Heating
Author Anton
Date
Sep 9, 2016
0
2 671
Share
A common problem in multi-storey buildings is the occurrence of extraneous noise in the heating system. Loud sounds disturb the comfort of living, and the heating season turns into a painful test for the nervous system. Soundproofing pipes in an apartment is the only correct solution to such problems. In half of the cases, you can eliminate the noise yourself. To do this, it is necessary to correctly determine the reason for what turns pipes into an annoying “musical” instrument.
- LiveJournal
- Blogger
Such insulation will help not only from unnecessary sounds but also protect against freezing.
- Causes of extraneous noise
- Noise Elimination Solutions
- Noise in heating pipes
- Bubbling in radiators
- Crackling, knocking and rumble
- Sound insulation of heating elements
- Vibration compensators for heating
Types of noise and its diagnosis
If water makes noise in the heating pipes during heat supply operation, then there are certain reasons for this effect. First you need to identify them, and then begin to reduce the noise or eliminate it completely.
Why is the water noisy in heating pipes and how to correct this problem? Let's look at the main types of extraneous sounds. They point to the objective factors in the occurrence of an undesirable effect:
- Crackling in pipes. Occurs when the heating system is turned on;
- Clicking sounds that appear at regular intervals;
- Constant hum in transport highways;
- A barely audible knock.
All these extraneous effects - noise in the heating radiator or radiators - significantly reduce the comfort of living in the house. In addition, they may indicate improper operation of the heating supply. If action is not taken to correct the situation in time, some heating element may fail.
If the heating pump or other system component is noisy, you should first try to localize the cause of the extraneous sounds. To do this, it is recommended to use the following method:
- Monitor the frequency of occurrence of the effect.
- Try to identify the relationship - temperature increases in pipes, pressure surges, etc.
- Make sure that the noise in the heating boiler comes from it, and not from other objects located in the boiler room.
If it has been determined that the source is a component of the heating system, certain actions should be taken to eliminate this phenomenon.
Often noise in the heating riser appears due to faulty elements of the safety group - the air vent and drain valve. Therefore, it is recommended to first check their functionality.
Knocking, rattling
The cause of the knocking noise is usually a poorly secured pipe or radiator bracket. The slightest vibration when the coolant passes through such a unit causes rattling, and if the supports are very loose, the radiator hits the fasteners. The system will stop making noise if the brackets are firmly fixed. To dampen vibration, you can install a heat-resistant rubber gasket between the device and the support.
Sometimes knocking noises can be caused by parallel or intersecting pipes being too close together. During temperature deformations, one pipeline begins to touch another, beats against it and becomes a source of noise. Sound insulation can save the situation if the available gap is enough to accommodate it. Otherwise, to eliminate the knocking, you will have to shift the problem area.
In some cases, knocking on heating pipes in apartment buildings is caused by dissatisfaction with neighbors. This type of noise is usually characterized by a lack of periodicity and occurs in the form of a reaction to certain provoking actions. It’s just that all residents have to “enjoy” the specific sounds. Technical measures will not help here; sound insulation can only partially save. Conflicts with neighbors can only be resolved through dialogue and diplomacy.
Noise in radiators
To determine why heating radiators are noisy, you must first check their condition. Often the reason for this is their breakdown - damage to the case or other obvious design defect. In this case, the battery is replaced or restoration work is performed.
If everything is normal with appearance and integrity, the type of noise is determined. More often the effect occurs in the form of clicks or a constant hum. This can be explained by several factors:
- The appearance of a small air lock . It only slightly impedes the movement of hot water, but at the same time a hum occurs in the system;
- A large number of foreign elements in the heating device . This is a common reason why radiators make noise;
- Malfunction of the thermostat . The shut-off rod has moved, resulting in unwanted noise defects;
- Incorrect battery installation . Vibration during coolant flow is transmitted to the mounting units in the wall.
These are the main causes of noise in radiators. After correct diagnosis, you can begin to work to reduce sound effects.
In a centralized heating system, only the management company can fix a noisy riser. To do this, you need to draw up an application and submit it to representatives.
Removing the air lock can be done using the installed Mayevsky crane. It is designed specifically for these purposes.
If the heating radiators are noisy, the autonomous heat supply should be stopped so that the water temperature drops to a level of +25-30°C. Then you should do the following:
- Open the Mayevsky tap.
- Gradually fill the heating system with water.
- Wait until coolant flows from the tap pipe. He must weave for 1.5-2 minutes so that the air lock is completely removed.
Then the system is fully restarted and checked to see if the noise in the heating radiators has returned. If the cause has been identified correctly, this effect will no longer occur.
To eliminate noise in the heating radiator due to a large amount of debris, first check the condition of the mesh filter. The presence of foreign elements in it (residues of rusting pipes and radiators, limescale) indicates a clogged system.
Having found out the cause of the noise in the heating radiators, you should clean the system. There are several ways you can do this:
- Hydrodynamic . Debris and limescale are removed from the mains and batteries under the influence of strong water pressure;
- Chemical . Special reagents decompose the blockage into small fractions, which are then washed away from the heating.
This way you can eliminate noise.
Before choosing a cleaning technology, especially chemical, you need to read the instructions for using the composition or method. In some cases, they can negatively affect the integrity of system components.
The easiest way to diagnose noise in heating radiators is due to improper installation. Its source is fastening elements installed in the walls. In this case, you need to replace them and reinstall them.
Noise in heating radiators can be caused by more than just a problem within them. In some cases, the cause is malfunction of other system components - boilers or pumps. Experts recommend a comprehensive approach to solving the issue of noise in heating radiators. Only a complete diagnosis will help determine the true cause.
Murmuring and gurgling in pipes
Quite often gurgling and babbling can be heard in pipes. As a rule, these sounds are typical at the beginning of the heating season when the system is filled with water.
If these sounds are not a consequence of starting hot water, then they may indicate the following problem: an obstacle has arisen inside the radiator and the coolant has to flow around it, which is why these sounds are heard.
In order to determine the cause, it is necessary to verify the position of the valve and its functionality, and also try to determine the presence of a blockage. For prevention, it is recommended to clean the system; this can be done using the following methods:
- Using powerful water pressure.
- Using special chemical reagents with further flushing of the system with a jet of water under pressure.
If these measures are ineffective, you should seek help from a specialist, since in case of serious blockage you will need to seek help from a welder.
Noise from heating pumps
Constant noise in the heating pump may appear due to partial breakdown of its components - the impeller or rotor. At the same time, the functioning of the entire system deteriorates, which leads to a decrease in its efficiency. To eliminate this reason, the pump should be repaired or a new one installed.
Also, constant noise in the circulation pump can be caused by its unstable operation. Voltage drops lead to loss of synchronization and, as a result, uneven movement of the coolant. This can cause noise in the heating system in other areas - in pipes and radiators. The operation of the pump can only be checked after a complete diagnosis. It is impossible to do it at home without special equipment.
In addition, noise effects in the riser or other areas of the heating supply may occur due to pump malfunction for the following reasons:
- Incorrect installation . The rotor of the device must be strictly horizontal;
- Inconsistency of equipment power with calculated data . This leads to a significant increase in the rate of coolant flow through the lines. The only way out is to install a pump of appropriate power.
In practice, it is extremely difficult to diagnose noise in a heating circulation pump. To do this, it is necessary to dismantle it and disassemble the structure. This can only be done with special skills and diagnostic tools. Therefore, this work is best left to professional repairmen.
To correctly calculate the pump power, it is recommended to use special software systems.
The batteries are knocking
Another common case is when heating pipes begin to make not a uniform noise or hum, but periodic clicks, as if someone is hitting the radiator with a hammer with tiresome consistency. Drum? Aliens?
Cracking in heating pipes can sometimes be identified by grateful listeners in a very unique way. The author met with a respectable old woman who, in the case described, wrote letters to certain government agencies, assuring that her upstairs neighbors were printing money at night.
So, why do heating pipes click?
In fact, there are only three typical reasons for such immoral behavior of pipes and batteries:
Debris in the radiator or riser
Various pieces of slag that have fallen into the heating device and are now spinning in a leisurely stream of water, periodically tapping on the walls, can be tried to be removed by ordinary washing.
We connected the flushing hose, opened the flushing tap (if, of course, there is one) - and off we go. If you want to know how to flush heating pipes, it’s easy to find videos on the Internet.
However, be prepared for an emergency shutdown of the heating riser: any plumber is ready to list dozens of cases when the notorious piece of scale jammed the flusher, making it impossible to close it.
In the worst case, you will have to remove the heating device (after the end of the season, of course) and disassemble it: in the case of a cast iron or aluminum radiator, unscrew the plugs; in the case of a register, alas, open it with welding.
Torn valve valve
A torn valve is a typical problem with all types of screw valves, never mind. When installed “against the grain”, when the water flow does not come from below the valve, but from above, the inevitable erosion of the valve sooner or later leads to the inevitable end: the valve is completely or partially torn off.
It can completely block the flow of water, leaving a dozen or two apartments without heat, or with a slight distortion it can tumble in the stream, creating turbulence, and periodically block the water flow for a moment, creating a water hammer (an instant stop of water - it is practically incompressible, and the pressure jumps several times in a fraction of a second).
So the heating pipes are knocking. These periodic heavy blows will be unclouded and sincerely rejoiced by the entire entrance, and perhaps more than one.
This is evil in its purest form
This is the case when a short-term shutdown of the home heating system to replace the valve is completely justified. An hour of torment with replacement and restart is much more pleasant than warming up and restoring risers and radiators that have defrosted into rubbish in the event that one night the valve finds its desired position and completely blocks the flow of water.
Thermal expansion coupled with temperature instability of the riser or radiator
Finally, the third scenario: periodic quiet knocking in the heating pipes or in the battery. Quietly, like a gnome using a hammer. As annoying as a toothache. The interval is from ten seconds to several minutes. Do we still remember the school physics course? When heated, any body expands slightly. When cooled, it cools down.
If we are talking about a sufficiently long object (for example, a heating riser, fixed on one side in a sleeve welded to the bracket; the bracket, in turn, is tightly fixed to the wall) - then its loose end will move with any significant change in temperature in space by fractions, and sometimes by several millimeters.
If it is pressed tightly against something, you can hear a creak. Only due to the extremely slow expansion and compression will this creak be perceived by the ear as rare clicks in heating pipes.
The problem, to be honest, is more typical for hot water supply systems - simply because there the temperature of the supply is less constant: the water is drained - it heats up, there is no water supply - it cools down. However, cases when a section of the heating system noticeably changes its temperature several times a day is also not something far-fetched.
A typical example is a window that opens for ventilation directly above an aluminum radiator hung on metal pins. Opened it - it cooled down a little, closed it - it warmed up again.
Noise in heating boilers
Constant noise in a heating boiler occurs for the same reasons as in pipes and radiators. Most often this is lime deposits and clogging of the heat exchanger. But it all depends on the design of the equipment and the principle of its operation.
If timely cleaning of the heating system does not produce results, you should look for reasons elsewhere. In practice, noise in the boiler may indicate that it is not working properly. Therefore, it is best to call specialists from the service center, who will eliminate the cause under warranty or charge a reasonable fee.
If it is impossible to perform these steps, you can try to independently determine the cause of the noise in the boiler. It largely depends on the design and type of fuel used:
- Solid fuel models . Extraneous sounds may occur in the chimney. This is facilitated by its clogging and reduced traction. To eliminate this, clean the pipe and run the boiler at full power;
- Gas . Uneven burner operation. This is typical for older models without flame and CO2 level control devices. It is best to install a new modulating burner;
- Diesel and used oil . A characteristic whistling sound arises from the nozzle nozzle. This indicates an excessive amount of soot, which also prevents complete heat transfer from the burned fuel.
After identifying the causes, you should try to correct them at home. Cleaning is carried out only according to the method recommended by the heating equipment manufacturer. It is important to choose the right cleaning products and technology for their use.
It is also necessary to remember that there may be several reasons for the appearance of foreign probes in the heating system. Eliminating one will not solve the problem. Only comprehensive diagnostics will reduce the noise level in the heating supply of a home.
In the video you can familiarize yourself with the technology for removing air pockets that cause noise in heating:
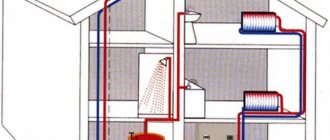
With centralized heating, hot water passes through a heating point before entering the heating radiators of apartment buildings. There it is brought to the required temperature using special equipment. For this purpose, in the vast majority of home heating units built during the Soviet era, an element such as a heating elevator was installed. This article is intended to tell you what it is and what tasks it performs.
Purpose of the elevator in the heating system
The coolant leaving the boiler room or thermal power plant has a high temperature - from 105 to 150 ° C. Naturally, it is unacceptable to supply water at such a temperature to the heating system.
Regulatory documents limit this temperature to 95 °C and here’s why:
- For safety reasons: you can get burns from touching batteries;
- not all radiators can function at high temperatures, not to mention polymer pipes.
The operation of the heating elevator allows the temperature of the network water to be reduced to a standardized level. You may ask, why can’t water with the required parameters be immediately sent to homes? The answer lies in the plane of economic feasibility; supplying a superheated coolant allows you to transfer a much larger amount of heat with the same volume of water. If the temperature is reduced, then the coolant flow will have to be increased, and then the diameters of the heating network pipelines will increase significantly.
How does an elevator work?
In simple terms, an elevator in a heating system is a water pump that does not require external energy. Thanks to this, and even its simple design and low cost, the element found its place in almost all heating points that were built in Soviet times. But for its reliable operation certain conditions are required, as will be discussed below.
To understand the structure of the heating system elevator, you should study the diagram presented in the figure above. The unit is somewhat reminiscent of a regular tee and is installed on the supply pipeline; with its side outlet it is connected to the return line. Only through a simple tee would water from the network pass directly into the return pipeline and directly into the heating system without reducing the temperature, which is unacceptable.
A standard elevator consists of a supply pipe (pre-chamber) with a built-in nozzle of the calculated diameter and a mixing chamber into which cooled coolant is supplied from the return. At the outlet of the assembly, the pipe expands, forming a diffuser. The unit operates as follows:
- coolant from the high-temperature network is directed to the nozzle;
- when passing through a hole of small diameter, the flow speed increases, which is why a rarefaction zone appears behind the nozzle;
- vacuum causes water to be sucked in from the return pipeline;
- the flows are mixed in the chamber and exit into the heating system through a diffuser.
How the described process occurs is clearly shown by the diagram of the elevator unit, where all flows are marked in different colors:
An indispensable condition for stable operation of the unit is that the pressure difference between the supply and return lines of the heating network is greater than the hydraulic resistance of the heating system.
Along with obvious advantages, this mixing unit has one significant drawback. The fact is that the operating principle of the heating elevator does not allow regulating the temperature of the mixture at the outlet. After all, what is needed for this? If necessary, change the amount of superheated coolant from the network and sucked water from the return. For example, in order to reduce the temperature, it is necessary to reduce the supply flow and increase the flow of coolant through the jumper. This can only be achieved by reducing the nozzle diameter, which is impossible.
Electric elevators help solve the problem of quality regulation. In them, by means of a mechanical drive rotated by an electric motor, the diameter of the nozzle increases or decreases. This is achieved through a cone-shaped throttle needle that enters the nozzle from the inside at a certain distance. Below is a diagram of a heating elevator with the ability to control the temperature of the mixture:
1 – nozzle; 2 – throttle needle; 3 – actuator housing with guides; 4 – shaft with gear drive.
Note. The drive shaft can be equipped with either a handle for manual control or an electric motor activated remotely.
The adjustable heating elevator, which appeared relatively recently, allows for the modernization of heating points without a radical replacement of equipment. Considering how many other similar units operate in the CIS, such units are becoming increasingly relevant.
Flushing
The next scenario is flushing. If you hear a loud, uniform noise in your heating riser, if your radiators are noisy and this happens for several hours, perhaps one of your neighbors is simply flushing their radiator. In fact, flushing usually takes from 10 to 20 minutes, but most residents find that the longer the battery is flushed, the better it will perform in the future. Therefore, the noise may linger.
Battery during cleaning
Flushing is performed in order to remove blockages from the outer sections. They silt over time due to the slow flow of water into them. Flushing involves connecting a regular hose to the faucet instead of the lower radiator plug, which is directed to the toilet, sink, or bathtub. And through this tap and hose a certain amount of water is simply discharged. The silt that has accumulated here in the outer sections, if it has not yet petrified, flies out along with this water.
Quite exotic cases also happen. It's probably worth mentioning this. When the residents warmed themselves in this way, the radiator stood on the return side and, accordingly, heated rather weakly. The apartment owners found a simple way out of the situation - they set the riser to discharge. They shut off the valve on their riser below, below the radiator, and connected a hose, directed it into the toilet and thus used the discharge battery. This did help them survive the extreme cold that year, but naturally all the neighbors in this case enjoyed the noise from the radiators.
Heating elevator calculation
It should be noted that the calculation of a water jet pump, which is an elevator, is considered quite cumbersome; we will try to present it in an accessible form. So, to select a unit, two main characteristics of elevators are important to us - the internal size of the mixing chamber and the bore diameter of the nozzle. The chamber size is determined by the formula:
- dr – required diameter, cm;
- Gpr – reduced amount of mixed water, t/h.
In turn, the reduced flow rate is calculated as follows:
- τcm – temperature of the mixture used for heating, °C;
- τ20 – temperature of the cooled coolant in the return, °C;
- h2 – resistance of the heating system, m. water. Art.;
- Q – required heat consumption, kcal/h.
To select the elevator unit of the heating system according to the size of the nozzle, it is necessary to calculate it using the formula:
- dr – diameter of the mixing chamber, cm;
- Gpr – reduced consumption of mixed water, t/h;
- u is the dimensionless injection (mixing) coefficient.
The first 2 parameters are already known, all that remains is to find the value of the mixing coefficient:
- τ1 – temperature of the superheated coolant at the entrance to the elevator;
- τcm, τ20 – the same as in the previous formulas.
Note. To calculate the nozzle, you need to take a coefficient u equal to 1.15u'.
Based on the results obtained, the unit is selected according to two main characteristics. The standard sizes of elevators are designated by numbers from 1 to 7; you need to take the one that is closest to the design parameters.