The modern system of warm water floors is identified with a high level of coziness and comfort. This floor effectively heats the room and does not have a harmful effect on the life and health of residents. Such results can only be achieved if the calculations are correctly performed and the installation work is carried out correctly.
Calculation of water heated floor
A warm water floor can be the main source of heating for a living space or serve as an auxiliary heating element. The main calculations of such floors are based on data from the operating scheme: light heating of the surface to improve comfort or providing full heat to the entire area of the room. The second option requires a more complex design of the heated floor and a reliable adjustment system.
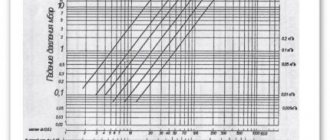
Comfortable temperature chart
Data for calculations
Calculations and design are based on several characteristics of the room, as well as the choice of heating option - main or additional. Important indicators are the type, configuration and area of the room in which the installation of this type of heating system is planned. The optimal option is to use a floor plan indicating all the parameters and dimensions necessary for calculations. You are allowed to take the most accurate measurements yourself.
Heated floor calculation schedule
To determine the amount of heat loss, you will need the following data:
- the type of materials used in the construction process;
- glazing option, including type of profile and glass unit;
- temperature indicators in the region of residence;
- use of additional heating sources;
- exact dimensions of the room area;
- expected temperature in the room;
- floor height.
In addition, the thickness and insulation of the floor, as well as the type of floor covering to be used, are taken into account, which has a direct impact on the efficiency of the entire heating system.
When performing calculations, you should take into account the desired temperature for the room being equipped.
Consumption of underfloor heating pipe depending on the loop pitch
| Pitch, mm | Pipe consumption per 1 m2, m p. |
| 100 | 10 |
| 150 | 6,7 |
| 200 | 5 |
| 250 | 4 |
| 300 | 3,4 |
Warm water floor calculation program
- There are two methods to calculate water heated floors, these are:
- visual method;
- and online calculator.
The first method uses graph paper, a pencil and an eraser for calculations.
The area of the room is drawn on paper, with all the preliminary data and calculations are made using formulas. This method is more accurate, but it takes a lot of free time and requires special skills. Therefore, to quickly calculate heated floors, a program for calculating heated floors is used - an online calculator.
Using such a program, you can easily, in just a few seconds, obtain all the information of interest, basic characteristics and the result of calculating the heated floor.
The essence of this method is that all data is entered into the calculator online, with the necessary sizes and selections already installed in it. Then, when you click on the total, the computer produces the results.
To calculate the number of pipes, you can use various computer programs that make it easier to determine the length of materials. For example, the VALTEC underfloor heating pipe length calculator (the program is provided free of charge, it can be found at the link).
- To calculate you will need:
- enter data describing the room in which the floor is supposed to be installed;
- determine the initial data for the calculation. Basic data includes;
- the region where the room is located, which determines the average air temperature and the required floor temperature;
- indoor humidity;
- floor covering area;
- the number of windows, entrance doors and walls facing the street;
- calculate heat losses;
- determine the location of equipment and pipe laying.
- Design is carried out according to the specified parameters, that is, the program will reflect the entered information schematically:
- calculate the amount of materials for the floor. The program will automatically calculate the pipe footage for a heated floor and other parameters that need to be taken into account when installing an additional heating source;
- You can also calculate using the program;
- hydraulic resistance parameters;
- the required power of the heating boiler and other equipment required for arranging the floor: expansion tank, pump supplying water to the system, and so on.
Correct calculation is the key to installing the optimal floor structure. It is advisable that the calculation be carried out by qualified specialists who, having determined all the conditions, will be able to calculate the optimal parameters. If you are laying the floor yourself, then it is recommended to use computer programs for calculations.
When all the results are ready and you can start installing a water-heated floor, you should familiarize yourself with several nuances.
Design Features
All calculations of water heated floors must be made extremely carefully. Any defects in the design can only be corrected by completely or partially dismantling the screed, which can not only damage the interior decoration of the room, but will also lead to a significant expenditure of time, effort and money.
Recommended temperature indicators for the floor surface, depending on the type of room, are:
- living space - 29 °C;
- areas near external walls - 35 °C;
- bathrooms and areas with high humidity - 33 °C;
- under parquet flooring - 27 °C.
Short pipes require the use of a weaker circulation pump, which makes the system economical. A circuit with a diameter of 1.6 cm should not be longer than 100 meters, and for pipes with a diameter of 2 cm the maximum length is 120 meters.
Decision table for choosing a water heated floor system
Calculating the circulation pump
To make the system economical, you need to select a circulation pump that provides the required pressure and optimal water flow in the circuits. Pump passports usually indicate the pressure in the circuit of the longest length and the total coolant flow in all loops.
The pressure is influenced by hydraulic losses:
∆ h = L*Q²/k1 , where
- L —contour length;
- Q - water consumption l/sec;
- k1 is a coefficient characterizing losses in the system; the indicator can be taken from hydraulic reference tables or from the equipment passport.
Knowing the pressure value, calculate the flow rate in the system:
Q = k*√H , where
k is the flow coefficient. Professionals assume the flow rate for every 10 m² of a house is within 0.3-0.4 l/s.
Among the components of a warm water floor, a special role is given to the circulation pump. Only a unit whose power is 20% higher than the actual coolant flow will be able to overcome the resistance in the pipes
The figures regarding pressure and flow rates indicated in the passport cannot be taken literally - this is the maximum, but in fact they are influenced by the length and geometry of the network. If the pressure is too high, reduce the length of the circuit or increase the diameter of the pipes.
Calculation rules
To install a heating system on an area of 10 square meters, the best option would be:
- use of 16 mm pipes with a length of 65 meters;
- the flow rate of the pump used in the system cannot be less than two liters per minute;
- the contours must be of equal length with a difference of no more than 20%;
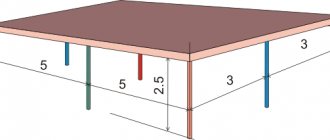
- the optimal distance between pipes is 15 centimeters.
It should be taken into account that the difference between the temperature of the surface and the coolant can be about 15 °C.
The optimal method for laying a pipe system is represented by a “snail”. It is this installation option that promotes the most uniform distribution of heat over the entire surface and minimizes hydraulic losses, which is due to smooth turns. When laying pipes in the area of external walls, the optimal step is ten centimeters. To perform high-quality and competent fastening, it is advisable to carry out preliminary markings.
Table of heat consumption of various parts of the building
Selecting the laying step
The laying step depends on the resulting length of the pipeline (see above). First, calculate how many meters need to be heated - the heated area of the room minus the furniture, for example, 20 m²). Then the actual pipe length per square meter of floor is calculated:
When laying pipes on the floor, the pitch can be varied - with a step of 15 cm in the soft corner area it will be a little warmer, and with a step of 20 cm in the center of the room it will be a little cooler.
Pipe and power calculations
The data obtained as a result of measurements is the basis for calculating the power of equipment such as a heating heat pump, gas or electric boiler, and also allows you to determine the distance between pipes when performing installation work.
Fastening pipes to reinforcement mesh
In order to correctly calculate the length of pipes required for installation, you should determine the type and features of these elements:
- stainless steel corrugated pipes are characterized by efficiency and high-quality heat transfer;
- copper pipes are characterized by a high level of heat transfer and impressive cost;
- cross-linked polyethylene pipes;
- metal-plastic version of pipes with an ideal ratio of quality and cost;
- foam propylene pipes with low thermal conductivity and affordable price.
Corrugated pipe for underfloor heating is one of the best options for water floor heating
The use of special computer programs can significantly simplify calculations and make them as accurate as possible. All calculations must be carried out taking into account the installation method and the distance between the pipes.
The main indicators characterizing the system are:
- required length of the heating circuit;
- uniform distribution of released thermal energy;
- the value of the permissible limits of active thermal load.
It should be taken into account that if the area of the heated room is large, it is possible to increase the laying step while simultaneously increasing the temperature of the coolant. The possible range of steps when laying is from five to sixty centimeters.
The most common ratios of distances and thermal loads:
- a distance of 15 centimeters corresponds to a coolant of 800 W per 10 m²;
- a distance of 20 centimeters corresponds to a coolant from 500 to 800 W per 10 m²;
- a distance of 30 centimeters corresponds to a coolant of up to 500 W per 10 m².
To know for sure whether it is enough to use the system as the only source of heating or whether “warm floors” can serve solely as an addition to the main heating, it is necessary to perform a rough, preliminary calculation.
Connection diagram for a water heated floor to a boiler
Rough calculations of the thermal circuit
To determine the density of the effective heat flux given off by m² of heated floors, you must use the formula:
g (W/m²) = Q (W) / F (m²)
Where:
- g is the heat flux density indicator;
- Q is the total indicator of heat loss in the room;
- F is the floor area expected to be installed.
To calculate the Q value, the area of all windows, the average height of ceilings in the room, and the thermal insulation characteristics of floors, walls and roofs are taken into account. When performing underfloor heating as an additional option, it is advisable to determine the total volume of heat loss in the form of a percentage.
When calculating the value of F, only the area of the floor involved in the process of heating the room must be taken into account. In areas where interior items and furniture are located, free zones about 50 centimeters wide should be left.
To determine the average temperature of the coolant under the conditions of the heating circuit, the formula is used:
ΔT (°C) = (TR + TO) / 2
Where:
- TR is the temperature indicator at the entrance to the heating circuit;
- TO - temperature indicator at the exit from the heating circuit.
The recommended temperature parameters in °C at the inlet and outlet for a standard coolant are: 55-45, 50-40, 45-35, 40-30. It should be taken into account that the supply temperature cannot be higher than 55 °C, with the condition of the return temperature being a difference of 5 °C.
In accordance with the obtained values of g and ΔT, the diameter and pitch for pipe installation are selected. It is convenient to use a special table.
Tables for calculating heat flow for heated floors depending on the flooring material
Tables for calculating heat flow for heated floors depending on the flooring material
Tables for calculating heat flow for heated floors depending on the flooring material
Tables for calculating heat flow for heated floors depending on the flooring material
At the next stage, the approximate length of the pipes involved in the system is calculated. For this purpose, it is necessary to divide the area of the heated floor in m² by the distance between the laid pipes in meters. To the obtained indicator, you should add the length reserve for making bends and the connection length is added to the length for pipe bends and the length for connecting to the collector system.
With a known length and diameter of the pipes, the volume and speed of the coolant can be easily calculated, the optimal value of which is 0.15-1 meter per second. At higher travel speeds, the diameter of the pipes used should be increased.
The correct choice of pump used in the heating circuit is based on the coolant flow rate with a margin of twenty percent. This increase in the indicator corresponds to the parameters of hydraulic resistance in the pipe system. The selection of sediment for the circulation of several heating systems consists in matching the power indicators of this equipment with the total flow rate of all heating circuits used.
Calculation of the cost of heated floors
What is needed for the calculation
In order for the house to be warm, the heating system must compensate for all heat losses through the building envelope, windows and doors, and the ventilation system. Therefore, the main parameters that will be required for calculations are:
- house dimensions;
- wall and ceiling materials;
- sizes, number and designs of windows and doors;
- ventilation power (volume of air exchange), etc.
You also need to take into account the climate in the region (minimum winter temperature) and the desired air temperature in each room.
These data will allow you to calculate the required thermal power of the system, which is the main parameter for determining the pump power, coolant temperature, length and cross-section of pipes, etc.
A calculator located on the websites of many construction companies that provide installation services will help you perform a thermal calculation of a pipe for a heated floor.
Screenshot from the calculator program page Source www.apostroy.ru
Note! If a water heated floor is used as an additional, rather than the main source of heat, the resulting power values are reduced to a certain proportion.
Tips and tricks
To get the most accurate calculations, it is advisable to seek advice from professionals who specialize in installing internal utilities.
It is possible to use an online calculator, which will facilitate the calculations, but will give very rough calculations that provide general information about the scale of the upcoming installation work.
An example of calculating a water heated floor
To heat old and dilapidated buildings that do not have high-quality insulation, it is not advisable to use a warm water floor system as the only heating element, which is due to the low degree of efficiency and high energy consumption.
The level of technical literacy of all calculations performed has a direct impact on the quality characteristics of the installed heating system. Correct calculations allow you to optimize financial costs not only for the process of installing water floor heating, but also to minimize costs during operation and maintenance of the entire heating system.
Video - Calculation of a water-heated floor (part 1)
Can the outline be of different lengths?
The branch of a warm water floor should not exceed 120 meters. Otherwise, you should make several separate loops. Ideally, they should all be approximately the same length. Then there will be no need for additional work on balancing and setting up the system.
If we consider an apartment with three rooms, one of which is a bathroom, then it is natural that the length of the pipeline in this room is much shorter than in the rest. The question arises: is it necessary to divide the coil in other rooms into parts so that it is equal to the size of the pipes in the bathroom?
This is not necessary; there is an acceptable discrepancy along the length of the pipeline of up to 30 to 40%, in rooms of different sizes. In addition, by using different pipe diameters and varying this by changing the laying step, you can reduce the area of a large room.
For your information! Do not forget to exclude from the area of the largest room the places where large-sized furniture will be installed.
Regardless of the chosen scheme, you should first prepare a drawing for laying the pipeline, taking into account the size of the contours and the intervals between the branches of the warm water floor.