Fittings are installed on any industrial or domestic pipeline. A pipeline valve allows you to regulate or shut off the flow of passing liquid or gas. To correctly select a valve for a particular system, you need to know the design of the valve and the principle of its operation.
Various types of valves
Classification of water valves
This element of shut-off valves is classified according to various criteria.
- According to the type and design of the locking device.
- According to the material of manufacture.
- According to the method of connection to the pipe.
Type of locking device design
There are three positions here:
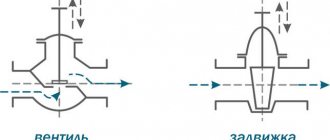
- Valve valve.
- Cork, also known as conical.
- Ball.
Valve valve
A valve valve, often called a valve tap, is a device body divided by a horizontal or inclined partition. The latter has a hole with a groove for the valve. This area is called the saddle.
The valve is the part of the stem that is located at the bottom. An elastic gasket is inserted into it, which rests against the saddle, thereby cutting off the water supply.
The rod itself has a thread at the top that fits into the thread of the seat nut. It is through the threaded connection that the valve is raised or lowered when the stem rotates.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Valve taps can withstand high pressure. | The gasket wears out quickly because it comes into contact with metal at the bottom. |
| With their help you can regulate the volume and pressure of water. | Short service life compared to other types. |
| The controls are simple. | You have to rotate the rod for a long time to shut off or open the water. |
| Possibility of repairs. |
We recommend that you read: How to determine why a water tap is humming and eliminate the cause?
Conical
A cone-type water valve is a subtype of a valve device, because the design of the valve itself differs from the first one only in the valve. It is a cone-shaped plug, which, when the rod rotates, falls into the hole in the partition, closing it with itself.
All the pros and cons of a valve-type valve can also be attributed to cone models.
Ball
The device received its name due to the shape of the locking device. This is a ball in which a through slot (channel) is made. If the latter turns out to be perpendicular to the pipeline when the rod is turned, the water flow is blocked. Conversely, when the channel is located along the pipe, the valve is considered open.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| The simplicity of the opening and closing mechanism creates conditions for operating the valve for a very long time. | Can not be repaired. |
| Completely sealed structure. | According to the instructions, the ball valve should only be used as a locking device. You can regulate the water with it, but in this case, manufacturers do not guarantee long-term operation. |
| To close or open the water supply, you only need to turn the handle 90°. |
Touchless taps and mixers
Taps with touch controls are increasingly being installed in the bathrooms of large institutions. The device is equipped with a photocell that is activated when you simply bring your hands to the tap. As soon as the visitor removes his hands, the photocell turns off the flow of water. This is a very hygienic and economical solution, since visitors do not come into contact with the device, and the water is turned off as soon as it is no longer needed.
Contactless or touch-sensitive water taps can significantly save water consumption. They are especially popular in establishments with a large number of visitors
To regulate the temperature and pressure of water, a special rod located on the faucet body is usually used. There is also an option when the initial temperature is set on the water heater control panel or using a temperature sensor in the device body. In this case, the mixer is equipped with an electronic control unit.
Material for making valves
Here it is necessary to divide the valves into those that will be used in internal water supply networks, and those installed externally.
For internal networks, devices are made of bronze, brass, stainless steel and plastic. For exterior use models made from all of the above materials, as well as steel and cast iron.
- Devices made of brass and bronze are the most expensive, but at the same time the most durable. They have a low specific gravity, small dimensions, and can be installed on both cold and hot water pipes. More recently, they were the only ones used in the heating system, because scale does not settle on the surfaces of brass and bronze appliances.
- Stainless steel valves also boast a long service life. But they are an order of magnitude cheaper than the first two models.
- Plastic shut-off valves are the cheapest with good technical characteristics. Today it is used on all types of water supply and heating networks.
Attention! Stainless steel valves are not recommended for installation in hot water supply and heating systems. On their surface, under the influence of hot water, scale forms, which reduces the cross-section of the throughput channel.
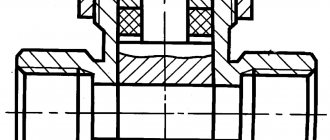
Device design
The valve design is quite simple, and the product consists of the following main parts:
- Frame.
- Locking device.
- Handwheel or locking handle.
The body of the product is made by casting. A locking device is installed inside the housing, and the flywheel is brought out. The body also has threads on both sides, through which the valve is connected to a water or gas pipeline. The cross-sectional diagram of shut-off valves is as follows:
Pipe connection methods
According to the installation method, water valves are divided into two positions.
- Coupled or threaded. The connecting element is based on a thread, which can be internal or external. In household networks, valves of this particular type are used, especially for internal wiring. Fittings with such a connection are mainly installed in pipelines through which water moves with a pressure of no more than 1.6 MPa.
- Flanged. These are either cast iron or steel devices with flanges at the ends of the pipes. These are more powerful devices with greater weight and overall dimensions. They are mounted only on main or industrial pipelines in which water moves under a pressure of more than 10 MPa.
We recommend that you read: The use of shut-off valves to shut off the flow in water pipelines
Coupling valves are installed in the water supply through threads, which must be cut at the ends of the connected pipes. This can be done with a special tool - a die. Its size is selected according to the valve diameter and thread size. The second option is to weld bends of the same diameter as the valve to the pipes, taking into account the thread number. When connecting the device to pipes, in order to create a complete seal at the joint, use FUM tape or thread.
Valves with external threads are attached to pipes using fasteners, which are popularly called American. Essentially, it is a union nut with a rubber gasket. To do this, an American one is first put on the pipe, and then a pipe with a lip at the end is welded to the first one. It is against this that the union nut will rest while screwing onto the valve thread.
Flanged models cut into the pipeline by installing flanges of identical size at the ends of cut pipes. The latter are connected to pipes by welding (gas or electric).
Note! A rubber or paronite gasket must be installed between the valve and pipe flanges. Fastening is done with bolts, usually four.
Method of fastening plastic valves
For this, welding technology and a special welding machine are used. Since a plastic device is used when installed in a water supply system assembled from plastic pipes, the welding technology consists of heating the pipe and valve fitting to a certain temperature.
The pipe is heated along the outer contour, the valve along the inner hole of the pipe. The plastic softens, the pipe is inserted into the pipe and allowed to cool. The material of the pipe and valve are soldered at the molecular level, resulting in a single, non-separable structure that is one hundred percent sealed.
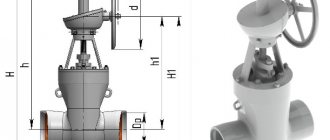
How does a valve differ from a ball valve by type of installation?
Both types of fittings have a threaded and flanged type of connection to the pipeline. However, each has differences in the range of nominal diameters. For a coupling connection it looks like this:
- valves - DN from 15 to 300 mm;
- taps - DN from 8 to 100 mm.
At the same time, ball valves also have other types of installation:
- Wafer - DN from 15 to 200 mm;
- for welding - DN from 10 to 600 mm;
- combined - DN 15 to 200 mm.
How to repair a valve
This applies to valve-type valves, in which the gasket most often fails. It must be replaced with a new one, and the device will continue to work without creating problems.
Attention! The valve can be repaired without removing it from the pipeline.
- To do this, you will need a gas or adjustable wrench, which must be used to unscrew the valve axle box.
- The gasket is tightened by the nut. It must be unscrewed using a wrench of the required number or pliers.
- Ready-made gaskets are sold in stores, but you can cut them from a piece of rubber with scissors to the size of the old one.
- A hole is made in the center of the new cuff for the threaded pin protruding from the valve.
- The gasket is put on the pin and tightened with a nut.
- While the valve is disassembled, it is recommended to clean its internal cavities with a knife. The same must be done with the internal planes of the crane axle box.
- A new sealing thread is wound onto the threads of the valve axle. Linen is better.
- The axle box crane is screwed into the body by hand and pressed with a gas wrench. Don't screw it in too hard to avoid stripping the thread.
We recommend that you read: Crab fastening - connection system for profile pipes
Differences in designs [ edit | edit code ]
Seal designs [ edit | edit code ]
According to the method of sealing the movable connection between the spindle (stem) and the cover, valves are divided into stuffing box
,
bellows
and
membrane
(diaphragm).
Stuffing box fittings [ edit | edit code ]
In stuffing box fittings, the tightness of the connection between the cover and the moving part of the valve is ensured by a stuffing box device. The essence of the stuffing box device is that on the outside of the cover or body, in the place where the rod or spindle passes through it, a stuffing box is created into which sealing material is placed - stuffing box packing. Using special devices, the packing is pressed along the axis of the spindle (rod), resting against the walls of the stuffing box and compacted. This creates a tight seal and the working environment does not penetrate outside the housing. In fittings of small diameters, the packing is compressed with a union nut, in larger diameters - with a special part - an oil seal using two folding or anchor bolts with nuts.
Types of spindles
All valves are also divided into two large groups depending on the mechanism of spindle movement:
- Flange gate valve with rising stem. The device operates due to helical or translational movements of the spindle. This valve option is equally suitable for any working environment. The ease of maintenance of such devices is also considered one of their undoubted advantages. Among the disadvantages, it is worth noting the significant height of the valve, especially when raised.
- Flange gate valve with non-rising stem. The shutter is raised or lowered by rotating the spindle directly inside the device. An important advantage of this type of valves is their compact dimensions, which allows them to be used in hard-to-reach places. The disadvantage is that the choice of working media is limited in favor of the least aggressive ones, since the impact is on the entire mechanism.