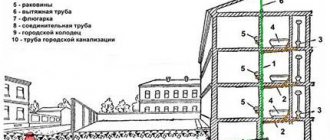
Modern private houses, country houses, as well as many apartments are difficult to imagine without an autonomous water supply system. It provides for the presence of a reservoir in which water is accumulated and pressure is created to the required value. One of the main elements of such a system is the water valve. This is a small passage channel mounted into the pipe contour.
Types of check valves
Depending on the type of shut-off element, all check valves are divided into several categories:
- Ball. The locking element is a plastic or metal ball supported on top by a spring. Under the influence of liquid pressure, the spring is compressed, lifting the ball and allowing liquid to flow into the channel.
- Rotary. The shutter is made in the form of a folding flap. It opens as the fluid flow moves and closes when it weakens or stops. They are often used in metal pipeline networks that take water from a well or borehole, since they are characterized by low sensitivity to environmental pollution.
- Disk. The permeability of the pipeline is regulated by a steel disk that can rotate around its axis. In everyday life, their use is justified in networks made of metal-plastic, where contamination of the working environment is minimal.
- Lifting. In this type of valve, the valve can be moved up or down by a spring. The compression and expansion of the spring occurs under the pressure of the water pressure. It can only be located on horizontal sections of the pipeline, and the valve axis must be oriented strictly in the vertical direction. The advantage of this type of valve is the ability to repair it without removing it from the system.
Based on the method of connecting the check valve to the pipeline, the following types of devices are distinguished:
- Wafer. Mounted between two flanges located at adjacent ends of the pipeline. The valve itself does not have fastening elements. Fixed with bolted connections.
- Flanged. They are equipped with special connecting elements with sealing gaskets. Like wafer-type ones, they are more often used on large trunk networks.
- Couplings with thread. More often used in pipeline networks of small diameters. They are secured using threads located on the outer or inner surface of the couplings.
- With welding fastening. Installation of such valves is carried out by welding. The connection is permanent, so locking elements of this type are used quite rarely, mainly for networks with aggressive working environments.
In addition, check valves can be made of steel, cast iron, brass, polypropylene, etc. In this case, the component parts can be made from different materials. For example, a stainless steel or brass body, a plastic shutter and a steel spring.
Cast iron products are rarely found in everyday life, due to their susceptibility to corrosion and the gradual accumulation of deposits. Their main area of application is main pipelines. Stainless steel devices are almost completely devoid of such disadvantages, but have a fairly high cost.
Polypropylene products are intended for installation in pipeline networks mounted from the same material. Installation is carried out using polyfusion welding.
Purpose and principle of operation
The main function that a water check valve performs is that it protects the water supply system from critical flow parameters of the liquid transported through the pipeline. The most common cause of critical situations is stopping the pumping unit, which can lead to a number of negative phenomena - draining water from the pipeline back into the well, spinning the pump impeller in the opposite direction and, accordingly, breakdown.
The installation of a check valve on the water allows you to protect the water supply system from the listed negative phenomena. In addition, the water check valve prevents the consequences caused by water hammer. The use of check valves in pipeline systems makes their operation more efficient, as well as ensures the correct functioning of the pumping equipment with which such systems are equipped.
Operating principle of a check valve
The principle of operation of the check valve is quite simple and is as follows.
- The flow of water entering such a device under a certain pressure acts on the locking element and presses the spring, with the help of which this element is kept closed.
- After the spring is compressed and the shut-off element is opened, water begins to move freely through the check valve in the required direction.
- If the pressure level of the working fluid flow in the pipeline drops or the water begins to move in the wrong direction, the spring mechanism of the valve returns the shut-off element to the closed state.
By acting in this way, the check valve prevents the formation of unwanted backflow in the piping system.
Spring type check valve with nylon spool plate
When choosing a valve model installed on a water supply system, it is important to know the regulatory requirements that manufacturers of pumping equipment impose on such devices. The technical parameters by which a check valve for water is selected in accordance with these requirements are:
- working, test and nominal closing pressure;
- diameter of the landing part;
- conditional capacity;
- tightness class.
Information on what technical requirements a water check valve must meet is usually contained in the documentation for the pumping equipment.
Single-disc coupling check valve
To equip domestic water supply systems, spring-type check valves are used; the nominal diameter is in the range of 15–50 mm. Despite their compact size, such devices demonstrate high throughput, ensure reliable operation of the pipeline, low noise and vibration levels in the pipeline system on which they are installed.
Another positive factor of using check valves in a water supply system is that they help reduce the pressure created by the water pump by 0.25–0.5 Atm. In this regard, a check valve for water allows you to reduce the load both on individual elements of pipeline equipment and on the entire water supply system as a whole.
Installation location
Sewer and water systems are not the only places where installing a valve is a necessity. Other areas are:
- Autonomous heating system circuit. The rooms where heating radiators or heated floors are located differ radically in hydraulic and pressure indicators, and therefore require the installation of automatic shut-off valves. The device fits in front of the boiler and allows you to balance the technical indicators.
- Water heater inlet. A check valve installed in front of the boiler prevents the hot water mass from moving back into the cold water pipeline.
- Submersible pumps. If the water supply system is connected to a well or borehole, it is important to install a submersible pump. Its main task is to lift water masses from depth and transport them under pressure to the house. When there is a power outage, the pumped water naturally flows into the pressure tank. To avoid this, a shut-off valve must be installed in front of the pump.
- In front of the water flow control meter. All metering devices, in particular the household water meter, are especially sensitive to disturbances and changes in water supply. Water hammer has a negative effect on the device, up to its failure. Also, the locking device prevents the turbine from turning in the opposite direction.
The safety valve does not allow reverse circulation of water in any of the cases described above.
Valve device
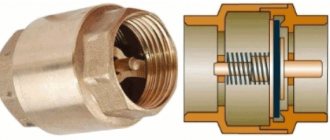
Standard valve models are formed by two cylinders perpendicular to each other, which are connected in such a way that a single cavity is created. The ends of these cylinders have different outputs - one is connected to the pump pipe or another water supply channel, and the second is plugged. As a result, a controlled cavity is created, the locking mechanism of which regulates the passage of water flow in one direction. Again, there may be different principles for the operation of this control system, but the standard is considered to be an operating mode in which the open valve condition will correspond to normal operation of the system. Of course, the device parameters may be different. For example, there is a check valve for a water pump provided by a hydraulic accumulator. The design of such models is specifically focused on the possibility of integration between the pumping station and the storage tank, which insures the equipment against water hammer.
Types of check valves
A water check valve may differ in design, material of manufacture, installation features and dimensions. Let's try to classify them according to these distinctive features:
By type of locking element
- lifting type. The shutter in such a device moves up and down. When water flows from the pump, the valve opens, and when the pressure in the line drops, the valve returns to the closed position under the action of a spring;
- rotary type. The shutter in such a valve has the form of a flap, which opens when the water moves, and closes under the action of a return spring when the pump is turned off.
The photo shows a rotary type check valve for water
- ball type. The shutter in the check valve is a ball that blocks the passage. The ball is supported by a spring. The water pressure lifts the ball, which moves, and allows water to flow into the channel;
- wafer type. It is divided into disc and bicuspid. A disc check valve for water has a disc valve that can move along its own axis under the action of a spring attached to it. In a double-leaf reverse valve, the shutter consists of two connected flaps that can fold when water passes through, and close when there is no water.
Double-leaf water return valve
According to the material of manufacture
- made of brass. This is a reliable, corrosion-resistant material that is durable and easy to maintain. It is considered an ideal material for household use;
- made of cast iron. This material is used relatively rarely, as it is susceptible to corrosion and gradual accumulation of deposits. Cast iron valves are used on large diameter pipelines. Cast iron valves are not used in everyday life;
- made of stainless steel. They are devoid of almost all disadvantages. They are durable, resistant to corrosion and aggressive substances, and durable. The price for a stainless check valve for water is the highest, but the quality of such a product is always at its best.
In most cases, the components of a check valve are made of different materials. So, the body can be brass or stainless steel, the shutter is usually plastic, and the spring can simply be steel or stainless. Therefore, when purchasing, immediately ask what materials were used in the manufacture of the valve.
By mounting method
- coupling fastenings. The vast majority of check valves are attached in this way. For fastening, 2 threaded transitions are used. Their diameter can be completely different, depending on the diameter of the pipeline;
- flange mountings. They are attached to pipelines using flanges. These are predominantly cast iron valves used on pipelines of very large diameters;
- Wafer mounts. The valves are mounted between two flanges, which are tightened with bolts. Their use is also limited to pipelines of large diameter.
To size
- standard valves. Used on most pipelines;
- miniature products inserted inside water meter outlets. They are used if there is no space on the pipeline to install a standard check valve;
- small valves installed at the outputs of meters;
- Large cast iron valves installed on pipelines for public use and industrial purposes.
Types and differences of designs
The tasks of all types of water valves include simplifying plumbing work and protecting against pressure drops in the pipeline, in particular if the operation of the pump is disrupted. In addition, each individual type also has specific tasks, as it is needed in the water main. There are several varieties that make the water check valve multifunctional:
Types of water check valves
- devices with a locking mechanism are divided into ball disk, leaf, spool;
- divided by type of fixation: wafer, flange, coupling;
- According to the speed of shutting off the water, the valve can be either slamming or smooth.
Each option has its own individual characteristics, which are important to consider when purchasing. So, a ball valve is a ball spring mechanism
The disc type valve contains a special disc in its structure. Both of these designs are capable of working with the highest water pressure that is permissible for polypropylene pipelines at home. Often such a structure is installed after a pump from a well or other source. Look at the photo to see what the device looks like
So, a ball valve is a ball spring mechanism. The disc type valve contains a special disc in its structure. Both of these designs are capable of working with the highest water pressure that is permissible for polypropylene pipelines at home. Often such a structure is installed after a pump from a well or other source. Look at the photo to see what the device looks like.
Ball check valve for water
The flap device can be used exclusively in pipes with low pressure; spool options are characterized by a spool design, which is the main working element. All these devices are made of brass or polypropylene, and are mainly installed before and after the meter.
A wafer check valve for water is installed in home pipelines strictly using outdated technology, while flanged and coupling versions are bolted or threaded for normal fixation. If necessary, a ball spring operating mechanism can also be used.
The slamming mechanism works instantly when water enters, while the smooth mechanism works somewhat slower, but at the same time maintains a longer service life. The photo will tell you how the mechanism works.
Check valve with slam mechanism
Each type of return device can be used both for a water pump and for placement in a working pipeline. Moreover, all valves have separate functional features and are fixed outside the meter.
Product sizes
Speaking about the dimensions of a check valve, first of all, the nominal bore and nominal pressure of the device are distinguished. The nominal diameter is fixed at values from 10 to 400 mm, inclusive. There are models of 15, 20, 25, 65, 80 mm, and with other passage diameters. Conditional pressure refers to the amount of water pressure in the circuit at which the check valve opens. Here the values range from 0.25 MPa to 2580 MPa. Among the intermediate values, there are: 6.3 (MPa), 10 (MPa), 16 (MPa). It is worth noting that check valves differ in the range of operating temperatures, among which there are models capable of operating with liquid from -60 to 600 degrees Celsius.
Spring coupling check valve: types by material
Products can be made from different materials:
Brass valve body
Cast iron body
Stainless steel body
Universal reverse type device with strainer
Differences in mounting method
Most devices are attached using a coupling. This requires two threaded transitions, which are selected according to the size of the pipeline. Flange type fastenings can also be used. Most often they have cast iron elements of large diameter. Such flanges are tightened with bolts. This type of fixation is also relevant for small products when there is no room on the pipe for other fastening.
Flange connection is one of the best options
The spring clutch check valve is the most commonly used. It is used in apartments for installation on a pipeline or water heater; such products are installed after the meter, which does not allow it to spin in the other direction. Devices of this type prevent the pipes from emptying if water drains in the riser.
The structure of the spring mechanism: it consists of a brass body, which can be disassembled into two parts. A movable spool is placed between the halves. It is usually made of plastic. This spool is driven by water pressure and a spring.
Spring elements: body and inner part
Related article:
Installation and installation procedure
In order to answer the question of where the valve is installed, you should pay attention to its design features and the availability of free space in the intended mounting area of the device body. The rather delicate moment associated with disconnecting the entire access riser must also be taken into account (this applies to the case when it is planned to install a check valve before the inlet valve of the water supply network)
In order to avoid the need to coordinate this issue with neighbors, it is recommended to install the valve device on the water immediately after the valve distributor. The main thing that needs to be taken into account during installation is the direction of normal movement of the drains, which is usually indicated by an arrow marked on the side of the body. In this case, the valve is fixed on the pipe in such a position that the arrow coincides with the direction of the natural flow of waste.
Other features of installing a check valve can be presented as follows.
Firstly, the installation of a plastic non-return valve is carried out according to the classical scheme, which involves the use of a standard socket and sealing gasket for this purpose. The working section of such a pipe is joined to the socket with the valve, and the place where they meet is additionally treated with silicone for reliability.
Secondly, for the installation of cast iron products, special sealing rubber bands must be used, complete with bolts that reliably tighten the mounting metal plates. At the same time, there are also models on sale equipped with a bell-shaped expander, designed for traditional tow while simultaneously sealing the resulting seam.
When choosing a check valve model suitable for given conditions, special attention should be paid to the presence of a special cover on the body that provides access to the internal parts.
During installation, you should take into account such an important detail as the location of the inspection hole. For ease of maintenance, free access must be provided to it, allowing, if necessary, to check the internal mechanism or carry out its control cleaning.
Options for working connection schemes
Heating systems are very diverse and the presence of a check valve is not necessary in all of them. Let's consider several cases when its installation is necessary. First of all, a check valve must be installed on each of the individual circuits in a closed circuit, provided that they are equipped with circulation pumps.
Some craftsmen strongly recommend installing a spring-type check valve in front of the inlet pipe of the only circulation pump in a single-circuit system. They motivate their advice by the fact that in this way pumping equipment can be protected from water hammer.
This is in no way true. Firstly, installing a check valve in a single-circuit system is hardly justified. Secondly, it is always installed after the circulation pump, otherwise using the device loses all meaning.
If two or more boilers are included in the heating circuit, the occurrence of parasitic flows is inevitable. Therefore, connecting a check valve is mandatory
For multi-circuit systems, the presence of a reverse-acting shut-off device is vital. For example, when two boilers are used for heating, electric and solid fuel, or any others.
When one of the circulation pumps is turned off, the pressure in the pipeline will inevitably change and a so-called parasitic flow will appear, which will move in a small circle, which can lead to trouble. It is impossible to do without shut-off valves here.
A similar situation arises when using an indirect heating boiler. Especially if the equipment has a separate pump, if there is no buffer tank, hydraulic arrow or distribution comb.
Here, too, there is a high probability of a parasitic flow, to cut off which a check valve is needed, which is used specifically for arranging a branch with a boiler.
It is mandatory to use shut-off valves in systems with bypass. Such schemes are usually used when converting a scheme from gravitational fluid circulation to forced circulation.
In this case, the valve is placed on the bypass parallel to the circulation pumping equipment. It is assumed that the main mode of operation will be forced. But if the pump is turned off due to lack of electricity or breakdown, the system will automatically switch to natural circulation.
When installing bypass units for heating circuits, the use of check valves is considered mandatory. The figure shows one of the possible bypass connection options
This will happen as follows: the pump stops supplying coolant, the check valve actuator unit ceases to experience pressure and closes.
Then the convection movement of the liquid along the main line resumes. This process will continue until the pump starts working. In addition, experts suggest installing a check valve on the make-up pipeline. This is not necessary, but highly desirable, since it allows you to avoid emptying the heating system for a variety of reasons.
For example, the owner opened a tap on the make-up pipeline to increase the pressure in the system. If, by an unpleasant coincidence, the water supply is cut off at this moment, the coolant will simply squeeze out the remaining cold water and go into the pipeline. As a result, the heating system will be left without liquid, the pressure in it will drop sharply and the boiler will stop.
In the circuits described above, it is important to use the correct valves. To cut off parasitic flows between adjacent circuits, it is advisable to install disk or petal devices. In this case, the hydraulic resistance will be lower in the latter option, which must be taken into account when choosing.
In heating systems with natural coolant circulation, the use of spring check valves is impractical. Only paddle rotators can be installed here
To install a bypass unit, it is preferable to choose a ball valve. This is due to the fact that it provides almost zero resistance. A disc-type valve can be installed on the make-up pipeline. This should be a model designed for fairly high operating pressure.
Therefore, a check valve may not be installed in all heating systems. It is necessarily used when installing bypasses of all types for boilers and radiators, as well as at pipeline branch points.
Types of check valves, their design and operating principle
The check valve device is simple. There is a slightly tapered seat and a locking element. With the “correct” flow, the shut-off element is pushed away from the bottleneck. As soon as the direction changes, he presses against the saddle, blocking the passage. By the way, there should be an arrow on the body that indicates the “correct” direction of water movement.
How a water check valve works and how it works
Basically, check valves are distinguished by the type of shut-off element. He can be:
- ball type (ball);
- disc-shaped;
- disk;
- petal or bivalve.
In a ball valve, the ball is “free floating”. It is not attached to anything and is transported by water. Quite a reliable system. It’s just that it doesn’t always cover the saddle tightly enough, so it’s used quite rarely.
Types of check valves for water
Disc-shaped ones can be lifting or rotating. Rotary, as well as ball, open and close under the influence of water flow. Lifting ones have a spring-loaded rod. In the “normal position” the passage is closed; when water pressure appears, it presses the spring, pushing the locking element upward.
The most common type in home water supply systems is the disc check valve. It differs in that fittings of this type can be small in size. And the design is simple and reliable. The locking disc is placed across the flow and is pressed against the seat by a spring. Water squeezes the spring, clearing its way.
A check valve is a device to prevent the reverse movement of the transported medium
There is also a two-leaf valve for water. Its locking element consists of two halves of the disk (petals), which are fixed to the axis. Hence another name for this model - petal. They are held closed by springs. The water entering the water supply system presses them back, folding them and pressing them against each other. This type has the least hydraulic resistance. In some cases (with a long suction line) this may be important.
Warm water floor mixing unit
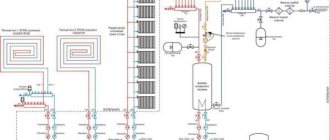
Now let's look at a device such as a mixing unit for a heated floor or, simply, a mixer for a heated floor (it is also called a mixing module).
Purpose of the mixing unit
Why do you need a mixing unit, you ask?
I’ll answer with a question: what to do if the temperature of the coolant leaving the boiler is 90 degrees, but in a heated floor you need no more than 55 degrees?
The mixing unit for heated floors is used to solve this problem.
Operating principle of a check valve
First of all, it should be noted that check valves are not installed “just in case,” but only if necessary, if there is no other technical solution. This is due to the fact that the elements often have considerable hydraulic resistance, depending on the design. This introduces some restrictions when using check valves for heating with natural circulation. The reason is too low coolant pressure in the system.
Despite the differences in design, most products are equipped with one key part - a spring. It is an actuator that closes the valve when normal conditions change; this is the principle of operation of the check valve. The force expended to overcome the elasticity of the spring determines the magnitude of the hydraulic resistance of the mechanism. For circuits with different operating parameters, products are selected that have the appropriate elasticity and massiveness of the spring.
What does the spring act on? Its task is to keep the locking device closed; this is its normal state. Then the fluid flow flowing from one side can overcome the elastic force of the spring, open the obstacle and move further along the pipe. An attempt to change the direction of the flow and flow in the other direction will lead to nothing - the shut-off device will slam shut, relying on the tide in the body. In this place there is a sealing element that makes the check valve in the heating system completely sealed.
Shut-off valves intended for use in heating circuits are made from the following materials:
- gray cast iron;
- steel;
- brass;
- stainless steel.
Connection type
When choosing the type of device installation, it is important to pay attention to the advice of experts in order to avoid mistakes and not disrupt the operation of the system:
- Often there are parasitic fluid flows in the system. They involve the installation of a device with high hydraulic resistance, such as a reed check valve. The reed valve must be mounted strictly horizontally, otherwise its valve will not work, which promotes the outflow of water in the opposite direction.
- If a bypass assembly is provided, it is best to use a ball check valve here, since its hydraulic resistance is zero.
- If you are going to install a check valve at the charging point of the heating system, then it is better to install a device with a poppet valve designed to work with high fluid pressure.
- Give preference to modern types of devices, which include check valves in brass and stainless steel housings.