Preparatory work or where to start?
The main task of a gutter is to drain water from the roof of a house. For the normal operation of the system, its throughput is important, so the first point in calculating the drainage is the choice of the type of system, as well as the diameter of the pipes and gutters.
As a rule, in small private houses an external system of 120x90 is used, where 120 is the diameter of the gutter, 90 is the diameter of the drainage pipes.
For large cottages and houses , it is preferable to use the 150x100 system. Its capacity is sufficient to function normally even in heavy rain.
There are formulas for accurately calculating the volume of rainwater depending on the roof area, region, and precipitation intensity, but ordinary citizens do not need to delve into such subtleties.
It is enough to know the total roof area , plan the location of the drain pipes and, based on this data, select the diameter of the drainage elements.
Initial data
To correctly calculate and select a drainage system, you must:
- Measure the height of the house. The measurement is made using a construction tape. The distance from the blind area (ground) to the edge of the cornice is measured.
- Measure the length of the eaves on all sides of the roof. It is important to know the length of each slope, since the accuracy of calculations of the required number of structural elements depends on this.
- Calculate the total roof area . Based on the data obtained, you can optimally select a drainage system.
- Count the number of outer and inner corners of the roof.
Important: if the roof of your house has a complex structure with a large number of angles, then to correctly calculate the drainage elements it is better to use online calculators from the system manufacturer.
The estimated collection area of gutters depending on the diameter and location of drain pipes.
A gutter with a diameter of 110 mm, when installing a drain pipe in the center of the slope, can serve up to 177 m2. A gutter of the same diameter with a drain pipe installed along one edge of the slope serves up to 89 m2. A gutter with a diameter of 120 mm is capable of receiving water from an area of 238 m2, and the 150th from 380 m2.
By installing a drain pipe along one edge of the slope with a 120 mm gutter, you can ensure the drainage of water from a roof with an area of 118 m2, and the 150th, under similar conditions, can cope with maintenance of a roof with an area of up to 190 m2.
The catchment area of drain pipes depending on location.
A pipe with a diameter of 70 mm, when installed in the center of the slope, serves up to 217 m2 of roofing.
By installing one along one edge, you can ensure drainage from an area of up to 149 square meters. The 90th pipe, with a central location, is capable of collecting water from 355, and 110 from 620 square meters.
By moving the 90th and 110th pipes to one edge of the slope, the catchment area will decrease and amount to 245 and 423 m2, respectively.
Obviously, installing bends in the center of the slope is more profitable, because with the same pipe diameter, the throughput of the system is significantly higher.
According to recommendations , for normal functioning
systems, one drain section should serve no more than 12 linear meters of drainage. If the length of the drain on one side of the house exceeds 12 meters, then two or more need to be installed, depending on the total length.
What does the diameter of the drainage system affect and what does it depend on?
Proper calculation of the diameter is a key factor that affects the efficiency of the structure and its ability to perform its assigned functions. The larger d, the better the throughput capacity of the gutter and pipe, but the price also increases.
Such a wide “range” of diameter and its choice depend on the following points:
- Water collection areas
- Schemes for the placement of drain points and their number (loaded and unloaded drain scheme)
Collection area
To calculate this parameter for one gutter, use the formula:
S= L (a+b/2), where
L – length of the roof along the ridge;
a – projection onto the horizontal plane of the roof slope from which precipitation flows;
c – roof height.
Let's give an example. Roof data:
- Height – 2 m.
- Length – 10 m.
- Projection width – 5 m.
Therefore, using the formula, we will perform the calculation: S= 10(5+2/2)=60 m2.
Placement of drain points
With a sufficient number of drain points, i.e. with an unloaded system, you can choose drainage parameters - 125/100 mm with a roof area of 100 sq. m. m.
The exact number of drain points depends on the diameter of the gutter. The data is presented in the table.
| S, sq. m | d gutters, mm | d pipes, mm |
| Up to 79 | 90 | 75 |
| More than 100 | 125 | 100 |
With a loaded scheme (drainage system to one funnel) - 150/120 mm with a roof area of 100 sq. m.
A loaded system requires the use of oversized dimensions. The data is presented in the table.
| Area, sq.m | d gutters, mm | d pipes, mm |
| Up to 42 | 75 | 63 |
| Up to 52 | 100 | 80 |
| Up to 75 | 125 | 100 |
| Up to 100 | 150 | 120 |
When choosing, it is better to choose elements with a larger d, which reduces the risk of contamination or the formation of an ice crust. It is important that all elements are from the same manufacturer, this will help to avoid errors in calculations and installation.
What to look for when choosing
When choosing, we recommend paying attention to:
- Precipitation rates for a specific region.
- Roof area.
- The specifics of the building's architecture.
- Roof slope.
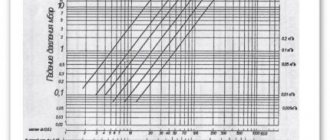
According to the requirements of DIN 18460-1989, the diameter of the drainage system pipe is selected based on the roof area and water throughput. The data is presented in the table.
| Roof area, m2 | Water throughput, l/s | Drainpipe | |
| d, mm | Cross section, cm2 | ||
| 40 | 1,2 | 60 | 28 |
| 60 | 1,8 | 70 | 38 |
| 86 | 2,6 | 80 | 50 |
| 156 | 4,7 | 100 | 79 |
| 253 | 7,6 | 120 | 113 |
| 283 | 8,5 | 125 | 122 |
| 459 | 13,8 | 150 | 177 |
To calculate the number of drainage pipes, use the following option: 1 pipe per 50 m2 of roof slope area, the distance between them should not exceed 10 m. In the case of diameter, there is 1.5 mm2 of pipe cross-sectional area for each square meter of roof area.
Kinds
Based on the name of drainage systems, you can understand what their difference is. The external system is installed along the perimeter of the eaves in such a way that water flowing from the roof falls directly into the gutter and then, due to the slope, moves towards the drain pipes through which it descends to the ground.
With this scheme for draining rainwater, drain pipes can be placed almost anywhere along the perimeter of the roof, and the water can be directed by adjusting the angle of the gutters.
The external system is preferable for private houses or multi-storey houses with a gable or hip roof.
Internal gutters are installed inside the building, and, as a rule, only drains are visible from the street; gutters are built into the roof or there may be no gutters at all.
Such systems are used mainly for flat or slightly concave roofs with soft roofing. The design can work on the principle of a sink.
Gutter: varieties
For a private house, 2-3-story building and outbuildings, various water drainage options are implemented.
- Unorganized drainage - involves free flow of water from the roof. This is often allowed on small buildings with a pitched roof, but it is not a good solution even in this case, since the foundation of the house is unprotected.
- Organized internal - vertical elements of the system are installed inside the building. Plus - the drain does not affect the appearance, minus - installation is more difficult.
- Organized external - the most common option: water drainage through pipes located on the external walls of the house.
The third solution is used more often, since it is quite practical and quite simple to implement.
Calculation of internal drainage for a flat roof
To calculate the drainage of internal systems, you will need to measure the perimeter of the roof and calculate its area.
The total length of such a drain will be equal to the length of the roof perimeter.
It is important to know the length of each side of the roof and the number of corners. Depending on the drainage design, the number of drain pipes is different, but the total length of the pipe is constant and equal to the height of the building, so the distance from the ground to the edge of the roof also needs to be measured.
If you plan to install an internal drain using the funnel principle, then the length of the drain pipe depends on how it will be located inside the building. Such a structure should be planned and installed at the stage of wall construction.
Number of funnels
Please note that at least two drainage funnels must be installed on the flat roof of the building and in one valley. If one is clogged, the second will work.
The length of the roof along its longitudinal axis is divided by the number of funnels, and the pitch between the funnels is obtained.
Calculation example for internal drainage (SNiP 2.04.01-85* clause 20.9.)
2500 (roof area with a slope of 1.5%) * 80 (l./s. with HA)/10000 = 20 h.p. with a norm for a funnel of 10 cm - 12 h.p., therefore, for internal drainage, 2 funnels are needed 10 cm.
Current drainage diameters
The sizes offered by Russian manufacturers range from 50 to 200 mm. Previously, only three main parameters were used - 100, 150 and 200 mm. But due to the large assortment from manufacturers and imported products supplied to our market, the diameter of drainpipes has changed significantly. Today there is no single established standard according to GOST in Russia.
Below we present common sizes of downpipes and gutters:
- 80/100;
- 90/125;
- 100/125;
- 120/150;
- 150/200.
Our company offers pipes and gutters that are optimal for many roofs. If the system is needed to drain precipitation from a large roof area, for example, from a warehouse or commercial building, pay attention to a large drainage system made of galvanized steel 120/150 or 150/200 mm. This design can handle high loads without deformation. Large-sized gutters are also suitable for roofs of production and industrial premises.
The thickness of the steel is 0.5 mm, the protective polymer coating is polyester. The homeowner can choose any shade from the RAL catalog so that the drainage system becomes not only protection, but also a decoration for the roof.
Vodostokstroy also offers systems for private construction - “Standard” and Euro “Aquarius” with dimensions of 100/125 mm. The systems have good throughput and affordable cost.
For oversized buildings for household purposes (household buildings, bathhouses, gazebos), we recommend a small drainage system of 80/100 mm.
Outdoor system
The classic drainage scheme for a private house is external. It is easy to calculate and install even without construction skills.
As mentioned earlier, for the calculation you will need to measure the perimeter of the roof and the distance from the ground to the eaves. To calculate the exact number of structural parts, you need to understand what it consists of and the rules for installing the system.
For ease of calculations, it is most convenient to schematically depict the roof of the house and the location of all drainage elements on a piece of paper. Indicate all known dimensions of the future structure.
What does an external drain consist of?
The main structural elements are drain pipes and receiving gutters. Corner elements, outlets, connecting and fastening elements are also used.
For systems in which drains are installed in the center of the slope, the function of connecting elements can be performed by diverters. The appearance of the design parts may differ depending on the system manufacturer, but the principle is the same for all:
- connecting – used to connect gutter parts;
- corner - can be external or internal, or combined with outlets;
- outlet parts are designed to connect gutters with receiving elements;
- plugs are installed along the dead-end edges of gutters;
- gutter fasteners , metal plates that are mounted on the sheathing;
- drain pipe fasteners;
- drain - installed at the end of the drain pipe, necessary to adjust the direction of wastewater with an open drainage system;
- coupling and elbow of the drain pipe , designed to connect and change direction.
In order to correctly calculate the required number of additional structural elements, you need to know the assembly principle.
Rules for installing the structure to the roof and walls of the house for a specific model of the drain manufacturer. This information can be found on the manufacturer's website.
Calculation example
For example, it is necessary to calculate PVC drainage from the Alta Profile company. Plastic fasteners for such a system, according to the recommendation, should be installed at a distance of no more than 60 cm.
To calculate the required number of fastenings, it is enough to divide the total perimeter of the roof in meters by 0.6. You will also need to count the number of clamps for attaching the outlet pipes.
They must be installed in increments of 180 cm, which means that for correct calculation it is necessary to divide the height of the house in meters by 0.18 and multiply by the number of drain pipes that are planned to be installed.
Connecting couplings and drainage elbows are calculated depending on the number of turns and the length of the drain pipes. The higher and more complex the contour of the house, the more connecting elements of the drain pipe will be required.
External drain design
The system for a private house consists of several elements, the number of which is determined by the area of the roof.
- A gutter is a wall or suspended horizontal channel through which water is directed into a funnel.
- A drainage funnel is a device that connects a horizontal and vertical drainage element.
- A pipe is a vertical element of different cross-sections through which water is transferred to a rain collector.
- Connecting elements - for water conduits with a spiral, vertical seam, with zigs, etc., different parts are used.
- Brackets for fixing elements.
- Contours - required to bypass ledges, niches, columns and other things.
Assembling the structure itself does not pose any particular difficulties: diagrams can be found in the GOST documentation; the standard diameter of the drainpipe and all other parts of the system greatly facilitates installation. However, before building a drain, it is necessary to calculate the required number of parts and their dimensions.
Online calculators from manufacturers
For those who are unfamiliar with the drainage system, but want to independently calculate and install gutters, manufacturers offer online calculators for calculating the number of required parts.
Calculating the number of parts using such a program is quite simple. You need to enter the initial data:
- length;
- width;
- height;
- width of the eaves overhang;
- type (single slope, gable, four slope, curly);
- material of the house facade (for calculating and selecting the type of fastenings for drain pipe clamps).
After the data has been entered, click the “calculate” button. The program will make calculations and give recommendations on the type of system and the number of parts required. Everything is simple and convenient.
Below are links to calculators from well-known manufacturers of drainage systems:
- Grandline
- Vestmet
- Prof-listi
- Docke - quantity and cost calculation
- Alta-profile
- Galeco
How to calculate the diameter and number of funnels
When calculating the number of elements, you also have to focus on the roof area: one funnel is able to serve 0.75 m2 of roofing. This usually equals 10 m of gutter. If there are obstacles to expansion along a 12 m section, you have to install a compensation funnel. The diameter of the funnel must correspond to the cross-section of the drain in the lower section.
These dimensions are calculated taking into account the passport data of the pipeline and its throughput. Moreover, each drainage system is equipped with a personal funnel. The number of compensators used is determined taking into account the total length of the gutter and the number of obstacles that need to be bypassed.
Bandwidth
One of the main characteristics of drainage structures is its throughput, which is directly affected by the diameter of the roof drain. Thanks to this parameter, you can find out the volume of liquid that it is capable of removing from the surface of a particular roof.
In order to correctly perform calculations, you need to take into account the type of roof, its configuration, as well as the climatic characteristics of the region regarding the frequency and abundance of precipitation.
If a mistake is made in the process of calculating the drainage, then the system will not be able to cope with the water flow that comes in the event of heavy rains or rapid melting of snow masses. In this case, water will begin to overflow over the edges of the gutters and there will be no benefit from such a design.
When calculating the amount of precipitation per drainage area, use the formula:
Q = S xq : 10000, where
Q is the desired value, expressed in liters per second;
S – roof surface area from which water must be drained, measured in square meters;
q – maximum intensity of precipitation in l/(s x ha).
Optimal number of funnels
The main purpose of the internal drainage system is to ensure the removal of water from the roof at any outside air temperature and regardless of the amount of precipitation. It is recommended to dispose of water into a general or storm sewer system. The number of funnels for internal drainage is calculated according to the rule: 1 funnel per 0.75 m 2 of roof and 1 cm 2 pipes for water drainage. The funnels of the internal system are located along the longitudinal axis of the roof. It is prohibited to install funnels and risers in the thickness of external walls, due to their possible freezing in the winter.
The number of drainage funnels is calculated taking into account the following requirements
:
- if there are no obstacles to the linear expansion of a gutter up to 12 meters long, then one funnel will be sufficient;
- if the gutter length is over 12 meters and there are obstacles to its expansion, then one special compensating funnel will be required at the end of the slope;
- if the gutter encircles the perimeter of the building, then the combined installation of funnels and compensators will be required.
Calculation of drainage funnels must be carried out based on their passport data, which contains information about geometric dimensions, method of fastening and throughput. The number of drainage funnels must correspond to the number of drainpipes in the entire drainage system.
Gutter materials
Manufacturers make gutters from various materials: PVC, metal, zinc, aluminum, copper, etc.
The choice of one or the other determines the quality and service life of the entire system. Plastic. Installation of a plastic drainage system is the most popular and attracts owners due to its cost. The use of modern high-strength polyvinyl chloride in the production allowed the gutters to withstand significant mechanical and chemical loads and the influence of UV rays. The advantages also include:
- Variety of colors;
- Possibility of manufacturing pipes of various sections (square, round, etc.);
- Poor adhesion of plastic to ice.
PVC products react quite significantly to temperature, changing their volume; at low temperatures they shrink and harden, and at hot temperatures they expand. However, this does not mean that the gutter will not function normally for its intended purpose.
Metal. Most often made of stainless steel, they are extremely durable; the effect of water on the material is not noticeable even after many years. A significant design disadvantage is weight. Therefore, installing such a gutter will be more difficult and more expensive than PVC models.
Galvanized. Proponents of galvanized gutter systems (often containing titanium, copper and aluminum) praise their sophisticated aesthetics. In addition, they can be used for up to 100 years and during this period do not require painting or repairs. Unfortunately, these models are quite expensive.
Aluminum. They are cheaper than metal and galvanized ones. A positive feature of the material is that it ensures a high water flow rate due to the slight roughness of the pipes. However, they are not recommended for use in buildings located near the sea due to their lack of salt resistance.
Copper. They have an unusual appearance and an impressive price, despite this they are durable - their service life is up to 300 years. Disadvantages include a limited color palette and easy corrosion.
Roof drains for flat roofs
Such drainage elements are made from a large number of materials. It can be either plastic or metal, and so on.
It is recommended to select elements based on the material from which the roof is made. For example, if the roof is made of metal, the funnels should be the same. If polymers are used at the base of the roof, it is recommended to use gutters made from polymer compounds.
The simplest funnel design has a side for receiving water, a glass and a cap. Each product must meet the following conditions:
- The installation location of the element with a layer of insulating roofing must be airtight. To achieve this effect, it is recommended to glue waterproofing to the side of the funnel itself.
- The drain cover must be removable. The glass can be a single device with a fixture.
- The cap must be tightly fixed to the seat in the system.
- To prevent debris from getting into the funnel, the funnel is protected with a special filter.
Main manufacturers
Among the popular manufacturers of funnels for water drainage, the following should be noted:
TechnoNIKOL
Offers high-quality water inlets with compression flanges, sheet catchers, heating capabilities and without them in various sections.
SK TUOTE OY (Finland)
It produces mainly polymer water receivers with different diameters.
Tekhnoresurs (RF)
It produces various versions of water receivers with filters, equipped with or without heating.
How is an external drain constructed?
The external drainage system includes several elements, the exact number of which depends on the roof area:
- Gutter It looks like a suspended channel that transports water towards the funnel.
- Drainage funnel. With the help of this element, the horizontal and vertical sections of the drainage system are connected.
- Pipe. May have different diameters. Serves to transfer water to a collection container.
- Connectors. Vertical, horizontal and zig drainage systems can be equipped with various connecting elements. For their fixation, the system includes brackets.
- Contours. They make it possible to bypass various niches, ledges, columns, etc.
When calculating the side drainage, the following conditions should be taken into account:
- If the length of the gutter is within 10 meters and there are no obstacles to linear expansion, one funnel is sufficient;
- If the length is longer and/or there are obstacles to linear expansion, an additional compensating funnel is installed at the end of the slope.
Tags: drainage, calculation, section, pipe
« Previous entry
Content
- Selection of the optimal manufacturing material.
- Construction of a drainage wiring diagram.
- Calculation of the number of required parts.
Galvanized steel products should not be considered for installation on a residential building. The low cost of materials will not make the installation cheaper: installation will take a lot of time, and it is almost impossible to hermetically assemble homemade parts. Steel coated with a thin protective layer of galvanization will begin to rust after 2–3 years, and a new system will have to be installed. Modern budget gutters are made by:
- Made of metal with a polymer protective coating.
Aesthetic appearance and reasonable price: advantages of plastic gutters
Inexpensive plastic parts can last for decades without breaking. The components are made from polyvinyl chloride, a polymer based on acrylic resins. Gutters and pipes are ultra-light weight, easy to transport and do not require special skills for installation.
Plastic system elements
Plastic systems are perfect for installation on low one-story residential buildings, outbuildings, garages, and country houses. Mounted on old roofs with fasteners on a wind board. Manufacturers recommend PVC for organizing drainage on the roofs of attic floors: plastic trays are almost silent, unlike metal ones.
The material is quite fragile and not durable. Susceptible to mechanical damage, especially at low air temperatures. Therefore, when choosing a system for installing a plastic roof drain in a region with a cold climate, it is worth considering the simultaneous installation of a heating cable. The roof covering is equipped with the mandatory presence of snow retainers in order to reduce the risk of gutter failure when snow melts.
Gutters made of metal with a polymer layer belong to the middle price category. The parts are made from a steel alloy; several layers of polymer are applied on top to protect the box from exposure to water. When calculating a drainage system, you should also take into account the cost of installation: it is difficult to install metal-plastic parts yourself. Gutters are quite heavy; it is impossible to install trays at height alone.
Metal-plastic drain: details
Metal-plastic is the best choice for:
- Drainage assemblies for country cottages of large area and height.
- Installation of trays on rafter boards - it is allowed to increase the interval between fastenings to 90 cm.
- Installations in difficult climatic conditions.
Only after selecting the manufacturing material do they begin to design the circuit. To calculate the roof drainage system without errors, you need a roof plan. To design, you will have to take simple measurements, so you will need: a long tape measure, a calculator and about an hour of time.
Drain installation diagram
Conventionally, the entire roof drainage system can be divided:
- Roofing horizontal lines, the main function of which is to collect water flowing from the roof.
- Vertical gutters receiving water from trays.
- Drainage system - above-ground or dug into the ground rainwater receivers connected to the bottom of the drain.
Marking lines for roofs of different shapes
To correctly calculate the drainage system, it is necessary to determine the diameter of the pipes and the cross-section of the trays. The correctly selected size of the parts is a guarantee that water will not begin to overflow over the edges of the gutter during heavy rain.
Calculation of roof slope area
Determine the standard size of products based on the following indicators:
- The area of the roof slope served.
- Average rainfall in the region.
Do I need to calculate the total area of the entire roof? In fact, it is enough to navigate according to the plan and select the largest overhang for measurements. The length of the slope is multiplied by the height. According to the standards, when calculating the diameter of products, it is necessary to take into account the angle of inclination of the roof overhangs and the amount of precipitation drained from the roof. But practice shows that when choosing the diameter of components, you can rely on the manufacturers’ recommendations, calculated based on the roof area:
- If the slope area is up to 50 m2, the cross-section of the tray is 100 mm, the diameter of the outlet is 75 mm.
- Area up to 100 m2. Gutter cross-section – up to 125 mm, pipe diameter – 87 mm.
- For roofs with an area of up to 200 m2, the cross-section of the trays is up to 150 mm, the diameter of the drain is 100 mm.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Water heated floor screed thickness above the pipe
Standard sizes of drainage parts
The dimensions of trays and pipes are determined first of all; depending on the selected standard size, related parts will be selected: connections, adapters and fasteners.
Trays are installed along the bottom edge of each overhang. The protruding parts of the roof are equipped with separate lines:
- The lower edges of balconies and canopies.
Horizontal lines on the roof of a complex shape
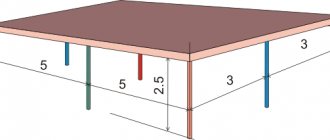
How to calculate the length of the gutter lines of a drainage system? This is the easiest planning stage. It is enough to measure the length of the edge of each overhang. Add all the obtained values. The result is the total length of the horizontal drains.
It is a little more difficult to correctly determine the required number of branches - vertical risers.
Calculation of the number of drains
A simple way to calculate vertical pipes of a drainage system:
- If the length of horizontal lines does not exceed 10 m, then it is planned to install 1 drain for each line.
- If the length of the gutter installed along one roof overhang exceeds 12 m, 2 outlets per gutter are calculated.
Connecting 2 gutters into a common pipe
For roofs of complex shapes, additional outlets are calculated for each projection if it is not connected by corner adapters to the gutters of other sections. For each line with plugs - 1 drain. When short sections are close, it is rational to connect 2 nearby sections into 1 riser by installing a splitter and bends.
When calculating the number of parts, the amount of materials for each part of the drainage system is determined separately: gutters, downpipes and ground drainage outlets.
Basic details of horizontal lines:
- Moldings: trays.
- Connectors: for gutters, funnels, corners, projections.
Most manufacturers of plastic gutters offer gutters in a standard size: 3 m long. Some make trays 3 and 4 meters long. When calculating the drainage system, you should select the factory length so that there is no waste left from the cut gutters.
Plastic tray
For example, for a line of 10 m it is better to purchase, if possible, four-meter products. For two ten-meter gutters you will need 5 factory trays. One will have to be cut in half. There will be no waste.
For each line, 2 plugs are required - plastic or metal-plastic parts that cover the edge of the gutter.
Tray connector with rubber seal
The connecting parts are calculated based on the number of junction points of the gutters in the line. For a 10-meter line of 3 segments, 2 connections will be needed. Separately calculate the number of couplings for each horizontal section and corners. For convenience, the footage of the trays and the junction points where the couplings are planned to be installed are marked on the diagram.
In order not to make a mistake with the type of fastener, it is determined whether the drain will be installed on the roof under construction, or whether it is better to fix the gutters on the front board. In this case, the drainage can be installed after the roofing work is completed.
When installing a gutter on rafters or on rafter sheathing:
- Select long metal brackets with straight extensions, which are bent at an angle of 90° after installation.
Hook with extension
- Prefabricated parts with a mechanical adjustable extension are used.
If you plan to attach trays to a finished roof, then calculate the number of short holders - non-adjustable brackets.
How to calculate the fastenings of an under-roof drainage system? Depending on the type of fastener, the distance between adjacent hooks is determined. For short brackets, the maximum interval is 60 cm, for fastening metal-plastic trays to rafter sheathing or boards - up to 90 cm. You should not exceed the distance, saving on brackets: the trays can bend under the weight of snow.
Mounting methods
Kk – total number of hooks per 1 line of gutter with plugs
Ll – tray length in centimeters
Example: For a 10 m long gutter you will need: (1000 – 30)/60 = 16 hooks. 30 is the distance in cm from the edges to the installation point of the 1st bracket.
Distance between fasteners
Separately calculate the quantity for each gutter, the resulting values are summed.
The number of funnels when calculating a roof drainage system is easy to determine: for each planned drainage pipe - 1 funnel.
Funnels with horizontal connectors
It is important to choose the right funnel type. Plastic systems usually include funnels with horizontal connectors with seals. Such parts are much easier to install. When choosing hinged funnels with locks, you will have to cut holes in the gutter and seal the joint.
Hanging funnel with lock
Each of the funnels will have to be correctly connected to the pipe. At each point, 2 corner bends are installed, which are connected with a straight piece of pipe.
Connecting a funnel to a pipe
When connecting 2 lines of trays in one vertical line, 1 tee with a side outlet must be added to the funnel adapters.
Vertical section: design
To plan the vertical sections of the drain, calculate:
- Footage and number of pipes.
- Number of coupling connectors.
- Number of clamps - holders.
- Shape, type and number of drain outlets.
Accurately measure the distance from the edge of the roof to the blind area. From the obtained value it is necessary to subtract the height of the transition formed by the outlets from the funnels connecting the gutter to the pipe. As a result, the exact length of the pipe is obtained from the lower edge of the adapter to the ground surface.
Device
Drainage structures on flat roofs are equipped in two types:
Gravity
Sediment is collected and freely discharged through gutters installed with a slope. However, the pipes are not completely filled with water.
The main principle of their operation is the complete filling of the drainpipe with sediment, as well as the formation of a water column, originating at the water intake and ending near the external outlet of the flow
When the precipitation level decreases, liquid is forced to be sucked from the receiver into the riser. This method is considered more effective than gravity
, however, for it to work all the time, careful sealing of all joints is required
due to the exact match of the diameter
of the pipes used, as well as the use of those materials with which high-quality sealing can be achieved.
A characteristic feature of siphon structures is the presence of flow stabilizers. They help direct water and prevent air from entering the system, which is usually installed using the butt welding method.
The advantages of this design are obvious and are that:
- with light precipitation it can work as a gravity flow , and if there is an excess of melt or rain water, it perfectly eliminates it;
- its installation requires fewer water inlets and risers than for gravity flow, and the pipes used can be smaller in cross-section, which reduces
costs; - Due to the rapid movement of sediments, the system can self-clean.
On a flat roof, the main function of collecting and receiving water is assigned to the funnel. Typically such a device consists of:
- a cover covering the top of the product;
- grates that protect the drain from contamination by foreign objects and debris;
- a ring that makes the funnel sealed;
- water receiving bowl, from where water is redirected to the drain;
- release - a special fitting located horizontally or vertically.
The kit also includes an oil seal that helps seal the outlet with the drainpipe, a flange or bolt with which the water receiver is secured.
There are different types of drain funnels for flat roofs:
Bell-shaped
With a convex, cap-like mesh that prevents various types of contaminants from entering the watercourse. The device performs well with large volumes of water flows.
Mounted flush with the roof covering, they are used primarily on roofs lined with paving slabs or asphalt concrete.
Heated
With a special electrical cable inside, which warms the structure in winter and protects it from ice.
One or two stage
The former are suitable for roofs with roll polymer or bitumen coating, the latter - on non-ventilated roofs.
There are also water inlets with a rebate, which is a universal fastener. The fold is suitable for all types of bases. It is selected depending on the type of roofing cladding.
Water inlets have different types of outlet: vertical - suitable for a regular flat roof, horizontal - works well on roofs that do not have an attic, hinged - making it possible to connect to a storm drain at any angle up to 90 degrees.
Rules for installing drainage funnels
Not only appropriate equipment is required, but also certain skills, as well as strict adherence to installation rules:
- in order to ensure perfect tightness of the junction of the water inlet with the roof covering in the connecting places, it is necessary to lay additional pieces of waterproofing material, attaching them directly to the side of the storm funnel;
- if the roof has two waterproofing layers, the edges of the water receiver are placed between them;
- the cap must be well secured;
- To prevent the water in the riser from freezing, it is important to take care of heating the funnels.
Flat roof drains: installation and heating
Today, buildings with a flat roof, familiar to industrial and multi-story buildings, are increasingly found in private housing construction. Such a roof makes it possible to obtain additional space for arranging a terrace, sports ground, swimming pool, or garden. To ensure the protection of the roofing covering from destruction under the influence of moisture, it is important to provide an effective system for draining melt and rainwater, and take care of the correct installation and heating of water intake funnels.
Selecting a drain funnel
Funnels for arranging internal drainage are made of polymers, metal or a combination of materials. When choosing a product, it is important to consider the type of material that is used as roofing on the roof. Metal funnels are used for installation on roofs covered with sheet metal. Polymer products are suitable for installation on soft roofs.
A flat roof drain can be round or rectangular, with a horizontal or vertical outlet. The choice depends on the installation location and roof features. The products differ in design, but in any case it is possible to rigidly attach the funnel to the base of the roof and ensure reliable waterproofing of the fastening point.
Funnels with a metal flange are fixed using a clamping method using stainless steel fasteners. Funnels with a polymer flange equipped with a sealing collar are attached using an adhesive method.
The drainage system must be protected from clogging. To prevent large debris from entering the drain, funnels are equipped with protective covers or nets. Products with flat covers with slots are used on roofs in use. The lids can support the weight of a person. If you plan to create a “green” roof, it is best to use funnels with a leaf filter in the form of a mesh cap
.