a circulation pump, is connected to the boiler.
Maintaining the optimal temperature in the circulation circuits can also be ensured by circulation pumps, the operation of which is controlled by a thermostat. When the water temperature in the circulation circuit reaches a predetermined level, the thermostat turns off the pump and turns it on when the water temperature drops a few degrees.
The pump can also be controlled by a programmable timer, and this scheme is quite common. Its advantage is that circulation in the DHW circuit occurs only during the period of its use. For example, the pump can be turned off at night when everyone in the house is sleeping. However, it makes sense to choose this option if the family lives according to a certain established regime, which, however, is not uncommon. Energy savings in this case are the highest. Typically, timer systems also allow manual pump control. For example, if on some holiday hot water will be used at night, then it is enough to turn on the pump and circulation will take place in continuous mode.
Manual control of the pump is, in principle, very reliable, but there are inconveniences, since you have to turn on the pump in advance and then remember to turn it off. For manual control, it is recommended to additionally equip the pump switch with a shutdown timer. However, even in this case, situations will often arise when one of the residents forgets to turn on the pump and drains all the water from the pipes.
What signs indicate the need to install an air valve?
In order to prevent air accumulation, heating engineers suggest using an air valve for heating from the very beginning of operation of the circuit, so heating specialists, in the drawn up heating diagram, give recommendations as to which air vent is suitable for a particular heating system.
However, in some cases, trying to save money on the purchase of this type of control valves, owners refuse to install the devices and thereby provoke a number of problems. To solve them, they have to install an air valve for the heating system after the circuit has been connected and connected to the boiler.
The following signs indicate the presence of air pockets and indicate the need to integrate an air vent into the heating circuit:
- uneven heating of batteries;
- the appearance of “cold spots” on the pipeline;
- poor circulation in the heating system;
- noise in heating devices;
- poor-quality heating of the house.
Automatic air vent installation areas
Where in a heating circuit with forced circulation should an air vent be present to most effectively fulfill its intended purpose? How to prevent the formation of air locks in the system? There are several specific requirements:
- The pipeline must be laid in such a way that the coolant and the released air move in the same direction. The idea is that the hot carrier rises from the main riser to the distant ones;
- The air vent is installed in the highest areas. There is a reason for this that is completely explainable by the laws of physics: the release of air begins when the speed of flow of the coolant decreases, and this process occurs precisely at the highest points;
- The likelihood of the risk of air jams forming is present to a large extent at pipeline turns, in areas of transition from larger to smaller diameter pipes, and directly on heating devices (radiators). Therefore, it is quite logical to install air collectors in such places.
Finding a suitable installation location in the system
Taking into account the operating principle of an automatic heating air vent, it is usually used in the following areas:
- The highest point of the heating circuit (tops on vertical risers, etc.). This is where the internal air of the system usually accumulates.
- End areas of dead-end pipeline lines.
- Boiler piping safety group. Boilers using solid fuels especially need this. In this case, an automatic air bleeder is included in the set of instruments, which also contains a pressure gauge and an emergency valve. Thanks to the air vent, air is released as the coolant fills the water jacket of the boiler. In addition, the device increases the rate of water drainage when the heat generator is disconnected from the general system.
- Together with a circulation pump, which allows you to optimize its operation. This option is used only for those models of pumping equipment whose design provides for the possibility of installing an air vent. If the coolant is pumped with air, there will be a noticeable deterioration in the quality of the pump, even to the point of stopping it. All this leads to rapid wear of the impeller and bearings. Using a bleeder, you can also remove steam from the coolant if it overheats.
- Areas of the heating circuit where there is constant airing of the system. One of the reasons for such phenomena is an incorrectly calculated angle of inclination of the pipe.
- Heating appliances.
Installation recommendations
Regardless of the type of automatic air intake for heating, you need to ensure that the exhaust cap faces up during installation. Bleed valves in systems are usually installed after ball valves or shut-off valves. An exception to the rule is the boiler safety group: secondary intermediate fittings are not used in this case.
Thanks to the shut-off check valve, it becomes possible to carry out maintenance or replacement of the air vent without emptying the entire heating system. Therefore, having such a device is very convenient. Only wrenches are suitable for installing an automatic bleeder: they, unlike adjustable ones, allow you to measure the effort required to screw the fastener. During installation work, it is not recommended to hold the device by the body to avoid damage. For these purposes, the design provides a hexagon at the bottom of the cylindrical chamber.
Types of automatic air vents
There are three types of these devices in total - despite this, the operation of the automatic air vent, or rather its principle, remains unchanged. In all cases, the same needle valve and the same float are used to open and close it - the only difference is in the position of the body relative to the connecting pipe, i.e. threaded connection.
- Direct automatic air valve for heating. The most common device for automatic air removal. It is intended only for vertical installation - in the sense that if you suddenly decide to use it for a battery, you will additionally need a 90-degree angle. The optimal area of their application is pipelines, or rather their upper points, where, according to all the laws of physics, the air generated in the heating rushes. If it were not for such devices, it would be very inconvenient to vent air at the highest points of heating systems. In addition, some heating system equipment is also equipped with automatic vents with direct connecting pipes. For example, an automatic air valve is an integral part of the boiler safety group, which also includes a pressure gauge and an explosion valve. Indirect heating boilers and other equipment are also equipped with air vents, at the top of which there is a possibility of air accumulations.
- Corner air vent. In short, corner air machines are used where it is not possible to install its direct counterpart - it may either not fit in the right place, or the equipment may have a side outlet with a thread. In general, there are many different situations, and it makes no sense to list them all, especially since the essence and principle of operation remain unchanged - only the location of the threaded outlet connection pipe and, as a result, the appearance of the Mayevsky automatic crane changes. A very important condition for the proper functioning of the corner air vent machine is the strictly vertical installation of its body. Horizontally and even at a slight angle, the machine will not be able to operate adequately - the float will get stuck and, as a result, air removal will be untimely or will not be removed at all.
- Automatic air vent for radiators. In essence, this is a type of angular machine for removing air, although you can’t tell from the outside - all these nuances are hidden inside the case. The outer part of the battery vent is created based on aesthetic considerations. In addition, these devices also differ in the diameter of the connecting pipe - on modern radiators they are installed directly into the battery, without the use of foot nuts. On old batteries they are mounted through a fitting with a threaded hole through it, and for steel convectors special machines with a half-inch pipe are used.
These are all the varieties that an automatic air valve for heating systems can boast of. In principle, you don’t need more, since regardless of the different installation conditions, one of them will still work.
Corner and modern radiator air vents
In a variety of residential heating systems, situations may arise when it is necessary to urgently remove the resulting plugs from the most remote and inaccessible areas. in certain situations, it is difficult or impossible to install a valve with a simple design; the threaded pipe is positioned strictly horizontally. In such cases, a special corner is ideal. an element such as a pipe comes out from the bottom and then turns at a right angle, so it is ideal for connecting to horizontal sections.
Important! Angled air vents equipped with an external threaded connection are practically no different from standard models; only a rotated pipe is present. It is for this reason that angular ones can be used instead of straight lines.
Very often, to automatically bleed air pockets from heating systems, instead of a conventional tap, specialists install an angle valve. This is ideal especially if gases are always formed in the heating network and this happens in the radiator part itself. The basis for this is the usual chemical reaction of various substances that are found in some types of water, and aluminum batteries and at a fairly high temperature. All valves equipped with angular pipes should not be installed, since there is already a special automatic water drain.
Radiator devices were originally designed to be mounted for batteries, which have threaded connections specifically for this purpose. They are mounted instead of manual valves on bimetallic and aluminum radiators, that is, where there is some contact with water. Here, installing a radiator air vent is mandatory. In all other cases, such a device is installed strictly at will, which many people have, as it provides convenience during use.
Important! Standard radiators made of cast iron, which are connected to standard centralized heating systems. In these cases, it is better to equip the equipment with a conventional manual tap and it is necessary to combine all this with a drain pipe
Accessories for automatic air vents
For convenient maintenance, complete devices are also sold. The automatic air vent with valve is a threaded adapter with a spring-loaded reed valve. It is screwed in front of the gas outlet so that it can be serviced while the network is running. Models from VALTEK, DANFOSS and other reputable brands are equipped with such adapters.
This video will help you understand the features of each type of drainage system:
Types of air vents in the heating system
Based on the principle of operation, they distinguish between ball and needle automatic devices, and according to design - straight, angular and radiator. Despite the different areas of use, the operating principle of all air vents is the same.
Special float devices are very popular. This is an automatic air vent that provides side air release. The device operates at an operating pressure of 10 bar, with a maximum permissible temperature of 110 degrees. The device can work not only with water, but also with various glycol solutions in concentrations up to 25%, and the connection thread is 1/2.
All modern automatic air vents are divided into several types, differing in general design. There are three main types of such devices:
- Angular;
- Straight;
- Radiator.
Direct air vent
The most common is the first type with a straight pipe. It is indispensable at the highest points of the system, where, according to all the laws of physics, the maximum amount of gases accumulates, and manual air release in such places is often difficult.
The closed system, which is constantly under pressure, is ensured by the boiler safety group. It is usually located on the supply pipe that exits the heat generator. In addition to the pressure gauge and safety valve, this kit also includes an automatic air vent for heating, which bleeds air when the tank is filled with liquid. If the unit is installed correctly, it can be separated from the system at any time and released for maintenance using a gas vent. For boilers operating on solid fuels, a safety group is required.
You can also find an air bleeder in circulator pumps. Its task is to create conditions for them to have an uninterrupted supply of water. The problem is that the pumping unit can only work with an incompressible medium. The penetration of air onto the pump impeller threatens to stop it completely. The active circulation of liquid is controlled by the gas vent.
Corner air vent
If the location is too inaccessible to install a simple valve (for example, the pipe is horizontal), use an angle version of the valve. Its pipe, rotated 90?, can be connected to the horizontal part. It is worth noting that the corner modification with external thread, except for the deployed pipe, is practically no different from its analogues, so these types are completely interchangeable.
Radiator automatic air vent
Sometimes, instead of the traditional Mayevsky tap, an automatic angle valve is installed on radiators. It is only slightly larger than its counterpart, a little more expensive (about $2), but does not require daily human intervention. This choice is justified if gases accumulate in the battery regularly due to the chemical reaction of the aluminum alloy from which the section is made and hot water.
Although for such cases they produce a special automatic device with a diameter like a radiator plug (see photo). The device is designed specifically for aluminum and partially bimetallic radiators and has a suitable connection type.
For cast iron batteries and old-type systems, the Mayevsky tap and drain pipe are more suitable.
Choosing an air vent: expert advice
Such an important mandatory safety device for any heating network as an automatic air vent for heating must be chosen correctly.
It is usually supplied complete with other boiler equipment. If the home owner still has to choose an automatic air vent on his own, it is recommended to pay attention to the quality of the material from which the valve is made. It is necessary to protect yourself from all kinds of silumin fakes that imitate copper modifications. Professionals recommend choosing automatic devices with exhaust pipes directed upwards. According to reviews from numerous customers, on models with side outlets, leaks occur much earlier.
In addition, during installation it is necessary to ensure the vertical position of the device. Main recommendations for selecting air vents:
- It is more reliable to purchase a motorized air vent with a plastic or iron handle; this eliminates the need to carry various keys or screwdrivers with you. This faucet is convenient to use even in hard-to-reach places.
- In the case where young children live in the apartment, it is recommended to install an ordinary manual air vent, made for screwdriver control. Otherwise, children will be able to unscrew the air vent with a handle and scald themselves with boiling water.
- It is advisable to purchase devices with a self-acting cut-off device.
- If the estimate allows, it is possible to order a mechanism with additional options that can make servicing the heating network more comfortable.
- The high-quality anodized coating of the air vent essentially plays absolutely no role, but only reduces the level of rust formation on metals.
- Today in the retail chain it is possible to find combined modifications of heating network devices, which are also equipped with air vents. This list includes balancing valve devices, a variety of shut-off and safety valves and electric coolant circulation pumps.
Reasons for appearance
Air can appear in the heating system for various reasons. If this is a one-time problem, you can simply delete it and not search for the source. If deflation is required several times during the season, you will have to look for the reason. Here are the most common:
- Repair and modernization of the heating system. During repair work, air almost always gets into the pipeline. It `s naturally.
- Filling the system with coolant. If you pour water into the system slowly, it carries little air with it, simultaneously displacing the air that is in the pipes and radiators. This is also an understandable process and does not require any special measures.
- Depressurization of joints and welds. This defect requires elimination, since airing will occur constantly. In individual heating systems, this phenomenon (leaky connections) is also accompanied by a drop in pressure. And this is another reason to look for faults. The most likely location is pipe and radiator connections. They may not be sealed. It is very difficult to look for them, since they do not always appear outwardly. If you notice that one of the compounds is leaking, everything is much easier - eliminate the drops. But if outwardly everything is normal, and air accumulates all the time, you have to coat the joints and seams with soap foam and observe whether new bubbles appear. After finding each “suspicious” connection, they are tightened, coated with sealant or repacked (the method depends on the type of connection).
Air can accumulate in pipe bends.
If the heating system already has air vents (valves for releasing air) and plugs begin to appear in it, you need to check the serviceability of the valves, as well as the tightness of the connections. The appearance of air in the heating system may be due to a rupture of the expansion tank membrane. In this case, you will have to change the membrane, and to do this you need to stop the entire system.
These are the most common places and ways in which air gets into radiators and batteries. It is necessary to kick him out of there from time to time, but when starting the heating in the fall, it is necessary.
Air removal methods
The air lock cannot be in an easily accessible place all the time. During installation or design errors, air accumulates in the pipes. It is quite difficult to remove it from there. To do this, you first need to identify the location of the plug. In the area where it appears, the pipes become cold, and you can also hear a murmur inside them. If there are no obvious signs, then you can check the pipes by sound by tapping. In the area where the airlock accumulates, the sound is louder and more sonorous.
Read also: how to properly bleed air from a heating battery.
After this, the air must be expelled. If we consider the heating system of a private house, then for this we need to increase the pressure or temperature. To increase the pressure, you need to unscrew the make-up valve and the nearest air release valve. Water will begin to flow into the heating circuit, increasing pressure, which forces air to move forward. The plug will come out after it hits the drain valve. When all the air masses are completely released, the air vent will stop hissing.
But not all air pockets can be removed in this way. In certain cases, it is necessary to increase both pressure and temperature simultaneously. These indicators need to be raised to values that are close to critical, but they cannot be exceeded. If after the procedure the air does not come out, you can try opening the drain and make-up valve additionally. It may be possible to move the air plug this way.
If the problem appears regularly in one area, it means that the culprit is incorrect pipe routing or an error in the design. In order not to suffer all the time during the heating season, a release valve is cut into the problem area. You can install a tee in the pipeline and install a valve at the free entrance. In this case, the problem can be solved very simply in the future.
Automatic fresh air valve AERECO:
Types of air vents
Automatic air vents differ in type of installation, size, and thread diameters. According to the location of the pipes they are:
- Vertical;
- Radiator;
- Corner.
The corner automatic air vent is convenient for installation on a radiator. In the place where the heating pipe enters it. With this installation, it will help to trap air and gases formed in the heating battery itself.
A vertical automatic air vent is best installed at the entrance to the heating system. With this arrangement, it will prevent air from entering the system.
The second option for installing a vertical model is at the top point of the heating system. This is where gases accumulate and prevent water or coolant from circulating effectively.
Radiator air vents are installed instead of a plug or Mayevsky valve in radiators. They are convenient, but it is advisable to install them on each radiator.
Link to video to text
A completely simple but important device - the air vent valve in the heating system performs an important function. The reliable circulation of the heating medium and the efficient operation of the heating network installation as a whole depend on its presence in the circuit. Moreover, the device is part of the so-called safety group, since it helps to automatically release air. The installation locations for vents are indicated by the heating network design. The same document establishes the standard size and modification of the protective device. Many types of heating equipment, including boilers running on gas fuel, are equipped with air vents already at the factory, during the assembly of devices and units.
What are the dangers of air in the heating system?
Everyone has probably experienced more than once that the heating is turned on, but some radiator or a whole group does not heat up well or is completely cold. The reason for this is the air in the heating system. It usually accumulates at the highest point, displacing the coolant from this place. If a lot of it accumulates, the circulation of the coolant may stop altogether. Then they say that an air lock has formed in the heating system. In this case, professionals say that the system is airy.
To resume normal heating operation, the accumulated air must be removed. There are two options for this. The first is more often used in central heating systems. Taps are installed on the outer radiators in the branch. They are called descents. This is a regular valve. After filling the system with coolant, open it and keep it open until there is an even stream of water without air bubbles (then the water flows in jerks). If we talk about multi-storey buildings, then when the system is launched, the air vents on the risers must first be opened, and the remainder can already be discharged to the apartments.
The air in the heating radiator interferes with the normal circulation of the coolant. This causes the battery to heat up poorly
In private systems or after replacing radiators in apartments, special air valves, rather than ordinary taps, are installed to bleed air. They are manual and automatic. They are placed in the upper free manifold on each radiator (preferably) and/or at the highest point of the system.
What else threatens the air in the heating system? It promotes faster destruction of heating system components. Although polymers are used more and more today, there are still plenty of metal parts. The presence of oxygen promotes the activation of oxidation (ferrous metal rusts).
Mayevsky crane
Of course, Mayevsky’s faucet does not belong to the category of automatic air vents, so it seems to be off topic of the article. But there’s not much to write about it, and since it’s still an air vent, a few words about it here.
Mayevsky taps are installed on radiators:
To bleed air, you just need to slightly open the screw on the tap with a screwdriver:
The blue arrow shows where the air will come out from.
If initially (when installing heating) we plan to install a Mayevsky tap, then we need to install the radiator so that the part where the tap is “looks” upward (1...2 cm higher).
Installation of an automatic air vent
Before installation, a comprehensive check of the device is performed. The housing must be free from dirt, rust and scale, if any. Next you need to do the following:
- The most convenient area for placing the air vent is calculated. It is advisable to think it over at the design stage of the heating system. The installation point must be as high as possible, must collect air and gases from all circuits and at the same time be accessible for maintenance.
- Using a shut-off channel or other connecting fittings (if necessary), tighten the automatic air vent valve so that the sealing material ensures a tight joint. If a corner or radiator device is used, then the working part of the housing with the chamber and float must be facing upward for unhindered air release.
- The air vent can only be tightened with an open-end wrench - it is not advisable to use lever wrenches.
- The tightness of the connection is checked, after which the cap at the top of the device body is unscrewed. Next, you can fill the branch with coolant.
Prices for automatic air vents
Price catalog for automatic air vents
Most popular models
At the moment, air vents from and Danfoss are popular. Each device is characterized by certain qualities, advantages and application features.
| Device | Characteristics | Price |
| "Valtec" - VT.502 | The mounting diameter is ?, that is, DN 15. The model is used in private homes, that is, in autonomous systems. Nickel plated brass body. The device is designed for a pressure of 10 Bar and operation at 110 degrees. | 280-300 rubles |
| "Danfoss" | Made from high quality brass. The devices are designed to operate with a maximum pressure of 10 bar. They can withstand temperatures of 120 degrees. There are models DN 15 and DN 10. | 300-350 rubles |
| "Airvent" | Device category DN15. The air vent is designed to effectively remove accumulated gases from the pipeline, as well as from the air collectors that are equipped with the internal systems of heating systems of buildings and heat supply kits. | 484 rubles |
What is an air valve
The air valve for heating is a sealed cone-shaped or cylindrical body made of brass. Inside it is a hollow float made of Teflon or polypropylene. This float is connected by a lever to the drain valve, which is equipped with a locking plug. This plug prevents coolant leakage if the device breaks down.
Air vents for heating systems come in three types:
- Direct devices of traditional type. They are mounted only vertically.
- Corner type devices that are installed at right angles. They are mounted on radiators instead of Mayevsky taps or in the event that a direct type of air vent cannot be installed.
- Special models for installation on radiators.
According to the principle of operation, the air vent can be manual (Maevsky tap) or automatic. The last variety is the float-type devices described above.
Operating principle of manual valve
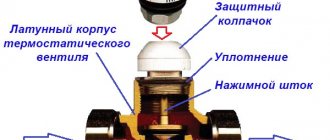
Let's figure out how a manual air bleeder for a heating system works. To understand the structure of this type, you need to look at the drawing of the Mayevsky crane. At the end of the brass body with external thread there is a hole with a diameter of 2 mm. It is covered by a screw with a cone tip. On the side of the same body there is a hole of a smaller diameter, which is used to bleed air.
The operating principle of a manual air vent is as follows:
- In operating mode of the heating circuit, the shut-off screw is tightly tightened. The outlet is hermetically sealed with a cone.
- To release the air lock, the screw is unscrewed a couple of turns. As a result of coolant pressure, air begins to escape through a small hole, then enters the outlet channel and is discharged outside.
- Moreover, at first only air comes out of the hole, then an admixture of water appears. The tap must be closed when only a stream of water flows from the hole.
Because there are no moving parts to clog, rust, or wear out, a manual air vent is a reliable, trouble-free device. This valve is installed only on radiators.
Manual type valves are divided into the following types according to the method of unscrewing:
- a metal or plastic handle is used for opening;
- More often you can find a slot for a screwdriver with a flat working blade;
- To unscrew it with a special key, there is a screw with a tetrahedral tip.
Operating principle of automatic valve
The automatic air collector for the heating system works without human intervention. It is essentially a vertical brass cylinder with threads and a plastic float inside. The float is connected by means of a lever to the air release valve pressed by a spring. This valve is built into the lid.
The operating principle of an automatic air vent in a heating system is as follows:
- When the heating system is operating, the internal chamber of the device is filled with water, which presses the float up. As a result, the air valve is pressed by a spring and tightly closed.
- When air accumulates in the upper part of the chamber, the level of the coolant decreases, which causes the float to lower.
- When the liquid level drops to a critical value under the weight of the float, the spring compresses and opens the valve. As a result, the air begins to bleed out.
- Due to the increased coolant pressure in the system, all air is displaced from the chamber of the device. The liquid takes the place of the displaced air and causes the float to rise, which pushes the valve up and tightly closes the hole.
While the network is being filled with coolant, air pockets are constantly being bled off, since the float lies at the bottom of the container. When water fills the chamber, a spring mechanism raises the valve. As a result, the bleeding process stops. However, some oxygen remains in the housing under the cover, but this in no way affects the operation of the heating circuit.
Automatic devices come with angular and direct connection. The latter type discharges vertically, and the first - to the side. The corner version is valued for its reliability, but collects air bubbles worse.
Prerequisites and consequences of the formation of air jams
In heating systems, untreated water saturated with air is most often used as a coolant. When heated, oxygen is released, and gradually accumulating microbubbles create a serious plug that blocks the free circulation of water.
If the liquid is supplied too quickly when filling the system, the gases do not have time to escape. The structure must be filled gradually: one floor of the branched system requires at least 1 hour to fill.
If there is a water leak in the system, or individual connections are not screwed tightly enough, air will enter the heating network. It can also penetrate during pipe repairs.
Tightness also depends on the type of material: the walls of polymer pipes without an anti-diffusion layer are permeable to oxygen. Some metals (such as aluminum) react to release gases from the coolant.
The accumulation of gas microbubbles can also be caused by errors during heating installation. To a greater extent, this relates to the absence of pipe slopes, which prevent air stagnation in certain places, from where the air does not enter the automatic air vent for heating. In such problem areas, it is necessary to install additional air exhaust devices.
Micro air bubbles reduce the efficiency of the system:
- Reduced heat transfer from radiators: the upper part, filled with air, remains cold.
- Internal corrosion: Oxygen in the air destroys the inner lining of the equipment.
- Circulation disturbance: the movement of the coolant may be partially or completely stopped.
- Rapid pump wear: the blades and bearings of the circulation pump experience regular overload, which leads to premature failure of the device.
- Additional noise: radiators, pump, pipes constantly hiss.
An effective way to eliminate all of these problems is to install a manual or automatic air vent - a device for bleeding air from the network.
Aluminum, present in modern battery alloys, acts as a catalyst for the decomposition of water. Gas bubbles accumulate in places where there are congestions for free circulation and create traffic jams.
Air blocks can often be observed at the top of heating radiators. In such places, the metal remains cold upon contact. Therefore, a manual air vent is installed in heating devices - a Mayevsky tap, familiar to more than one generation of Russians since 1930. Another name for the rare model is a radiator needle air valve.
Today, for modern batteries, various types of automatic valves have been developed to remove gases that do not require regular monitoring. You can see such a model disassembled in this video clip:
How the device works
An air valve (or several) is installed in the heating system, in places where air bubbles are most likely to accumulate. This prevents the formation of a large traffic jam and the heating operates uninterruptedly.
Mayevsky crane
Such devices are named after the name of their developer. The Mayevsky tap has a thread and dimensions for a pipe with a diameter of 15 mm or 20 mm. It's structured simply:
- There are 2 through holes made in the body of the valve body, which in the open position of the Mayevsky tap communicate with the heating system.
- These holes are closed by a threaded screw with a conical tip.
- Air is released through a small (2 mm) hole directed upward.
In order to bleed air from the system, unscrew the screw 1.5-2 turns. The air escapes with a whistle as the communications are under pressure. The end of the air plug exit is characterized by a drop in pressure and the appearance of water.
On the market you can find several varieties of the Mayevsky tap, which are identical in design, but differ in the way they regulate the shut-off screw. There are:
- with a convenient handle for unscrewing by hand;
- with a regular head for a flat screwdriver;
- with a square head for a special key.
For an adult, the principle of unscrewing the locking screw does not matter. However, in a house where there are children, it is safer to use devices that should be unscrewed with a special tool. By unscrewing a regular tap with a comfortable handle, a child can be scalded by boiling water.
Automatic crane
The automatic air release valve is designed on the principle of a float chamber, the design includes:
- vertical housing with a diameter of 15 mm;
- float inside the housing;
- a spring valve with a cover, which is connected and adjusted by a float.
The automatic air valve for the heating system operates without human intervention. In normal condition, when there is no air in the system, the float is pressed by the pressure of the liquid filler to the valve cover. The lid is tightly closed.
As air accumulates in the valve body, the float moves down. As soon as it drops to a critical level, the spring valve opens and bleeds air out. Under the pressure of the carrier in the system, the space is again filled with liquid. The float rises, closing the spring valve cover.
When there is no coolant in the communications, the float lies at the bottom of the valve. As the system fills, air comes out of the tap in a continuous stream until the coolant reaches the float.
The following configurations of automatic air valves for heating are distinguished:
- with vertical air discharge;
- with side air discharge (through a special jet);
- with bottom connection;
- with corner connection.
For an amateur, the design features of an automatic crane do not matter. However, for a professional there is a difference in choosing between devices.
It is believed that:
- a device with a jet and a side hole is more reliable in operation than an automatic valve with vertical air discharge;
- a bottom-mounted valve traps air bubbles more effectively than a side-mounted valve.
If the design of the Mayevsky crane has not undergone changes for many years, the design of automatic valves is constantly being improved and supplemented.
Manufacturers offer automatic valves with additional devices:
- with a membrane to protect against water hammer;
- with a shut-off valve for easy dismantling of the device during the heating season;
- mini valves.
Automatic heating air valves require frequent inspection and cleaning. The undoubted advantages of these devices include the ability to install them in hard-to-reach places.
Characteristics of air vents
It is convenient to present the technical features of the device in the table.
| Options | Peculiarities |
| Device service life | Up to 30 years old |
| Operating water temperature | From – 10 to + 120 C |
| Maximum room temperature | Up to + 60°C |
| Automation pressure | 10-12 bar (16 atm.) |
| Internal ? connections | 1/2, 3/4 inches (Du 15mm and DN 20mm - for metric units) |
| Thread type | External, internal |
| Valve material | Body – brass, float – polypropylene |
| Type of design | Straight, angular, radiator |
| Features of the coolant | Water or other liquid non-aggressive medium |
These parameters must be selected taking into account the type of network. For individual heating, the choice is unlimited; for centralized systems, you need to find out the pressure and temperature of your home at the housing department.
The cost of an air vent device depends on the model, manufacturer, material, connection (1/2 inch - 10-15% more expensive). The budget option can be purchased for $5, the most expensive is $15.
It is worth spending time choosing a supplier: in one store, an automatic air vent for heating Danfoss DU 15 is offered for $7.63, in another the same model is offered for $11.5.
When purchasing branded appliances from well-known brands (Danfoss, Wind, Valtec), beware of counterfeits. The price range for a shut-off valve is from $1.1 to $1.8.
Design and operating principle
The automatic air valve for heating systems has a simple and reliable design. The hollow metal body is equipped with a connecting pipe, which is located at the bottom or side, depending on the version of the product. In the inner chamber of the device there is a float made of polymer resin. The float is connected by a lever rod to a needle valve that closes the hole in the upper part of the air vent cover.
When removing the plug using a manual valve, you need to control the process in order to shut off the device in time - the air will be completely released when a trickle of coolant flows through the vent. Installing an automatic air vent eliminates the hassle of servicing the heating system.
The operating principle of the device is based on the use of gravity - a hollow float is lighter than water, but heavier than air. In the normal state, the air extractor is filled with coolant, due to which the float is in the upper position, pressing the needle valve. Over time, the coolant is displaced from the internal chamber of the device by accumulating gas.
As a result, the float falls down under the influence of gravity, opening the valve slightly. The accumulated air under the pressure of the liquid in the heating system comes out through the hole in the drain body, and the chamber is again filled with coolant, which raises the float, automatically closing the valve.
Float ventilators serve to remove air pockets and also help speed up the draining of coolant from the system during maintenance or repair work. Due to a decrease in the coolant level in the circuit, the valves automatically open, and the air entering through them causes the liquid to drain faster.
Reasons for airing the system
Air in the heating circuit negatively affects the function and durability of the system. Oxygen reacts with steel and causes corrosion. Air locks interfere with the normal movement of the coolant, blocking the heating of the upper part of the radiators or entire heating devices. The presence of air bubbles in the coolant leads to premature wear of the moving parts of circulation pumps.
Air-filled heating system
There are several reasons for the formation of air jams
:
- Using water from a water supply system as a coolant that has not undergone special treatment to remove dissolved air. When heated, gases leave the liquid medium and accumulate at the upper points of the pipeline and batteries.
- Excessively fast filling of the system with coolant or its supply is not from the lowest point. In such a situation, the liquid does not have time to displace air from all corners of the installed system.
- Loss of system tightness due to installation errors or damage to elements.
- The use of polymer pipes that do not have a barrier coating, which prevents the penetration of oxygen molecules into the coolant.
- Errors when developing a project or arranging a system (incorrectly chosen angle of inclination of pipes, etc.).
- Air entering the system during repairs that require dismantling circuit elements.
Features of installing an air vent in a private house
For installation you will need a wrench
. An air vent designed for heating communications in a private house must be installed strictly in a vertical position. For installation work you will need a threaded tee, FUM tape, and an open-end wrench.
The installation process is carried out in stages:
- Tee fastening. You will need a piece of pipe onto which a tee is fixed by soldering, glue or simple shrinkage.
- Preliminary check of the location of the vent at the highest point of the equipment. The device connection must have an upward direction.
- Installing the shut-off valve on the hexagon of the device using an open-end wrench.
- Connect the automatic air vent so that the protective cap with nipple faces upward.
- Screw the cap tightly to prevent debris from accumulating.
- Checking the tilt of the device (for radiator models). The battery section with the drain rises slightly.
After installation, the devices do not need to be adjusted - they will bleed air automatically.
It is better to install the air vent with a shut-off valve - this makes it easier to remove it for repair or replacement.
Features of a multi-stage scheme
The multi-stage deaeration scheme provides for the installation of automatic devices along the entire line. Connecting the vents in this way allows you to locally and simultaneously remove air pockets. The automatic device is placed in the zone of rotation, formation of a loop. To extend the service life of the valve, an additional filter is installed. Once assembled, the system operates with the radiator hot at the bottom but cold at the top.
In two-story houses, installation of diverter devices must be carried out on the top floor.
A corner, straight or radiator vent is suitable for the heating main of an apartment building or private building. The automatic device is simple, reliable and maintainable. After installing it, the owner does not have to waste time monitoring the system and manually bleeding air.
Combination with shut-off valve
Before purchasing an air vent, you should consider one important operational nuance. The valve can be installed on the connection pipe with or without a protective transition piece. This element is called a shut-off valve and serves as a kind of shut-off blocker that closes the circuit. That is, if it is necessary to remove the automatic air valve, then in a system with a shut-off block this can be done without shutting off the water on the branch. The design of this element is designed in such a way that when the drain valve is connected, its valve automatically opens - and, on the contrary, when the device is removed, the pipe closes. This device does not in any way affect the deaeration process, but it facilitates the operations of dismantling the air release system. In addition, the shut-off valve can be used as a fitting adapter when changing from one diameter to another, although this is not its main function.
How to organize yourself?
The circulation diagram of a private house is usually created independently, taking into account the configuration of the premises, the number of water points, branches, and additional lines. The main task is the constant operation of the heated towel rail, which is installed in a gap in the hot water supply line.
If the water cools down, the device will stop heating the room and drying towels, and the bathroom will be damp and cold.
For medium-sized buildings, one bottling is used, but for large cottages, several boilers with their own systems are often installed. Let's look at the most common options.
Through a storage boiler
A storage boiler is a container with insulated walls where hot water is accumulated and supplied as needed.
The circulation system is not important for it, since the return line temperature will be lower than in the main tank. This will require heating or changing the water.
If you refuse circulation, the water in the dead-end lines will completely cool down and the hot water supply mode will be disrupted.
Therefore, to organize the flow movement, perform the following actions:
- a direct DHW line is drawn to all consumers and returns to the storage tank;
- a circulation pump is installed before entering the container;
- The make-up pipeline from the boiler is connected either with a separate input or connected to the return pipe through a three-way valve.
The tank is recharged only when the pressure in the DHW system drops or when the temperature drops significantly. For the correct operation of such a system, a control unit with a system of sensors is required, which will continuously provide information about the state of the flow.
This scheme requires the use of a separate boiler not connected to the heating system. Therefore, it is used only in the southern regions.
Through an indirect heating boiler
An indirect heating boiler is a heater where the working “body” is a coil with hot coolant. As a rule, it is built into the heating system.
The hot stream passes through the coil at a sufficient speed to ensure that enough thermal energy remains to heat the home. At the same time, the DHW line is always ready to supply water at the required temperature. Circulation is needed only to prevent the water from cooling in dead-end lines.
Assembly order:
- The boiler is connected to the heating system. To do this, it has a separate pair of pipes for supply and exit of coolant. Typically, the boiler is located next to the boiler in order to receive coolant at the maximum temperature.
- The hot water supply line is looped and connected through a circulation pump to the boiler. As a rule, the return flow is connected to the farthest point of water collection and directed to the tank along the most direct path so as not to lose thermal energy.
- Connect the cold water make-up pipeline. It supplies water when the level in the tank drops. The float valve gives the start command.
- They start circulation and adjust the heating mode by changing the speed or volume of coolant supply to the heater.
- They check the system for operability and eliminate any deficiencies found.
The circulation option through an indirect heating boiler is considered the most efficient and stable. In the summer, the heating circuit is turned off and the boiler only works to heat the tank.
User manual
The automatic air vent practically does not require human intervention during operation. The maximum that may be needed is to monitor the correctness of its functioning. But how to bleed air from the battery if the device fails? In this case, you will have to control the process of bleeding gases from the heating circuit through the side plug. It is present in the simplest batteries, and radiator panels are equipped with more modern mechanical valves. The user just needs to turn the valve or plug, after which the accumulated air will escape under the influence of gravity.
When performing manual bleeding, it is important to consider several technical nuances. Firstly, at this moment the heating must be turned off - boiler, boiler or other heating source. Secondly, after bleeding, when tightening the valve or plug, sealing of the fittings must be ensured. How to bleed air from a battery without leaving a leak? At the joint, plumbing tape or other sealant should be wound, which will eliminate the possibility of maintaining gaps. The same is done in relation to the installation of automatic air vents, which also suffer from leaks if they are installed incorrectly.
What to do if the air vent does not work
Air vent malfunctions often occur when air is not released from the system. This happens because the drain hole becomes clogged with scale. From time to time it needs to be freed from scale and rust.
To do this, unscrew it, first closing it off from the environment with shut-off valves and draining the water from the repair section of the pipeline
Next, the valve is removed, disassembled, and the needle is carefully cleaned. After cleaning is completed, seal the housing parts and reinstall them
In order to prevent clogging of the automatic vent, experts recommend installing a Valtek filter to purify network water. For dismountable structures, there is often a leak through the seal between the body and the head.
It is almost impossible to replace it, since such seals are not sold in the retail chain, so if such a problem occurs, it is better to use fum tape or silicone sealant. The cause of the leak may be a misalignment of the float; it is easy to fix it yourself.
Thus, we can summarize that the air vent is a mandatory element of any heating system, both central and individual, its installation is in accordance with the current rules. Automatic air vents are used to continuously remove air pockets without operator intervention.
Cleaning the vent valve
- Close the valve separating the air vent valve from the column
- Hold the bottom of the valve with one adjustable wrench and carefully unscrew the top of the valve body counterclockwise with a second wrench.
- Remove the float, rubber gasket and plastic plate
- Clean all parts with citric or oxalic acid
- Lubricate all parts with silicone for water purification
- Reassemble the valve in the reverse order, tightening the cap with your hands with a little force (if it leaks, tighten it).
To make disassembling and cleaning the air exhaust valves easier, it is recommended to cut a service key out of plywood.