Register Login
Publication date: June 10, 2019
The constant increase in heating costs forces us to look for alternative ways to obtain thermal energy and hot water. If you have an unnecessary refrigerator at your disposal, you can solve the problem at minimal cost, namely, make a heat pump. It does not require expensive fuel, has low energy consumption and at the same time copes well with heating rooms in the cold season.
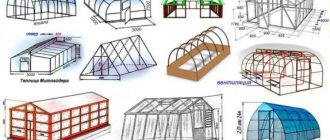
Types of heat exchangers
In the designation of the type of heat exchanger of a heat pump, the first indicator determines the method of constructing the external circuit of the heat supply system, and the second - the design of the internal circuit.
"Water - water"
In heat exchangers of this type, heat is taken from water bodies (well, river, lake, etc.), solar energy or other objects. A coolant—water or another liquid—circulates in the primary circuit. Circulation is carried out by creating pressure through the installation of a pump.
The circuit can be closed or open; which option to choose is determined by the type of coolant. In the heat pump, in the internal circuit, freon circulates, which, receiving energy from the external circuit, evaporates, enters the condenser, where it transfers the resulting heat to the consumer’s coolant.
"Water - air"
In heat exchangers of this type, the energy collected in the external circuit, in which liquid (water or other energy carrier) circulates, enters the heat exchangers of the heat pump, where it is transferred to the indoor air.
"Air - air"
In this type of heat exchanger, the external circuit is located on the outside of the building; it is the evaporator in this pump design. The heat from the outside air heats the refrigerant, which evaporates. Then, passing through the compressor, it is compressed and supplied to the indoor unit - a condenser, which is located inside the building. The condenser gives off heat to the air inside the room in which it is located, and the refrigerant is again supplied to the evaporator.
"Air - water"
In this type of heat exchanger, thermal energy is taken from the outside air. The air enters the compressor, where its temperature rises under the influence of pressure, after which it enters the heat exchanger. In the heat exchanger, the supplied air is condensed and energy is transferred to the energy carrier of the consumer’s heating system.
"Earth - Water"
Heat exchangers of this type are based on receiving energy from the earth and transferring it to consumers. Brine (antifreeze) circulates in a closed external circuit located below the freezing level. Circulation is carried out by installing a pump. The brine enters the heat pump's condenser, where it transfers the resulting energy to the refrigerant, which in turn transfers it to the consumer's heating system by condensation in the pump's heat exchanger.
"Earth - Air"
In heat exchangers of this type, the thermal energy obtained by the brine circulating in the external circuit, which is located under the surface of the earth, is transferred in the heat exchanger chambers to the air inside the room.
Let's make the refrigerator body
Avoid using polyurethane foam: you will need special clothing. Buy a can of insulation (spray foam). There will be no need to look for a respirator. Polyurethane foam expands and gains volume relatively slowly. More airy material means better insulation.
To insulate with polyurethane foam, you will need to make a box with double walls and a similar door (lid). Not an easy task, since you need to fill the bottom with insulator. Decide for yourself how best to proceed; we recommend leaving technological holes in hard-to-reach places. After the polyurethane foam has hardened, cut off excess and patch unnecessary holes. The problem of insulation is being solved. Avoid contact of the polymer with the product.
DIY refrigerator
Polyurethane foam will seal the cracks where the Peltier elements enter the chamber. Ideal insulation, which is difficult to achieve in any other way. Peltier elements are expensive. The refrigerator should be smaller and better insulated. We suggest paying attention to Penofol with double-sided foil. Availability of material, check with the manufacturer or dealers for details, take it with double-sided foil, ignoring the complexity of installation. The material can be glued, avoid nailing, it will create heat leakage bridges.
We finish the outside of the box with polyurethane foam, eliminating the slightest cracks. Peltier elements do not fit inside the compartment. They are fenced off with a gasket of food-grade aluminum. It will prevent contact of food with polyurethane foam, as in a factory refrigerator. We recommend using a regular, passive thermostat that measures pressure. You can buy it on the market at the request “refrigerator thermostat”, remove it from old equipment. It looks like a small metal cube with a long thin tube, the end of which must be attached to the cold side of the Peltier element. Select the position of the sensitive area of the sensor so that the modes are maintained. The advantage is that such a device turns off the power at the right moment and is itself configurable. A purely passive element, as mentioned above, consisting only of a membrane and a contact group. The design is sealed, do not worry too much about the device. The whole story is about how to make a refrigerator with your own hands. It is better to store food on shelves, with the insides lined with food-grade aluminum. Avoid plastic.
Don't forget the grounding; it won't hurt to install thermal fuses in the right places. The story showing how to make a refrigerator with your own hands is over. We hope the text was useful. We believe that every reader will be able to make a refrigerator with their own hands.
The owners of country houses have always been sensitive to the issue of hot water supply and heating.
Installing a gas, electric or diesel boiler makes it possible to heat a country house and supply it with hot water and heat, but nowadays there are alternatives to the heating we are used to.
One such alternative is a heat pump. This is quite an expensive pleasure, but you can make it yourself. We'll talk about how to do this in this article.
How to make a DIY heat pump from an old refrigerator
Before you begin manufacturing a heat pump, you need to select a heat source and resolve the issue with the installation’s operating diagram. In addition to the compressor, you will need other equipment, as well as tools. Making diagrams and drawings. To install a heat pump, you need to make a well because the energy source must be underground. The depth of the well should be such that the ground temperature is at least 5 degrees. Any body of water is also suitable for this purpose.
The designs of heat pumps are similar, so regardless of what the heat source is, you can use almost any circuit found on the network. When the scheme is selected, it is necessary to make drawings and indicate in them the dimensions and joint locations of the nodes.
Since it is quite difficult to calculate the power of an installation, you can use average values. For example, for a residential area with low heat loss, a heating system with a power of 25 W per square meter will be required. meter. For a building that is well insulated, this value will be 45 W per square meter. meter. If the house has sufficiently high heat losses, the installation power should be at least 70 W per square meter. meter.
Selecting the required parts. If the compressor removed from the refrigerator is broken, then it is preferable to purchase a new one. It is not recommended to repair an old compressor, as this may negatively affect the operation of the heat pump in the future.
A thermostatic valve and 30 cm L-shaped brackets will also be needed to make the device. Additionally, you will need to purchase the following parts:
- sealed stainless steel container with a volume of 120 liters;
- plastic container with a volume of 90 liters;
- three copper pipes of different diameters;
- metal-plastic pipes.
To work with metal parts you will need a welding machine and a grinder.
Assembling components and installing a heat pump
First of all, you should install the compressor on the wall using brackets. The next step is working with the capacitor. The stainless steel tank must be divided into two parts using a grinder. A copper coil is mounted in one of the halves, then the container must be welded and threaded holes made in it.
To make a heat exchanger, you need to wind a copper pipe around a stainless steel container and secure the ends of the turns with slats. Attach plumbing transitions to the terminals.
It is also necessary to attach a coil to the plastic tank - it will act as an evaporator. Then secure it to a section of the wall using brackets.
As soon as the work with the components is completed, you need to select a thermostatic valve. The structure should be assembled and the system should be filled with freon (grade R-22 or R-422 is suitable for this purpose).
Connection to the intake device. The type of device and the nuances of connecting to it will depend on the circuit:
- "Water-earth". The collector should be installed below the ground frost line. It is necessary that the pipes are at the same level.
- "Water-air". Such a system is easier to install, since there is no need to drill wells. The collector is mounted anywhere near the house.
- "Water-water." The collector is made of metal-plastic pipes, and then placed in a reservoir.
You can also install a combined heating system to heat your home. In such a system, the heat pump operates simultaneously with the electric boiler and is used as an additional heating source.
It is quite possible to assemble a heat pump for heating a house yourself. Unlike purchasing a ready-made installation, this will not require large financial costs, and the result will definitely please you.
The principle of frost generation by a refrigerator
Before making a refrigerator yourself, review existing designs. Below we offer a short thematic excursion. We apologize for the lack of adsorption models, they also work on freon. There are hardly anyone capable of obtaining the necessary materials and substances to facilitate the implementation of the concept.
First, know: 99% of household refrigerators use freon. Devices based on Peltier elements can be found as car freezers. Electric current flows through the junction of two dissimilar semiconductors, resulting in cooling of one material. The other, on the contrary, heats up. The external radiator of a refrigerator based on Peltier elements requires intensive cooling. This is achieved by choosing a large-sized cut aluminum part, or by introducing a fan, forced airflow. We see the idea inside modern system units of personal computers.
Anyone who wants to make a refrigerator on their own can start here. Find a Peltier element for cooling the processor, preferably two or three. Actually, the detail is very interesting.
In hot weather, it easily brings the processor temperature to minus 10 degrees Celsius. Therefore, it is suitable as a cooler for a homemade device. The problem is limited to small volume. Think! The power of a typical processor is 80 – 100 W. Half is released by heat. Consequently, the Peltier element for cooling the processor is not so powerful (less than 100 W).
Let’s make a reservation right away: ice cream power (cooling capacity) and consumed from the outlet are two different things. Refrigerators have an efficiency of up to 200 percent. Applies to most types of climate control equipment:
The abilities of Peltier elements are not known for certain. Cooling capacity is not given. Peltier elements are designed for fixed power, the manufacturer offers to trust. There is only one problem: the rate at which the processor temperature drops cannot be used to judge the parameter; there are too many unknowns. Found on the website https://forum.sirius.dn.ua/ a figure showing the dependence of the cooling capacity of the Frost-72 Peltier element. The graph is linear and makes it possible to calculate the necessary parameters for creating a refrigerator with your own hands.
Dependence of the cooling capacity of the Peltier element
As the supply voltage increases to 16 V (maximum permissible), the cooling capacity increases in parallel. You can improve the result a little. Let's think about the performance of the Stinol 102 refrigerator:
- The cooling capacity of the refrigerator compartment is 75-100 W.
- The cooling capacity of the freezer is 100-120 W.
- Refrigerator compartment – 200 liters.
- Freezer compartment – 120 liters.
We see how many Peltier elements are needed.
Do not rush to add and subtract according to the numbers 75-100 and 100-120, cooling capacity depends on temperature. But what is ΔT - the temperature difference between the plates.
We will better remove heat from the hot side, and the Peltier element will work more efficiently. Be too lazy to take measures, the temperature difference will reach 68 degrees Celsius (12 volt power supply), cooling will stop. Consequently, we are powerless to predict in advance. Suppose the room temperature is 22 degrees Celsius, the refrigerator compartment is plus 5 degrees Celsius, with ideal cooling the power is 38 W. It’s easy to see: for Stinol 102 you will need at least two or three Frost 72.
As for the freezer, the power cannot be realized with any conceivable losses. An article on this site explains: the peak efficiency of the device is 62% (ideal case), creating a homemade refrigerator from the point of view of energy saving cannot be called a good idea. There is no need to refill freon, the system is silent. We will provide a brief calculation for those wishing to build a freezer. The temperature difference will be 22 - (-18) = 40 degrees, the power is 20 W. Buy 6 Frost 72 elements. Let's look at it in monetary terms.
Peltier elements Frost 72
According to the website https://www.chipdip.ru/, one Frost 72 Peltier element costs 1,500 rubles. Whether you need a freezer for 9,000 rubles (subtracting the cost of the box material), decide for yourself. You will need a thermostat. Plus of the device: it can work for heating. Just change the power polarity. A homemade refrigerator will become an air conditioner; you can heat food inside. Ideal for defrosting mode. By the way, the fact needs clarification. The Peltier effect is reversible. By passing current in the opposite direction, we achieve heating. The operating principle of the refrigerator is limited by the effect of lowering the temperature of one side of the Peltier element; the effect is reversible.
Principle of operation
All the space around us is energy - we just need to be able to use it. For a heat pump, the ambient temperature must be greater than 1C°. Here it should be said that even the ground in winter under snow or at some depth retains heat. The operation of a geothermal or any other heat pump is based on transporting heat from its source using a coolant to the heating circuit of the house.
Scheme of the device operation point by point:
- a heat carrier (water, soil, air) fills the pipeline located under the ground and heats it;
- then the coolant is transported to the heat exchanger (evaporator) with subsequent heat transfer to the internal circuit;
- in the external circuit there is a refrigerant - a liquid with a low boiling point under low pressure. For example, freon, water with alcohol, glycol mixture. Inside the evaporator, this substance is heated and becomes a gas;
- The refrigerant gas is sent to the compressor, compressed under high pressure and heated;
- hot gas enters the condenser and there its thermal energy passes to the coolant of the home heating system;
- The cycle ends with the transformation of the refrigerant into liquid, and due to heat loss, it returns back to the system.
The same principle is used for refrigerators, so home heat pumps can be used like air conditioners to cool a room. Simply put, a heat pump is a refrigerator with reverse action: instead of cold, heat is generated.
What is geothermal heating?
This is heat extracted from the earth or water. At certain depths of the soil, a constant positive temperature is maintained, and there are no differences even in severe frosts, the same with water. A person’s task is to take heat from the earth or water, sending it to ensure comfort in living rooms.
Geothermal heating is like a regular refrigerator, but in reverse - the system produces heat, not cold. The pump algorithm is built on the transfer of heat from a source with a small potential of thermal energy to the coolant, and soil or water act as active heat sources.
Advantages and disadvantages of the system
Geothermal heating has several advantages:
- The release of thermal energy is many times higher than the cost of electricity consumed by the pump.
- Environmental cleanliness and safety. The system does not emit harmful substances, there are no emissions or slag after fuel combustion.
- There is no need to purchase fuel or gas; the entire structure is built without the use of chemicals or other substances, so heating with earth or water heat is considered the safest.
- If the installation and operation technology is followed, the equipment and the entire heating system will last without technical support for at least 50 years.
- The heat pump operates silently, there are no acoustic effects.
Maximum economic benefit is achieved without additional investments. The user needs to purchase all the equipment once, configure the design and no longer have to interfere with the operation of the system. An additional advantage is the location of all elements outside the building - heating from earth or water does not require the placement of large installations in the house, so the method of extracting and supplying heat is suitable for houses of any size.
The disadvantage is the large amount of one-time costs for purchasing equipment, installing and putting the system into operation. To form the structure, a pump, a certain amount of materials, installation of an external manifold and an internal circuit are required.
Operating principle of an air-water pump
As already mentioned, the main source of thermal energy for installations of this type is atmospheric air. The fundamental basis for the operation of air pumps is the physical property of liquids to absorb and release heat during a phase transition from a liquid to a gaseous state, and vice versa. As a result of the change in state, temperature is released. The system works like a refrigerator in reverse.
To effectively use these properties of the liquid, a low-boiling refrigerant (freon, freon) circulates in a closed circuit, the design of which includes:
- electric compressor;
- fan-driven evaporator;
- throttle (expansion) valve;
- plate heat exchanger;
- copper or metal-plastic circulation tubes connecting the main elements of the circuit.
The movement of the refrigerant along the circuit is carried out due to the pressure developed by the compressor. To reduce heat losses, pipes are covered with a heat-insulating layer of artificial rubber or foamed polyethylene with a protective metallized coating. Freon or freon is used as a refrigerant, which can boil at subzero temperatures and does not freeze down to -40°C.
The entire work process consists of the following sequential cycles:
- The evaporator core contains liquid refrigerant whose temperature is lower than that of the outside air. During active blowing of the radiator, thermal energy from low-potential air is transferred to the freon, which boils and turns into a gaseous state. At the same time, its temperature rises.
- The heated gas enters the compressor, where it heats up even more during the compression process.
- In a compressed and heated state, the refrigerant vapor is supplied to a plate heat exchanger, where the heating system coolant circulates through the second circuit. Since the coolant temperature is significantly lower than that of the heated gas, freon actively condenses on the heat exchanger plates, releasing heat into the heating system.
- The cooled vapor-liquid mixture enters the throttle valve, which allows only cooled, low-pressure liquid refrigerant to pass to the evaporator. After which the whole cycle repeats.
To increase the heat transfer efficiency of the tube, spiral fins are wound onto the evaporator. Calculation of the heating system, selection of circulation pumps and other equipment must take into account the hydraulic resistance and heat transfer coefficient of the installation's plate heat exchanger.
Video overview of the system design and its operation
Inverter heat pumps
The presence of an inverter as part of the installation allows for a smooth start-up of the equipment and automatic control of modes depending on the outside temperature. This allows you to maximize the efficiency of the heat pump by:
- achieving efficiency at the level of 95-98%;
- reducing energy consumption by 20-25%;
- minimizing loads on the electrical network;
- increasing the service life of the installation.
As a result, the indoor temperature is stably maintained at the same level, regardless of weather changes. At the same time, the presence of an inverter complete with an automated control unit will provide not only winter heating, but also the supply of cooled air in summer when the weather is hot.
At the same time, it should be taken into account that the presence of additional equipment always entails an increase in its cost and an increase in the payback period.
Waste oil dripper stove
One of the cheapest types of fuel is used oil. The oven can heat up to 800-900 °C. The initial temperature is 90°C.
Fill in some of the oil and add 50-100 g of ignition material (special fluids, fuel oil, kerosene or diesel fuel). This is necessary for quick ignition of the stove. Wait until the combustion process stabilizes. You can then complete the next section.
If oil spills, it must be removed immediately. Combustion occurs inside the pipe. This is a safe process. Fuel consumption ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 liters per hour. When the stove is burning, you can heat the water.
Recommended for use: solar oil, fuel oil, waste oil, fuel oil. Do not use gasoline, acetone or other solvents. Avoid getting water into the fuel.
The technical literature contains many detailed instructions for making a drip heater for water injection with your own hands. Each of these designs is unique and has its own advantages and disadvantages. You can also use the kiln in the workshop version, but you can finish it at your own discretion.
Take a look at the overview video on IV infusion. Oven on the solarium:
Drawings and tips for installing a waste oil furnace contain this video:
Types of heat pumps for home heating
There are compression and absorption heat pumps. Installations of the first type are the most common, and this is the type of heat pump that can be assembled from a refrigerator or an old air conditioner using a ready-made compressor.
You will also need an expander, evaporator, and condenser. For the operation of absorption units, an absorbent refrigerant is required.
Heat pumps are most often assembled from units of air conditioners and refrigerators. Such homemade designs are simple, effective, and if the master has the skills to do such work, they can be made in just a few days
Depending on the type of heat source, installations can be air, geothermal, or using secondary heat (for example, waste water, etc.). One or two different coolants are used in the input and output circuits, and depending on this, the following types of equipment are distinguished:
- "air-to-air";
- "water-water";
- "water-air";
- "air-water";
- "ground-water";
- "ice-water".
A system can only be efficient if it consumes less energy than it produces. This difference is called the conversion factor. It depends on many factors, but the most significant is the temperature of the coolant in the input and output circuits. The greater the difference, the better the system works.
Image gallery Photos from The source of heat is air from the street. The units are connected to water heating systems. They are able to work effectively as long as the outside air temperature is above -25 degrees. The water temperature in the heating system can reach 63 degrees
The equipment is designed to heat buildings using water resources. It is installed in areas located near natural bodies of water. Horizontal heat pumps of this type take energy from the bottom layers of water, and vertical ones are designed to extract heat from underground and groundwater
Professional installation of a geothermal pump is an expensive service, but the cost is recouped through low operating costs. The installations are characterized by increased reliability and safety. They are weather-sensitive and designed for connection to low-temperature heating systems, which include heated floors
The installations generate heat while freezing water. By turning 100-200 liters of water into ice, you can get enough energy to heat a medium-sized house for 1 hour. For the system to function, solar collectors and a tank with a large amount of clean water are needed.
Air-to-water heat pump
Block diagram for multiple heat pumps
Geothermal heat pump for home
Ice-water heat pump
There are no reliable formulas for calculating the performance of heat pumps, because... their work depends on many factors.
When you assemble a heating system yourself, you cannot expect it to be as efficient as industrially produced equipment, but it is quite enough to create an economical additional heating system.
Results
If you decide that you need a heat pump to heat your home, then do not rush to buy a ready-made installation. A homemade device is much cheaper and consumes less energy during operation, which will save on electricity bills. When assembling the unit, monitor the quality of welded joints. The system can only operate if it is completely sealed.
Video: homemade heat pump
Homemade heat pump - 1
Watch this video on YouTube
Video: DIY air water heat pump R-134
DIY heat pump air water R-134. Privatmaster Dnepr part 1
Watch this video on YouTube
Do you want to understand better than others?
- DIY vacuum pump from a refrigerator compressor. Topic: Vacuuming with your own compressor - What is a vacuum pump? A vacuum pump, in principle, is a fairly simple design. The principle of its operation is pumping air from a given volume. For pumping, of course...
- The principle of operation of compressor, absorption and thermoelectric refrigerators - Fundamentally, the refrigerator is a closed thermally insulated chamber in which a constant low temperature is maintained. If it were perfect...
- How to make a refrigerator for a moonshine still with your own hands from a copper tube + video - When assembling a moonshine still yourself, you cannot do without using an effective device for condensing alcohol vapor. Refrigerator for moonshine still…
- How can you use a compressor from an old refrigerator - If the refrigerator is no longer used for its intended purpose, then its parts can be used to make useful devices for the household. The most valuable element of the cooling…
- Air conditioning from a refrigerator: we make it ourselves - The operating principle of household refrigerators and air conditioners is the same. And although the types of compressors, layout, working volumes, “recovery” of heat and condensate are different, it is necessary to do...
Types of homemade heaters from the refrigerator
Based on the type of energy source used, home heat pumps are divided into the following types:
- geothermal (open and closed);
- air.
Units using secondary heat sources are usually installed in enterprises, since their operating cycle is associated with the generation of energy, which requires additional disposal.
In geothermal pumps, the energy source is soil or groundwater. Closed-type devices are divided into:
- Horizontal. The collector that collects heat is shaped like rings or zigzags. It is placed horizontally in trenches at a depth of more than 1.3 m. The distance between the pipes is about 1.5 m. Similar heat pumps are used to heat a small area. If the soil is sandy, then the length of the contour is increased by 2 times, since it is not able to retain moisture.
- Vertical. It is distinguished by the vertical location of the heat collector manifold. The depth of the well is about 200 m. They are filled with groundwater, which subsequently releases heat. This version of the system is used if there is no possibility of its horizontal placement or there is a high risk of damage to the landscape. 1 m of a well provides 50-60 W of energy, so for a pump with a power of 10 kW it is enough to drill 170 m. To get more heat, you need to make several small wells at a distance of 20 m from each other.
- Aquatic. The shape of the collector is identical to the horizontal type of heat pump, but it is placed at the bottom of the reservoir, below the freezing level (depth - from 2 m). This method of system installation is usually less expensive. The cost depends on the location of the reservoir, its depth and the total volume of water.
In open-type pumps, the water used for heat exchange is discharged back into the ground.
The circuit of water heat pumps is made of plastic pipes, which are pressed to the bottom of the reservoir at the rate of 5 kg per 1 m of length. Every 1 r.m. circuit provides about 30 kW of energy. If you need a system with a power of 10 kW, then the length of the circuit must be at least 300 m. The advantages of the design include ease of installation and low cost. The downside is the impossibility of heating the room in severe frosts, since energy is not generated.
As the name suggests, air source heat pumps use air as their energy source. These units are suitable for areas with a hot climate, since at sub-zero temperatures productivity will be greatly reduced. The main advantage is the absence of large material costs for drilling wells. The system is located near the house.
The efficiency of a pump depends on its conversion factor, which is the difference between the energy it consumes and the energy it outputs. The main factor influencing this value is the temperature of the input and output circuits. The system will work better if the difference between these parameters is large.
Manufacturing and installation
The pump is manufactured according to the following algorithm:
- the compressor is mounted on the wall;
- a coil is made from pipes (to make it, you need to wrap the pipes around a container of a suitable shape);
- the tank is cut in half, a coil is placed inside it and brewed;
- several holes are left in the container through which the coil pipes are led out;
- to make the evaporator, a plastic barrel is used, identical in size to the tank, and internal circuit pipes are inserted into it;
- PVC pipes (installation diagrams for warm water floors in the apartment) are installed, transporting heated water;
- It is not recommended to fill the unit with freon yourself; it is better to entrust this action to a specialist.
The cost of work in different regions of our country can vary dramatically. In addition, the cost of operation and the pump depend on its type and heating system.
- In St. Petersburg, installation of a heat pump, regardless of its type, will cost the Customer from 35,000.00 rubles;
- In Moscow, installation organizations, regardless of the type of heat pump, are ready to perform turnkey work for an amount over 45,000.00 rubles;
- In Krasnodar, installation of a heat pump will cost from 40,000.00 rubles.
- If we talk about the installation of heating systems using heat pumps, then the average prices for a set of works, taking into account the cost of equipment, are as follows:
READ MORE: Motoblock Patriot Ural TOP-3 rating of the best models of 2020, distinctive characteristics of the device, instruction manual and customer reviews
A) Installation of geothermal domestic heat pumps:
- Power – 4-5 kW (50 – 100 m²) – from 130,000.00 to 280,000.00 rubles;
- Power – 6-7 kW (80 – 120 m²) – from 138,000.00 to 300,000.00 rubles;
- Power – 8-9 kW (100 – 160 m²) – from 160,000.00 to 350,000.00 rubles;
- Power – 10-11 kW (130 – 200 m²) – from 170,000.00 to 400,000.00 rubles;
- Power – 12-13 kW (150 – 230 m²) – from 180,000.00 to 440,000.00 rubles;
- Power – 14-17 kW (180 – 300 m²) – from 210,000.00 to 520,000.00 rubles.
B) Installation cost of air source heat pumps:
- Power up to 6.0 kW (50 – 100 m²) – from 110,000.00 to 215,000.00 rubles;
- Power up to 9.0 kW (80 – 120 m²) – from 115,000.00 to 220,000.00 rubles;
- Power up to 12.0 kW (100 – 160 m²) – from 120,000.00 to 225,000.00 rubles;
- Power up to 14.0 kW (130 – 200 m²) – from 127,000.00 to 245,000.00 rubles;
- Power up to 16.0 kW (150 – 230 m²) – from 130,000.00 to 250,000.00 rubles;
- Power up to 18.0 kW (180 – 300 m²) – from 135,000.00 to 255,000.00 rubles.
Types of pumps
There are different types of heat pumps, but they are all based on the principle of producing heat or cold by separating thermal energy and transferring it. Only one TN Frenette is different. The cavitation method of obtaining thermal energy using a hydrodynamic generator is a type of heat pump.
The thermal energy that is used to heat the building is a consequence of energy conversion carried out using a heat pump. Moreover, they obtain heat without burning fuel, but by cooling the external environment and releasing thermal energy indoors, that is, in this case, the law of conservation of energy is observed: how much thermal energy is taken from the external environment, the same amount is released inside the building. Most of these household devices use heat from the sun, which is accumulated by the surface of the earth, water or air.
Therefore, according to the type of primary circuit, all structures can be divided into air, ground and water.
Based on the type of coolant (W - water, G - soil) in the circuits, pumps can be divided into eight types:
- B—B;
- G-V;
- G—air;
- air—B;
- air—air;
- To the air;
- refrigerant—B;
- refrigerant - air.
They can also use the heat of the exhaust air, heating the supply air, that is, operate in recovery mode.
Air-to-air
The principle of operation of a heat pump is similar to that used in an air conditioner in heating mode, but has the only difference. The heater is set to heating, and the air conditioner is set to reduce the temperature in the room.
The principle of operation of the B-B installation is as follows: the air, even at low temperatures, has a certain amount of energy. Only at absolute zero is there no thermal energy. Most HPs are capable of receiving heat at a temperature of –15 °C. Currently, some manufacturers produce stations that retain heat extraction at –30 °C. Heat is collected through the evaporation of freon, which circulates through the internal circuit. For this purpose, an evaporator is used in which the refrigerant is converted from liquid to gaseous state. This absorbs heat.
The next block, which is located in the B-V heating system, is the compressor, which converts freon from a gaseous state into a liquid. This generates heat. The efficiency of the V-V installation directly depends on the ambient temperature. The lower it is, the lower the station’s productivity.
Air-water
Air-to-water HP is the most universal model. It is very effective in the warm season, but in the cold season the performance drops significantly. Simple installation is an advantage of the system. Suitable equipment can be installed anywhere. The heat that is removed from the room in the form of gas or smoke can be reused.
A water heat pump takes heat from groundwater, which is pumped through the evaporator. Such a pump is distinguished by good efficiency and increased stability: efficiency is the result of significant heat transfer from water.
Of course, to use an installation of this type, there must be sufficient groundwater in the area. It is advisable that the water is no deeper than 30 meters.
Water-water
With such a system, an easily evaporating liquid, such as freon, circulates in the internal circuit. The indoor circuit can be water pipes, registers or radiators filled with water.
Any body of water with a sufficiently large amount of water can act as an external contour. This could be a river, lake or pond. In this case, the coolant takes heat from the external circuit and transfers it to the internal circuit.
Geothermal
The HP uses the stored thermal energy of the earth as a heat source. Such pumps are considered the most efficient because the ground temperature remains constant throughout the year.
These systems are divided into horizontal and vertical. But this method requires a fairly large area for horizontal pipes, and for vertical systems it is necessary to perform significant excavation work.
Prices for different types of heat pumps
Heat pump
How does it work?
The operating principle of geothermal heating involves the use of heat pumps. They operate according to the classical Carnot cycle, taking cold coolant deep below and receiving in return a fluid flow heated to 50 degrees inside the heating system. The equipment operates with an efficiency of 350 to 450% (this does not contradict the fundamental physical laws; why will be discussed later). A standard heat pump heats a house or other building using the heat of the earth for 100 thousand hours (this is the average interval between preventive major repairs).
Heating to 50 degrees was not chosen by chance. Based on the results of special calculations and the study of practically implemented systems, this indicator was recognized as the most effective. Therefore, earth heating, which uses the flow of energy from the subsoil, is mainly supplemented not by radiators, but by a warm floor or an air circuit. On average, for 1000 W of energy driving the pump, it is possible to raise approximately 3500 W of thermal energy to the top. Against the backdrop of the rampant increase in the cost of coolant in the main network and other heating methods, this is a very pleasant indicator.
Geothermal heating is formed by three circuits:
- ground collector;
- heat pump;
- actually, the heating complex of the house.
The reason is simple - the water that occurs in a sufficiently heated soil layer quickly corrodes the equipment. And even such a liquid can not be found in any random place. The choice of a specific coolant is determined by the design decisions of engineers. The pump is selected depending on the design of the remaining parts of the system. Since the depth of the well (level of installation of equipment) is determined by natural conditions, the decisive differences between types of geothermal systems are associated with the design of the collector in the ground.
The horizontal structure implies the location of the collector below the soil freezing line. Depending on the specific area, this means a deepening of 150-200 cm. Such collectors can be equipped with various pipes, both copper (with an outer layer of PVC) and those made of metal-plastic. To get from 7 to 9 kW of heat, you will have to lay at least 300 square meters. m collector. This technique does not allow you to get closer to the trees than 150 cm, and after installation is completed you will have to landscape the area.
A vertically aligned reservoir involves drilling several wells, necessarily directed in different directions, and each one is drilled at its own angle. Geothermal probes are located inside the wells, thermal output from 1 linear. m reaches approximately 50 W. It is easy to calculate that for an identical amount of heat (7-9 kW), 150-200 m of wells will have to be installed. The advantage in this case is not only in savings, but also in the fact that the landscape structure of the territory does not change. It will only be necessary to allocate a small area for the installation of the caisson block and for the installation of the concentrating collector.
A circuit heated by water is practical if it is possible to bring the external heat exchange unit into a lake or pond to a depth of 200 to 300 cm. But a mandatory condition will be the location of the reservoir within a radius of 0.1 km from the heated building and the area of the water surface at least 200 square meters. m. There are also air heat exchangers, when the external circuit receives heat from the atmosphere. This solution works well in the southern regions of the country and does not require any excavation work. The weaknesses of the system are low efficiency when the temperature drops to 15 degrees and a complete stop if the temperature drops to 20 degrees.
Heat pump for heating a house, principle of operation
The operation of a heat pump, refrigerator and air conditioner is based on the Carnot cycle. A heat pump for heating transfers heat from an area with a lower temperature to the consumer, where the value of this parameter should be higher. In this case, it is taken from the outside, where it accumulates, and after some transformations it goes into the house. It is natural heat, and not the energy released during the combustion of traditional fuel, that increases the temperature of the coolant passing through the pipes of the heating system.
In fact, the principle of operation of the pump is much more complicated. Therefore, devices of this class are often compared to refrigeration units, only working in reverse. But the general operating procedure is identical, despite the fact that there is a big difference both in the engineering solution and in the purpose of the main parts of the devices. The circuit assembled on a heat pump differs from a traditional heating system in the number of circuits and the specifics of their operation.
The external circuit is installed outside a private house. It is laid where heat accumulates when surfaces are heated by sunlight or for some other reason. Energy can be taken, for example, from the air, soil, or reservoir. Even from a well, if the house is on rocky soil or there are restrictions on installing pipes. Therefore, there are several modifications of heat pumps, despite the fact that heating is organized according to the same type of scheme.
Pump operating principle
The internal circuit (not to be confused with the heating circuit in the house) is geographically located in the unit itself. The cooled coolant circulating in the external partly increases its temperature due to the environment. Passing through the evaporator, it transfers the selected energy to the refrigerant with which the internal circuit is filled. The latter, due to its specific property, boils and turns into a gaseous state. For this, low pressure and temperatures of more than -5°C are sufficient. That is, the liquid medium turns into gas.
Next - to the compressor, where the pressure is artificially increased, due to which the refrigerant is heated. It is in this structural element, which is the second heat exchanger, that thermal energy is transferred to the liquid (water or antifreeze) passing through the return of the home heating system. Quite an original, effective and rational heating scheme.
The heat pump requires electricity to operate. But it is still much more profitable than using only an electric heater. Since an electric boiler or electric heater spends exactly the same amount of electricity as it produces heat. For example, if a heater has a power rating of 2 kW, then it spends 2 kW per hour and produces 2 kW of heat. A heat pump produces 3 to 7 times more heat than it consumes electricity. For example, 5.5 kW/hour is used to operate the compressor and pump, and the heat produced is 17 kW/hour. It is this high efficiency that is the main advantage of a heat pump.
It remains to add that a saline solution or ethylene glycol circulates in the external circuit, and freon, as a rule, circulates in the internal circuit. This heating scheme also includes a number of additional devices. The main ones are a reducer valve and a subcooler.
Features of device installation
The classic design of devices consists of a pair of circuits.
The most important role in it is played by the heat exchanger, which acts as a provoking factor.
The external circuit consists of pipes with high thermal conductivity; refrigerant circulates through them.
This circuit has various locations and implements the operation of the device in different ways, but it has the same function:
- Due to the circulation of freon (ammonia), heat from the environment moves to the compressor.
The second circuit consists of:
- compressor (read about plastic high-pressure hoses here);
- evaporator;
- capacitor;
- pressure reducing valve.
A hydrodynamic heat pump differs from others in design - the device consists of a coupling that transfers the generated energy to the generator, where the liquid, engine and heat generator are heated.
When installing the unit, it is important to take into account the location of the external circuit, depending on which one or another type of installation is carried out. So:
- for air-water pumps, the external circuit with pipes is located on the wall or roof of the building, and the device itself is located indoors;
- if a geothermal pump is installed, then the unit can be positioned vertically (a well is dug up to 100 meters deep, where the probe is placed) or horizontally (pipes are laid parallel to each other in a trench or pit one and a half meters deep).
- When installing water-to-water pumps, the external circuit is located in a reservoir, at its bottom.
Self-installation of an alternative heating system for a private home using a heat pump, made by yourself, is a sure way to save money and provide yourself with comfortable conditions.
Heat pumps can cope with heating a swimming pool and garage, a house and a greenhouse.
How to make a Frenette heat pump at home, watch the video.
To assemble a working model of a heat pump, you cannot do without knowledge of the theory, or rather, the operating principle of this device. I would like to initially note that statements about efficiency of 300, 500 and 1000% are a myth or simply a marketing ploy designed for the average user’s ignorance of the laws of physics.
An example is home refrigerators and air conditioners, whose design is based on the so-called Carnot cycle, which also uses the principle of operation of a heat pump for heating or domestic hot water. The essence of this cycle is the movement of a substance (working fluid) through a closed system and changing its state of aggregation from liquid to gaseous and vice versa. At the moment of transition, a huge amount of energy is released or absorbed.
To explain in a more accessible language, we list the main elements that a heat pump device includes:
- compressor;
- heat exchanger, where the working fluid passes into a gaseous state (evaporator);
- a heat exchanger in which the working fluid is condensed (condenser);
- expansion (reducing) valve;
- control and automation equipment;
- lines made of copper pipes.
Having passed the compressor, the freon moves under pressure to the second heat exchanger, where it will condense and transfer the resulting heat to the water, again taking on a liquid state. Next, the working fluid enters the expansion valve, the pressure drops again and it continues on its way to evaporation. The cycle is complete.
Factory-made heat pumps for residential buildings are capable of delivering coolant with a temperature of 55-60 ºС, this is enough to heat rooms with radiators or heated floors. At the same time, the entire heating system spends electricity for the following purposes:
- compressor power supply;
- rotation of the rotors of the circulation pumps of the external and internal circuits;
- power supply for automation and control equipment.
A heat pump is not called a single device, but an installation consisting of the following components:
- Circulation pump;
- Evaporator;
- Compressor;
- Capacitor;
- Other communications depending on the type of installation.
All elements are connected in a chain using a pipeline. The objectives of the system are to collect energy, release heat and transfer it to the point of consumption. Examples of the operation of a simple heat pump are a refrigerator, air conditioner or split system. The evaporator and condenser act as heat exchangers.
Having understood the principle of operation of the heat pump, it will not be difficult to make such a device yourself.
Heat pump installations can be classified according to the source and heat carrier.
Types of devices are distinguished according to two criteria. The first of them is the medium, which is a source of energy, the second is the carrier to which the energy is transferred, and which directly provides heating to the home. The following types of systems are distinguished:
- Air - air;
- Air - water;
- Water – water;
- Earth - water;
- Earth is air.
The pump is driven by electric current, a diesel generator or powered by a solar panel. The coolant (water or air) circulates through the tubes, passes through the evaporator and transfers heat to the refrigerant. The refrigerant transitions from liquid to gaseous state. The compressor compresses the gas as the temperature increases.
The condenser releases energy and heats the coolant. Next, the substance, heated to a high temperature, enters the heating system of the house. The coolant comes out already cooled, the cycle repeats. Thus, the cost of electricity (or another energy source) goes only to the operation of the circulation pump and the heating device. The house is heated not with electricity, but with the heat of a natural energy storage device.
How does a heat pump differ from other installations for heating private houses:
- unlike boilers and heaters, the unit does not produce heat on its own, but, like an air conditioner, moves it inside the building;
- The HP is called a pump because it “pumps out” energy from sources of low-grade heat - ambient air, water or soil;
- the installation is powered exclusively by the electricity consumed by the compressor, fans, circulation pumps and control board;
- The operation of the device is based on the Carnot cycle, used in all refrigeration machines, for example, air conditioners and split systems.
In heating mode, a traditional split system operates normally at temperatures above minus 5 degrees; in severe frost, efficiency drops sharply.
The Carnot heat exchange cycle involves a working fluid - freon gas, boiling at sub-zero temperatures. Alternately evaporating and condensing in two heat exchangers, the refrigerant absorbs energy from the environment and transfers it inside the building. In general, the principle of operation of a heat pump repeats the operation of an air conditioner turned on for heating:
- While in the liquid phase, freon moves through the tubes of the external evaporator heat exchanger, as shown in the diagram. Receiving heat from air or water through metal walls, the refrigerant heats up, boils and evaporates.
- Then the gas enters the compressor, which pumps up the pressure to the calculated value. Its task is to raise the boiling point of the substance so that freon condenses at a higher temperature.
- Passing through the internal heat exchanger-condenser, the gas turns into liquid again and transfers the accumulated energy to the coolant (water) or room air directly.
- At the last stage, the liquid refrigerant enters the receiver-moisture separator, then into the throttling device. The pressure of the substance drops again, freon is ready to go through a second cycle.
READ MORE: Geotextiles: what is it and how is it used in construction? The operating diagram of a heat pump is similar to the operating principle of a split system
Domestic air conditioners and heat pumps use various types of thermostatic valves that reduce the refrigerant pressure in front of the evaporator. In household split systems, the role of a regulator is played by a simple capillary device; pumps are equipped with an expensive thermostatic valve (TRV).
Note that the above cycle occurs in all types of heat pumps. The difference lies in the methods of heat supply/removal, which we will list below.
Types of throttle valves: capillary tube (photo on the left) and thermostatic valve (TRV)
According to the generally accepted classification, heat pumps are divided into types according to the source of energy received and the type of coolant to which it is transferred:
- Air-to-air pumps are the closest to traditional split systems, the difference being the area of the outdoor evaporator. The device takes heat from the environment and directly transfers it to the air in the room, as happens in a conventional air conditioner.
- The design of air-water generators is identical, but involves heating water or antifreeze circulating through the heating system of a residential building.
- A water-to-water installation takes low-grade heat from a reservoir and transfers it to a liquid coolant. Here, an additional external heat exchanger made of pipes is used, immersed in a well, lake, borehole or sewer septic tank. The circulation of water through the evaporator is ensured by a second pump.
- Geothermal heat pump uses the heat of the soil and heats the in-house coolant. The external heat exchange circuit is a coil with antifreeze, buried 1.5-2 m and occupying a large area. The second option is several vertical probes made of pipes lowered inside the wells to a depth of 10-100 meters.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of using a heat pump include:
- Possibility of use in remote villages where there is no gas pipeline.
- Economical consumption of electricity only for the operation of the pump itself. Costs are significantly lower than when using electrical appliances for space heating. A heat pump consumes no more energy than a household refrigerator.
- Ability to use a diesel generator and solar panels as an energy source. That is, in the event of an emergency power outage, the heating of the house will not stop.
- The system is self-contained and does not require adding water or monitoring its operation.
- Environmentally friendly installation. During operation of the pump, no gases are generated and there are no emissions into the atmosphere.
- Work safety. The system does not overheat.
- Versatility. You can install a heat pump that operates for heating and cooling.
- Durability of use. The compressor requires replacement once every 15–20 years.
- Releasing the premises that were intended for the boiler room. In addition, there is no need to purchase and store solid fuel.
Disadvantages of heat pumps:
- Installation is expensive, although it pays for itself within five years;
- In the northern regions, the use of additional heating devices will be required;
- The ground installation, although slightly, disturbs the ecosystem of the site: it will not be possible to use the territory for a garden or vegetable garden, it will be empty.
Bivalent heating scheme ↑
Using such a scheme will help save money at the stage of manufacturing and installation of the pump. The fact is that the heat pump power is calculated based on the minimum possible temperature. But the peak low temperatures outside only last for a very short time, which means that for most of the year the heat pump will use only part of its power potential.
In order to be able to install a less powerful pump, an additional heat source is connected in parallel with it - an electric boiler. Then, in severe frosts, you can additionally “heat” the room. Considering that there are few such days a year, such heating will not hit your wallet hard, and you can save significantly on the cost of the pump.
It is also possible to use a solid fuel boiler as additional equipment. In this case, a bypass must be included in the heating system.
Manufacturing of geothermal installation
It is quite possible to make a geothermal installation with your own hands. In this case, the thermal energy of the earth is used to heat the home. Of course, this is a labor-intensive process, but the benefits are significant.
Calculation of the pump circuit and heat exchangers
The circuit area for HP is calculated at the rate of 30 m² per kilowatt. A living space of 100 m² requires about 8 kilowatt/hour of energy. This means the contour area will be 240 m².
The heat exchanger can be made from a copper tube. Inlet temperature 60 degrees, outlet 30 degrees, thermal power 8 kilowatt/hour. The heat exchange area should be 1.1 m². Copper tube with a diameter of 10 millimeters, safety factor 1.2.
Circumference in meters: l = 10 × 3.14 / 1000 = 0.0314 m.
Quantity of copper tube in meters: L = 1.1 × 1.2 / 0.0314 = 42 m.
Necessary equipment and materials
In many ways, success in the manufacture of heat pumps depends on the level of preparedness and knowledge of the contractor himself, as well as on the availability and quality of everything necessary for installing a heat pump.
Before starting work, you need to purchase equipment and materials:
- compressor;
- capacitor;
- controller;
- polyethylene fittings intended for assembling manifolds;
- pipe to the earth circuit;
- circulation pumps;
- water hose or HDPE pipe;
- pressure gauges, thermometers;
- copper tube with a diameter of 10 millimeters;
- insulation for pipelines;
- set of seals for sealing.
How to assemble a heat exchange block
The heat exchange block consists of two components. The evaporator must be assembled according to the “pipe-in-pipe” principle. The inner copper tube is filled with freon or other rapidly boiling liquid. Water from the well circulates through the outside.
Construction of the soil contour
In order to prepare the required area for the soil contour, a large amount of excavation work is required, which should preferably be carried out mechanized.
You can use 2 methods:
- With the first method, it is necessary to remove the top layer of soil to a depth below its freezing. At the bottom of the resulting pit, lay the free part of the outer pipe of the evaporator in a snake and reclaim the soil.
- In the second method, you first need to dig a trench across the entire planned area. The pipe is laid in it.
Then you need to check the tightness of all connections and fill the pipe with water. If there are no leaks, you can fill the structure with earth.
Refueling and first start
After installation is completed, the system must be filled with refrigerant. It is best to entrust this work to a specialist, because special devices are used to fill the internal circuit with freon. When filling, you need to measure the pressure and temperature at the compressor inlet and outlet.
After refueling is completed, you need to turn on both circulation pumps at the lowest speed, then start the compressor and monitor the operation of the entire system using thermometers. When the line warms up, frosting is possible, but after the system is completely warmed up, the frosting should melt.
The main disadvantages of geothermal heating
1. The need for electrical energy. The simplest geothermal system requires at least 1 (kW) electricity to produce 4 (kW) of thermal energy.
Heat absorption from the ground does not occur on its own. For heat exchange, a pump is necessarily and certainly used. If something happens to the electrical network, the heating circuit will immediately stop providing the object with heat, since the heat pump will stop without power supply.
2. Low level of heat transfer. A traditional horizontal geothermal heating system, which goes underground to a depth of 15-30 meters, provides only 40 (W) of thermal energy from each linear meter of underground pipeline.
To obtain 4 (kW) of thermal energy, you need to use at least 100 (m) of the pipeline circuit. If you plan to heat an object with a total area of 250 (m2) (ceiling height 2.5-3 meters), you need to use a heating system with a capacity of at least 27.5 (kW). To operate such equipment, a minimum of 688 linear meters of underground pipeline will be required.
These are not all the disadvantages of a geothermal heat pump.
3. Limited scope. Geothermal heating cannot be installed at every facility. For example, it will definitely not be possible to heat a separate apartment in a high-rise building or a store in the central areas of the city. It is unlikely that anyone will allow mining in densely populated residential areas.
It’s a different matter if geothermal heating is organized on the territory of a residential property from the private sector or for some enterprise on the outskirts of the city.
4. The high cost of installing geothermal heating. The equipment itself for organizing geothermal heating costs at least 10 times more than gas equipment of similar power.
But purchasing equipment is far from a complete expense. The cost of installing geothermal heating must additionally include the costs of creating and equipping underground communications. We must not forget about commissioning and maintenance.
Geothermal heating is very expensive.
5. Long payback. The payback period for the average geothermal system largely exceeds 10-15 years. The long payback period is due to the high cost of equipment and installation of communications.
For comparison, a traditional household gas boiler with a power of up to 12 (kW) pays for itself in an average of 5 years.
Homemade heat pump from a refrigerator: stages of creation
A heat pump is a fairly expensive device. But if you wish, you can build a device with your own hands from an old refrigerator or air conditioner. The refrigeration device has in its system two parts necessary for the pump - a condenser and a compressor.
Steps to assemble a heat pump from a refrigerator:
- First, the capacitor is assembled. It looks like a wavy element. In the refrigerator it is located at the back.
- The condenser must be placed in a durable frame that retains heat well and withstands high temperatures. In certain cases, you have to cut the container in order to install the capacitor without problems. Upon completion of installation, the container is welded.
- Next comes the installation of the compressor. The unit must be in good condition.
- The function of the evaporator is performed by an ordinary plastic barrel.
- When everything is prepared, you should fasten the elements together. The heat exchanger is attached to the heating system with PVC pipes.
This is how you get a homemade heat pump. Freon injection must be carried out by a professional, since the liquid is not easy to work with. In addition, to download it you need to have special equipment.
The refrigerator can act as a radiator. You will need to make two air vents that will ensure its circulation. One outlet accepts cold air, the second exhausts hot air.
From tubes with a rarefied medium
This method of heating liquid can be used not only in summer, but also in winter; it is one of the most complex. The installation location of the device made of vacuum tubes should not be shady, directed to the south. Overheating is not allowed, fluid circulation should be from top to bottom.
You will need the following tools:
- Adjustable wrench.
- Screwdrivers.
- Device for welding plastic pipes.
- Drill.
First, build a frame and place it in the intended installation location, the best option is the roof, then secure it, for example, with anchor bolts. Then connect the temperature sensor and air vent. Connect the water line using materials that are resistant to freezing temperatures.
Let's start installing the heating element, take a copper pipe and wrap it with sheet aluminum, insert it into the glass vacuum pipe. Place a fixing cup and a rubber boot on the bottom of the tube. Secure the metal end into the brass condenser (you may see sticky grease on the tube, do not wipe it off).
Close the fixing bowl and install the remaining elements in a similar manner. Install the mounting block and supply 220V electricity to it. Connect a temperature sensor and an air vent to it, although they are moisture-resistant, it is better to install a protective screen for them, then we connect the controller, with its help the operation of the system is monitored, and that’s the whole process of installing a solar boiler with your own hands. Program the system to the required parameters and start.
Characteristics
Most thrifty owners want to save money on heating and water supply for a private home. A heat pump is suitable for such purposes.
It is quite possible to build it yourself, while saving a lot of money - a factory-made device is very expensive.
Properties and device
The device has an external and internal circuit along which the coolant moves. Components of a standard device: a heat pump, a device for intake and a device for heat distribution. The circuit from the inside consists of a mains-powered compressor, an evaporator, a throttle valve, and a condenser. The device also uses fans, a pipe system, and geothermal probes.
Advantages of the heat pump:
- does not emit any harmful substances, absolutely environmentally friendly;
- there are no costs for the purchase and delivery of fuel (electricity is spent only on moving freon);
- no need for additional communications;
- absolutely fire- and explosion-proof;
- full heating in winter and air conditioning in summer;
- A self-built heat pump is an autonomous design that requires minimal control effort.
How to create a heat pump yourself
Regardless of the choice of system type (from the three options described above), to create the installation you will need a heat pump, which consists of a compressor station, evaporator, throttle valve and condenser. You can buy a ready-made system, but its cost will be quite high. If your budget does not allow you to purchase a unit, you can install it yourself.
Before designing and installing your own autonomous heating system, you need to make sure that all electrical wiring in the house is in proper condition.
There are two main ways to create a DIY installation: based on a refrigerator or an air conditioner. Let's take a closer look at them.
Design
The industry produces models with different performance characteristics, but they include equipment that performs the typical tasks described above.
As a design option, the figure shows a heat pump for heating a house.
Here, heat from geothermal sources is received through input pipelines, and on weekends it is transferred to the home heating system.
The operation of the heat pump is ensured by:
- system for monitoring circuit parameters and control, including remote methods via the Internet;
- additional equipment (washing and filling units, expansion tanks, safety groups, pumping stations).
Ground structures
They use three heat exchanger designs to take energy from the source:
- superficial location;
- installation of vertical ground probes;
- deepening of horizontal structures.
The first method is the least effective. Therefore, it is rarely used for heating a home.
Installation of probes in wells
This method is the most effective. It provides for the creation of wells to depths of about 50÷150 meters or more to accommodate a U-shaped pipeline made of plastic materials with a diameter of 25 to 40 mm.
Increasing the cross-sectional area of the pipe, as well as deepening the well, creates improved heat removal, but increases the cost of the structure.
Horizontal collectors
Drilling probe holes is expensive. Therefore, this method is often chosen as it is cheaper. It allows you to get by with digging trenches below the soil freezing depth.
When designing a horizontal collector, the following should be taken into account:
- thermal conductivity of soil;
- average soil moisture;
- geometry of the site.
They affect the dimensions and configuration of the collector. Pipes can be laid:
- loops;
- zigzags;
- snake;
- flat geometric shapes;
- helical spirals.
It is important to understand that the area of the site allocated for such a collector usually exceeds the dimensions of the foundation of the house by 2–3 times. This is the main disadvantage of this method
Water collectors
This is the most economical method, but it requires the location of a deep reservoir near the building. The assembled pipelines are placed and secured with weights at its bottom. For efficient operation of the heat pump, it is necessary to calculate the minimum depth of the collector and the volume of the reservoir capable of providing heat removal.
The dimensions of such a structure are determined by thermal calculations and can reach a length of more than 300 meters.
The picture below shows the preparation of lines for assembly on the ice of a spring lake. It allows you to visually assess the scale of the work ahead.
Air method
An external or built-in fan blows air from the street directly onto the evaporator with freon, like in an air conditioner. In this case, there is no need to create bulky structures from pipes and place them in the ground or reservoir.
A heat pump for heating a house operating on this principle is cheaper, but it is recommended to use it in a relatively warm climate: frosty air will not allow the system to work.
Such devices are widely used for heating water in swimming pools or rooms located next to industrial devices that are constantly involved in the technological process and release heat into the atmosphere with powerful cooling systems. Examples include power autotransformers, diesel stations, and boiler houses.
Refrigerator and its circuits
For reference. Household refrigerators are single-circuit and double-circuit. If there is only one cooling circuit, then it “serves” both the refrigerator and freezer compartments. Plus, each refrigerator is assigned from 0 to 4 snowflake stars. The more there are, the lower the temperature can be set in the freezer.
So, for models with single-circuit cooling and a 4-star freezer, the temperature is set depending on the refrigerator compartment. This is where the temperature sensor is located. And this compartment heats up much more slowly than the freezer.
To maintain the “cold weather” in the freezer at an optimal level, heating elements artificially increase the temperature in the refrigerator compartment. In this case, the sensor triggers the cooling process faster.
It turns out that you first need to heat something in order to freeze something else.
Primary circuits and system functionality
To operate the heat pump, a source of thermal energy is required, which can be any medium, provided that in winter its temperature stably exceeds +1°C. Thus, it is practiced to install units that receive thermal energy from water, air and earth (from soil or deep rocks).
Water
Any natural or artificial reservoir is suitable for laying the primary circuit, provided that it does not freeze to the bottom. The length of the pipeline submerged to the bottom is determined when calculating the power of the heat pump - one meter of pipeline mounted with a snake or rings allows you to obtain up to 30 W of thermal energy. That is, a heat pump with a pipeline 500 meters long is capable of heating a house whose heat demand is 15 kW.
Horizontal pipeline circuit laid with rings
The principle of operation of a water-to-water heat pump is that the resulting heat is used to heat the coolant liquid in a radiator heating system or a heated floor circuit. The functionality of a water-to-water heat pump is sufficient to provide stable underfloor heating, as it allows you to maintain the coolant temperature at 45-60 degrees. For full-fledged radiator heating with such a temperature regime, the house needs to be seriously insulated.
Air
For a water-to-water heat pump, the conversion coefficient is on average 1.5-2.2. While an air-to-air or air-to-water heat pump exceeds this figure approximately twice - the conversion factor is more than 4.
Air-to-air heat pumps are widely used because they do not require the installation of large circuits. Any inverter air conditioner or split systems that heat a room are essentially heat pumps with low efficiency.
Operating principle of an air source heat pump
An air heat pump has a significant drawback - in frosty weather it has nowhere to get heat. Some models of units are designed to operate at -20°C, in other cases the limit does not fall below -10°C.
In addition to air-to-air units, there is an air-to-water heat pump. Its difference is that the resulting thermal energy does not heat the air in the room, but the coolant in the heating circuit.
The operating principle of an air-to-water heat pump is standard. In this case, the evaporator, additionally equipped with a fan, is installed outside the house, and the compressor and condenser are installed inside. By connecting a water circuit to the heat exchanger, you can arrange underfloor heating of the room.
Earth
The most stable natural source of heat is rocks at a depth of over 20 meters, as they are constantly heated by heat from the earth's core. But to install a U-shaped pipe circuit, you have to drill deep wells, which affects the installation price. Geothermal installations are effective, but they pay for themselves only after 10-15 years of operation, provided that the house is properly insulated.
Heat pump "Earth-Water"
A cheaper installation option involves laying the circuit half a meter below the ground freezing level. Laying pattern - snake or circles. Installation of such a system requires a large amount of excavation work, in addition, the external circuit may be damaged during operation.
Part of the equipment
External contour
For the external circuit of the home heating unit you will need pipes. Metal products (but not stainless steel) have the greatest thermal conductivity, so it is better to use them for a heat collection system.
Fig.2. Collecting heat in the ground using a well for a homemade heat pump
Figure 2 shows a DIY geothermal heat pump using parts from an old air conditioner and refrigerator. The depth of the well for collecting heat from geothermal waters is about 60 - 120 meters. The diagram above does not show casing, but its use is mandatory, since casing protects the well walls from destruction. The external heat collection register must be located inside the casing.
Fig.3. Surface collection of external heat
The collection of spatial energy for heating a house can be done not only through a deep well, but also using a horizontal pipe system buried no less than the amount of soil freezing.
Collecting heat from a reservoir gives a sufficient result, since at the bottom the water temperature is always 4 degrees Celsius, since it is in this state that it has the greatest density. The attractive side is the significantly smaller volume of excavation work.
Systems that heat up under the influence of the sun are also used to collect heat. Such units are most often installed on the roof of a house and are intended to heat water or air. They significantly increase the temperature in the heat pump's evaporator, increasing the efficiency of the home's heating system.
Fig.4. Using a solar collector in a building heating system with a heat pump
Evaporator
This unit is a container in which a heat exchanger is located, carrying the heat carrier collected by the external circuit. The design of this part can be different, but most often it is made of copper pipes.
Rice. 5. The shape of the evaporator heat element should ensure maximum contact with the refrigerant
When making a heat pump with your own hands, they often use serviceable components and parts from an old refrigerator or air conditioner, as well as a failed split system.
Compressor
On homemade heat pumps, compressors from existing old equipment are most often used. When the unit system is assembled and tested, you can think about replacing the compressor from the old refrigerator with another, more or less powerful one
When choosing a compressor, it is best to pay attention to components from split systems, characterized by increased power and reliability. Modern units, as a rule, are equipped with automatic control and adjustment units, which greatly simplifies the management of these units
Fig.6. Compressor for heat pump
Capacitor
The choice of this element of the system must be approached especially carefully, since it is a vessel operating under pressure. It is preferable to use an old gas cylinder. It will have to be cut to accommodate the heat exchanger and then welded back together.
Recommendations for using the device
It is worth noting that variations of the Eugene Frenette pump using water as a coolant still exist. But usually these are large industrial models that are used in specialized enterprises.
The operation of such devices is strictly controlled using special instruments. It is almost impossible to provide a similar level of security at home.
General diagram of an industrial heat generator developed by Khabarovsk scientists: 1 - capacity; 2 — inlet pipe; 3 — outlet pipe; 4 - water heater; 5 - bearing shaft. Water is used as a coolant
The most popular version of the Frenette pump, which uses water rather than oil as a coolant, is a device developed by scientists from Khabarovsk: Natalya Ivanovna Nazyrova, Mikhail Pavlovich Leonov and Alexander Vasilyevich Syarg. In this mushroom-shaped design, water is specially brought to a boil and turns into steam.
The reactive force of steam is then used to increase the speed of movement of the coolant liquid through the pump channels to 135 m/min. As a result, energy costs for moving the coolant are minimal, and the return in the form of thermal energy is very high.
However, such a unit must be extremely durable, and its operation must be constantly monitored to avoid accidents.
What should you do if you plan to use a Frenette pump to heat a large room or an entire house? Water is a traditional coolant; most heating systems are designed specifically for it. And filling an entire heating system with the right liquid oil can be costly.
This issue can be resolved very simply. It is additionally necessary to build a conventional heat exchanger in which the heated oil will heat the water circulating through the heating system. Some heat will be lost, but the overall effect will remain quite noticeable.
The Frenette heat pump can be successfully used in combination with water heated floor systems. But instead of water, you need to pour liquid oil into the pipes
An interesting idea would be to use a Frenette pump in combination with a heated floor system. In this case, the coolant is released through narrow plastic pipes laid in a concrete screed.
This heating system functions in the same way as a conventional water heated floor. Of course, a project of this type can only be implemented in a private house, since high-rise apartment buildings are only allowed to use electric heated floors.
A practical and convenient way to use such a device is to heat a small room: garage, barn, workshop, etc. The Frenetta pump allows you to effectively and quickly solve the problem of autonomous heating in such places.
The energy consumption for its operation is small compared to the resulting thermal effect, and it is not difficult to build such a unit from the simplest materials.