Every owner of a private house or apartment with water heating should know how to bleed air from a heating radiator. The thing is that the accumulated air in the radiator becomes an insurmountable obstacle and blocks the flow of coolant.
As a result, the heating radiator ceases to function fully, that is, all or part of its surface ceases to heat up and release heat to the surrounding space.
Airing of the panel heating device (blue color)
To eliminate this phenomenon, you need to bleed the air from the battery. How to do this in a timely and effective manner will be discussed in this article. Carrying out such an operation does not cause any particular difficulties if the heating system is assembled correctly, taking into account all the features of water heating of premises. Throughout the heating season, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures of this nature from time to time.
Types of air vents and their installation locations
Air vents are manual and automatic. Manual air vents or Mayevsky taps are small in size. They are usually installed on the end of the heating radiator. The Mayevsky tap is adjusted using a wrench, a screwdriver, or even manually. Since the faucet is small, its performance is low, so it is used only for local elimination of air locks in the heating system.
Air vents for the heating system are of two types: manual (Mayevsky tap) and automatic (work without human intervention).
The second type of air vents - automatic - operate without human intervention. They are installed both vertically and horizontally. They have high performance, but are quite sensitive to contaminants in water, so they are installed together with filters on both supply and return pipelines.
Automatic air vents are installed in closed heating systems along the pipeline line at different points. Then air is released from each group of devices separately. A multi-stage deaeration system is considered the most effective. With proper laying and proper installation of pipes (at the required slope), removing air through air vents will be simple and hassle-free. Removing air from heating pipes is associated with an increase in coolant flow, as well as an increase in pressure in them. A drop in water pressure indicates a violation of the tightness of the system, and temperature changes indicate the presence of air in the heating radiators.
Design and operating principle of manual air valve
The needle manual air valve is also called a Mayevsky valve. His device:
- Brass body (plug) with external thread 1/2 // or 3/4 // for connection to the radiator. The case has two holes for air release Ø 2 mm - one at the end of the case, the second on the side wall;
- Brass locking screw. On one side of the screw there is a groove for a slotted screwdriver, on the other side the screw is machined into a cone that closes the air hole (the “closed” position);
- Plastic casing.
On sale you can find the so-called “faucet at hand”. To use it, you don’t need a key or a screwdriver—the plug can be easily unscrewed by hand.
To remove air from the housing, you need to unscrew the screw. To do this, you can, of course, use a screwdriver, but there are special keys that are most often included. After several revolutions, the screw cone comes out of the end hole and air enters the housing cavity, which is immediately released through the second side hole. The main thing is not to rush to turn off the tap. About 30 - 40% of the air should come out with water, so you need to stock up on time, a basin and rags. After the air has been released, the lost water must be added to the system.
Modern aluminum or bimetallic heating radiators already have a hole for installing a Mayevsky tap. It can be found on the side opposite the coolant supply, from above. Most likely, there is already a nut for installation there. There is a plastic plug screwed into it. After its removal, an air valve is installed in this place. Before this, the tap threads must be sealed with a rubber or silicone gasket.
Installing a Mayevsky crane on a cast iron battery is much more difficult. Let's start with the fact that these valves are much more powerful than those on aluminum radiators - they can withstand pressures of up to 16 atmospheres and temperatures of 150 C°. Sequencing:
- 1 Drain the water from the radiator;
- 2 Cut a hole in the top plug of the cast iron battery and cut a thread that matches the external thread of the air vent;
- 3 Screw in the Mayevsky tap;
- 4 Add water to the system.
Malfunctions and ways to eliminate them
If the faucet malfunctions, a leak appears. There may be several reasons for this:
- Manufacturing defects. One in fifty taps does not hold pressure at all. The only way out is replacement;
- The screw is too short. In this case, its conical part cannot completely block the hole, so you need to apply a certain force to screw the screw in until it stops;
- Solid particles of debris falling between the screw and the housing can damage the internal threads. Fum tape can help here once, but later you will still have to change the tap.
Why is an air lock in the radiator dangerous?
If there is air in the battery, nothing good will come from it.
Excess air is an obstacle to the normal functioning of the system. It can also cause corrosion on the walls of the radiator. If a circulation pump is installed in the circuit. an air lock can also disrupt its operation. When the system is functioning correctly, the plain bearings on the shaft of the pump unit are constantly in the water. And if there is air, a “dry friction” effect occurs, which negatively affects the sliding rings and can damage the shaft
Therefore, it is important to know how to remove air from your home heating system. Timely measures will help prevent damage to the heating network
Briefly about the main thing
The air vent allows you to bleed air from the heating system automatically or manually. Regardless of the modification, it includes 3 main working parts - a channel, a needle valve and a control mechanism. An automatic device operates on the principle of interaction of a float mechanism with a locking valve, while a manual device is activated by turning the lock screw.
Airing of the system can occur for various reasons - repair or replacement, long downtime, quick filling of coolant, initial operation, depressurization of seams. If you do not eliminate them in time and do not bleed the air, then a number of problems will arise with the technical parameters in the operation of the equipment and the system as a whole.
Modern air vents are divided into 3 main types:
- Automatic.
- Mechanical.
- Radiator.
Each of them has its own characteristics of design, operation and application. It is possible to ensure high efficiency of their operation, thereby creating stable operating conditions for the heating system, by correctly selecting and installing them - in the most important places in the circuit.
Ratings 0
Bleeding air through the plug
If there are no taps on the heating devices, a problem such as an air lock in the home heating system becomes much more complicated. You will need to unscrew one of the plugs.
For these purposes, you should prepare a large adjustable wrench. You need to place a container under the plug. Next, the key grabs the plug and turns it very carefully. It is unacceptable to completely unscrew the plug, since there may be high pressure in the heating system, the coolant will go straight into the room with high pressure, and it will be problematic to cope with the current situation
That is why the plug should be turned with extreme caution. It is advisable to first turn off all available equipment in the room and close window and door openings tightly. While turning the plug, you need to listen
If a slight hissing noise appears, do not turn the plug any further. At this moment you need to stop and put the key aside. Now you should wait until the excess air from the heating device gradually but completely leaves the system. It is very simple to determine that the plug in the heating system has come out - liquid will begin to leak from under the plug. Then, using a large adjustable wrench, you need to smoothly and carefully return the plug to its original position.
Dangerous consequences of airy radiators
Accumulation of gases in the heating system leads to the formation of air pockets. The radiators become cold, the pump cannot push the coolant through the air blockages. This can lead to failure of not only the pump, but also the boiler itself. Lack of normal water circulation in the system will cause them to overheat and ultimately break down.
Don’t know where to complain if there are cold radiators in the apartment?
In places where there is small accumulation of air, which does not greatly affect the heating of radiators, pockets of corrosion may occur. Oxygen actively interacts with the metal of the battery, which causes rust and destruction of the wall of the heating device segment.
The result of corrosion of the battery collector from air pockets
Uneven heating of the metal causes deformation forces, which negatively affect the tightness of the connections of radiator elements and pipes. As a result, the system will leak and hot water will flow out.
Types of air vents
Valves for removing air locks are automatic and manual. The second type of air vents includes Mayevsky taps. They are used not only to remove air, but also to start it up in order to drain the coolant from the system.
Mayevsky crane
This device is made of brass and has a simple but reliable design. The main parts of the Mayevsky crane are the body and the screw. All valve parts are located as closely as possible to each other, so that the coolant cannot escape outside. Open the tap using a special key, screwdriver or hand.
Before removing air from the heating system, it is necessary to prepare a container for the coolant and tools. Step-by-step instructions for removing air pockets using a Mayevsky crane:
- If the heating system operates using a circulation pump, it should be turned off while the air is being vented.
- Using a wrench, screwdriver or hand, turn the tap 1 turn counterclockwise. You will immediately hear the hiss of air escaping from the radiator.
- As soon as the coolant begins to flow out, it means that the air lock has been removed, the Mayevsky valve is closed back.
Automatic air vent
Automatic air vent VALTEC VT.502
This device independently removes air from the heating system. Installs either vertically or horizontally. Consists of a brass body, float, release valve and articulated arm. To prevent coolant from leaking through it, the air vent is equipped with a protective cap.
Note! Automatic devices are sensitive to impurities contained in water. For long-term operation, cleaning filters are additionally installed in the heating system.
The operating principle is as follows: if there is no air in the chamber, then the outlet valve is closed. As it moves in, the float lowers. Once the chamber is completely filled, the exhaust valve opens and the air is discharged outside. The float then closes the outlet valve again.
Air separator
This device consists of a metal body, an air vent, a drain valve and a tube with a mesh. Unlike conventional air vents, the separator itself removes air from the water. As the coolant passes through the mesh, it swirls, causing air bubbles to form. As a result, they rise to the top, and the gases are removed through the air vent. In addition to air, the separator separates sand, rust and other impurities. Remove sludge through a drain valve located outside at the bottom of the housing.
Installation recommendations
Regardless of the type of automatic air intake for heating, you need to ensure that the exhaust cap faces up during installation. Bleed valves in systems are usually installed after ball valves or shut-off valves. An exception to the rule is the boiler safety group: secondary intermediate fittings are not used in this case.
Thanks to the shut-off check valve, it becomes possible to carry out maintenance or replacement of the air vent without emptying the entire heating system. Therefore, having such a device is very convenient. Only wrenches are suitable for installing an automatic bleeder: they, unlike adjustable ones, allow you to measure the effort required to screw the fastener. During installation work, it is not recommended to hold the device by the body to avoid damage. For these purposes, the design provides a hexagon at the bottom of the cylindrical chamber.
What are air vents and what are they for?
Many owners of radiator systems have encountered a situation where, with hot pipes, some parts of the radiator do not heat well or are generally cold; similar problems arise with insulation with water floors. The main reason for this phenomenon is the presence of air in the pipes, which rises and impedes the movement of the coolant.
If in an open circuit air bubbles are sent to an unclosed expansion tank located on high floors of a building or attic, and bleeding is not so important, then in a closed system an air bleeder for the heating system is vital on all circuits and individual heat exchange devices.
When plugs interfere with the operation of the system, manual or automatic heating drain valves are used to remove accumulated air. One of the simplest devices is a regular valve installed at the top point of heating radiators. To bleed air from the batteries, open the valve and wait for the moment when the stream stops flowing jerkily along with the air - in radiators without air, the water flow will be uniform.
In individual heating lines of private houses, instead of ordinary valves, special locks are installed on the radiators, which function automatically or are manually adjusted. With their help, they remove not only air from devices in which gas formation occurs, but also, when necessary, oxygen from water, which causes accelerated corrosion of metal fittings.
Rice. 2 Air vent for venting air from the heating system - design
Selection rules
In order for the heating and hot water supply system of a private home to operate for a long time and uninterruptedly, air vents for it must be selected in accordance with the following rules:
- Purchase products from well-known brands with a guarantee and certificate. Cheap analogues jam, quickly break down and allow not only air to pass through, but also coolant even when the valve is closed.
- Models with rotating handles are not the best option when there are small children in the house.
- Auto-air vents are always best mounted on top of a pre-installed shut-off valve - for quick dismantling if repair or replacement is necessary.
- Anodized items do not rust and last longer.
- If the device is installed in a system operating under pressure, among its main technical parameters there must be an appropriate maximum permissible pressure value.
With the correct selection of parameters, proper installation and compliance with operating conditions, branded automatic air bleeders last at least 10 years, and manual analogues - about 15 years.
Causes and consequences of air locks in a closed heating system with forced circulation
The reasons are the same as for an open system, plus:
- A loose circulation pump impeller can “grab” air during operation;
- If hot water is supplied to the expansion tank from above, then air can enter the system through cracks or breaks in the tank membrane.
An air lock in a closed circuit will lead to increased pressure in the system and activation of the safety valve. The valve will bleed water over and over again until the boiler burns out or the heating pipes rupture. Therefore, security requirements for closed systems are much stricter. In particular, for air release, the closed circuit is equipped not only with manual Mayevsky valves, but also with automatic air vents. One of these automatic valves is included in the safety group. The group is placed on the water supply, immediately after the boiler.
Important! A leaky pipeline or radiator cannot cause an air lock. A working system, whether closed or open, is under pressure
The air will never go towards higher pressure - this contradicts all the laws of physics.
Finding a suitable installation location in the system
Taking into account the operating principle of an automatic heating air vent, it is usually used in the following areas:
- The highest point of the heating circuit (tops on vertical risers, etc.). This is where the internal air of the system usually accumulates.
- End areas of dead-end pipeline lines.
- Boiler piping safety group. Boilers using solid fuels especially need this. In this case, an automatic air bleeder is included in the set of instruments, which also contains a pressure gauge and an emergency valve. Thanks to the air vent, air is released as the coolant fills the water jacket of the boiler. In addition, the device increases the rate of water drainage when the heat generator is disconnected from the general system.
- Together with a circulation pump, which allows you to optimize its operation. This option is used only for those models of pumping equipment whose design provides for the possibility of installing an air vent. If the coolant is pumped with air, there will be a noticeable deterioration in the quality of the pump, even to the point of stopping it. All this leads to rapid wear of the impeller and bearings. Using a bleeder, you can also remove steam from the coolant if it overheats.
- Areas of the heating circuit where there is constant airing of the system. One of the reasons for such phenomena is an incorrectly calculated angle of inclination of the pipe.
- Heating appliances.
Air removal methods
There are heating systems with forced and natural circulation of coolant. In the first case, the liquid flows using a circulation pump, and in the second, due to a certain inclination of the pipes and the pressure in them.
Natural circulation systems
An expansion tank is used to remove air from this type of system. It is installed at its highest point. Most of the air is independently removed through it when the coolant is heated. If air pockets still remain, many experts recommend increasing the amount of fluid in the system by opening the air vents. Thus, the coolant itself will displace the air from the network with movement and pressure.
Forced circulation systems
In systems with a circulation pump, pipes and radiators are located level and without slope. Air vents are used to remove air from them. They are always mounted at the bends and at its highest points, since this is where the accumulation of gases occurs.
Note! If it is not possible to remove air from the system using air vents, then it is necessary to drain all the coolant and refill it. The coolant must be poured into the system slowly, as rapid filling will cause air bubbles to form.
At the same time, you need to remove air from radiators and other elements. The longer the system, the longer it takes to fill it with coolant. If a heated floor is connected to the heating network, then the installation of air vents is mandatory, since the pipes are often located at different heights. You also need to constantly monitor the amount of coolant in the system to exclude the possibility of air getting into it
It is necessary to pour the coolant into the system slowly, since rapid filling causes air bubbles to form. At the same time, you need to remove air from radiators and other elements. The longer the system, the longer it takes to fill it with coolant. If a heated floor is connected to the heating network, then the installation of air vents is mandatory, since the pipes are often located at different heights. You also need to constantly monitor the amount of coolant in the system to exclude the possibility of air getting into it.
Why does air appear in the heating system?
Many of our compatriots are familiar with the concept of “air jams”. This phenomenon is remembered at the beginning of the heating season, when heat is allowed into houses, but in apartments on the upper floors the radiators often do not heat up or only heat up in the lower part, and are absolutely cold in the upper part. Where does air come from in pipelines? There can be several reasons for airing:
- carrying out repair work (assembly, disassembly of the pipeline), during which the appearance of air is inevitable;
- non-compliance during installation with the magnitude and direction of the slope of pipelines;
- low pressure in the water supply. the water level drops, and the resulting voids are filled with air;
- when water is heated, bubbles of air contained in it are released and rise to the upper part of the pipeline, creating air jams there;
- the heating system is not filled correctly: after a summer period of inactivity, the pipes should be filled with water not quickly, but slowly, while simultaneously bleeding air from the heating system;
- unsatisfactorily sealed pipeline joints through which coolant leaks. Leaks in these places are hardly noticeable, since the hot water immediately evaporates. It is through loose seams that air is sucked into the system;
- malfunction of air intake devices;
- connecting a water “warm floor” to a heating system, the pipes of which are located at different heights during installation.
Causes of air
The logical question is: how does air get into the heating system if it is completely sealed?
There can be many reasons for this phenomenon:
- High blood pressure. Water contains not only magnesium and calcium, but also oxygen. The volume of oxygen depends on the pressure level in the system. As pressure increases, the concentration of oxygen in water increases.
- Violation of requirements for pipe slopes during installation work.
- Incorrect filling of the pipeline, leading to air congestion. Water should be supplied slowly while air is pumped out of the batteries, right? otherwise, the formation of bubbles is inevitable, which causes airing of the heating system. The general rule is: the more branches a system has, the slower its filling should occur.
- Diffusion. This phenomenon is a process during which the ability of molecules of one substance to penetrate between the molecules of another is realized. In the described case, we mean the penetration of oxygen molecules between the molecules of polypropylene or polyethylene. To prevent diffusion, special coatings are applied to the pipe material.
- Insufficient connection density between system elements.
- Faulty or missing air vents.
- Carrying out repair work during which depressurization occurred.
- Corrosive processes leading to violation of the tightness of equipment.
The above factors do not exhaust the reasons that cause air in the heating system, but they are the most common.
Heating air vent
Design, principle of operation of the air vent
But in addition to radiators, situations often arise when it is necessary to expel an air lock from the heating system in the pipes. To do this, it is necessary to install air vents in certain sections of the pipeline. Their design is in many ways similar to the Mayevsky automatic cranes described. However, there are significant differences - they are designed for the largest volume of air released and are installed not horizontally, but vertically.
In order to remove the resulting air lock from the heating system, you first need to install air vents in the right places:
- At the highest point of the highway. For an open system, this is only possible if a sealed expansion tank is installed on the return pipe;
- In collector heating - on each comb;
- For tee wiring - before each branching node of the main line.
After installation, it is necessary to correctly set the pressure value at which the air vent will operate. To remove an air lock from the heating system, coolant is pumped into the pipes until the air vent on the return line operates.
When removing an air lock in an autonomous heating system, you need to reduce the temperature of the coolant to a minimum. This will reduce the volume of water and will help resolve the problem more effectively.
In combination with the functional qualities of Mayevsky taps, this makes it possible to effectively break through any plug in the heating
It is important that the response parameters of the devices do not exceed the critical pressure value. Otherwise, the security of the system may be at risk
The video shows an example of venting a heating radiator:
How the device works
An air valve (or several) is installed in the heating system, in places where air bubbles are most likely to accumulate. This prevents the formation of a large traffic jam and the heating operates uninterruptedly.
Mayevsky crane
Such devices are named after the name of their developer. The Mayevsky tap has a thread and dimensions for a pipe with a diameter of 15 mm or 20 mm. It's structured simply:
- There are 2 through holes made in the body of the valve body, which in the open position of the Mayevsky tap communicate with the heating system.
- These holes are closed by a threaded screw with a conical tip.
- Air is released through a small (2 mm) hole directed upward.
In order to bleed air from the system, unscrew the screw 1.5-2 turns. The air escapes with a whistle as the communications are under pressure. The end of the air plug exit is characterized by a drop in pressure and the appearance of water.
On the market you can find several varieties of the Mayevsky tap, which are identical in design, but differ in the way they regulate the shut-off screw. There are:
- with a convenient handle for unscrewing by hand;
- with a regular head for a flat screwdriver;
- with a square head for a special key.
For an adult, the principle of unscrewing the locking screw does not matter. However, in a house where there are children, it is safer to use devices that should be unscrewed with a special tool. By unscrewing a regular tap with a comfortable handle, a child can be scalded by boiling water.
Automatic crane
The automatic air release valve is designed on the principle of a float chamber, the design includes:
- vertical housing with a diameter of 15 mm;
- float inside the housing;
- a spring valve with a cover, which is connected and adjusted by a float.
The automatic air valve for the heating system operates without human intervention. In normal condition, when there is no air in the system, the float is pressed by the pressure of the liquid filler to the valve cover. The lid is tightly closed.
As air accumulates in the valve body, the float moves down. As soon as it drops to a critical level, the spring valve opens and bleeds air out. Under the pressure of the carrier in the system, the space is again filled with liquid. The float rises, closing the spring valve cover.
When there is no coolant in the communications, the float lies at the bottom of the valve. As the system fills, air comes out of the tap in a continuous stream until the coolant reaches the float.
The following configurations of automatic air valves for heating are distinguished:
- with vertical air discharge;
- with side air discharge (through a special jet);
- with bottom connection;
- with corner connection.
For an amateur, the design features of an automatic crane do not matter. However, for a professional there is a difference in choosing between devices.
It is believed that:
- a device with a jet and a side hole is more reliable in operation than an automatic valve with vertical air discharge;
- a bottom-mounted valve traps air bubbles more effectively than a side-mounted valve.
If the design of the Mayevsky crane has not undergone changes for many years, the design of automatic valves is constantly being improved and supplemented.
Manufacturers offer automatic valves with additional devices:
- with a membrane to protect against water hammer;
- with a shut-off valve for easy dismantling of the device during the heating season;
- mini valves.
Automatic heating air valves require frequent inspection and cleaning. The undoubted advantages of these devices include the ability to install them in hard-to-reach places.
Why are there taps on radiators?
Each heating device is a separate element of the system that requires adjustment and periodic maintenance. If you control the coolant flow through the batteries depending on the heat demand, you can achieve good results in terms of energy savings. That is, radiator valves and heating taps are designed to solve the following problems:
- Complete isolation of the heating device from the system.
- Restriction of coolant flow through the battery.
- Change in coolant flow depending on external conditions.
- Bleeding air from the radiator and piping network.
There are many situations in which it is difficult to do without disconnecting the battery. For example, properly working central heating in the middle of spring, when it’s already warm outside, but it’s just hot in the apartment. Another case is the need to remove a heating device for the purpose of replacement, flushing or repair. In the absence of shut-off valves, carrying out any action with the radiator becomes problematic.
Valves are also installed on batteries in retro style
Restriction of the flowing coolant is carried out in order to balance individual heating in a private house or apartment
No matter what type of heating system you have, without balancing with valves, the first radiators will always receive more water than the last ones. Limiting the coolant flow at the beginning of the network and thereby balancing all devices with each other is the task of the control radiator fittings
Automatic control of the flow of incoming coolant is a way to save energy used to heat the house. If each tap on the heating radiator maintains the set air temperature in the room by controlling the flow of water through the radiator, then in general the system will consume only the required amount of heat, no more. And this is a considerable saving.
Well, the problem of air release when filling the system or during operation is also solved by special air valves installed on all modern radiators. Below is a list of types of shut-off and control valves, listed in the same order as the tasks they solve:
- Half-turn ball valves in straight and angle versions. Made from brass, bronze or polypropylene with a metal insert.
- Balancing valves for radiators – straight and angular.
- Regulating valves with thermal heads (thermostatic valves).
- Air drain valves – automatic and manual.
For reference. Some home craftsmen use three-way mixing valves to connect heating appliances. But such a solution is unreasonably expensive and is rarely used in practice.
Now we should consider in detail which taps are best installed on radiators in various conditions and circumstances. Some options are clearly shown in the video:
Automatic vent valve for heating system
A heating system with a liquid coolant uses a number of specialized elements to ensure reliability and efficiency of its operation. These include an air valve (separator) for heating. A device for releasing air from the heating system makes it possible to remove gases accumulated in the pipeline and radiators.
When an air plug forms in the pipeline, it tends to the highest point of the radiator or the heating circuit as a whole. If an automatic air release valve is installed in this place, the coolant from its internal chamber is displaced by gases.
When the liquid is displaced, the float moves down and opens the valve, as a result of which gases are released from the heating pipeline, and the chamber is again filled with coolant.
The valve for automatically releasing air from the heating system becomes silted over time and becomes overgrown with scale. This leads to jamming of the mechanism, loss of tightness of the valve - moisture begins to seep through it. Such a device requires replacement - automatic air vents cannot be repaired.
The number of automatic air vents depends on the characteristics of the heating system.
- Device required for installation:
- as part of the safety group of the boiler unit at the outlet pipe of the water jacket, where the coolant is heated to the maximum temperature;
- at the highest point of vertical risers - this is where gaseous substances rise and accumulate;
- on the distribution manifolds of underfloor heating so that air can be vented from the circuits;
- on U-shaped loops made of polymer pipes, which are installed to compensate for the thermal expansion of the pipeline.
Selection principles
Air valves for the heating system can be part of a safety group or a manifold kit for a heated floor, supplied with heating appliances.
The car air vent is selected taking into account its operating parameters (maximum permissible temperature and pressure), they must correspond to the characteristics of the heating system. Based on their design, they are divided into straight and angular devices, horizontal and vertical.
- Mayevsky cranes differ in the way they unscrew the working screw:
- with a rod head for a special key (the inconvenience is that the key may not be at hand at the right time);
- with a non-removable handle (cannot be used in places accessible to young children to avoid the risk of burns from heated coolant;
- with a slot for a flat-head screwdriver (the most convenient and safest option).
To equip your heating system with a reliable air release valve, it is recommended to choose products from well-known brands. You should avoid cheap products made from fragile silumin that imitates brass.
Why is air in a heating system dangerous?
Air dissolved in the coolant gradually damages steel pipes and radiators and elements of the boiler unit. The corrosive activity of air, which was first dissolved in water and then released during heating, significantly exceeds that of atmospheric air due to the increased oxygen content.
Gases accumulated in the pipeline not only provoke or accelerate corrosion of metal elements, but also form air locks that prevent the heating system from functioning fully: Due to gas locks, the circulation of the coolant worsens; in serious cases, the movement of liquid through the pipes can be completely blocked. In such a situation, heating devices quickly cool down. Air pockets act as a heat insulator, and if gases have accumulated in the upper part of the battery, it warms up worse and transfers less thermal energy to the room. If there are air pockets, the movement of the coolant along the heating circuit is accompanied by loud gurgling sounds and murmurs, which disrupts the acoustic comfort in the house.
Circulation pumps are not designed for pumping gases; when working with air-filled coolant, the bearing and impeller of the pump unit wear out much faster. Special air exhaust devices help solve problems associated with airing the heating system
It is important to choose the right valves for bleeding air and correctly determine the location of these elements.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Q4LOLnuFOoc
Ball
Sewage flooding is especially likely in high-rise buildings, where several apartments are located on one vertical pipe. Even one plastic bag may be enough to clog the riser, and then yes, not finding its way, will rush back, splashing out of all the drain holes. This situation is especially likely in old houses, where the pipes are covered on the inside with thick crusts of deposits.
The risk of backflow of waste water is especially high in apartments on the ground floor. Often at night in such apartments it is necessary to plug the drains with rags, plugs and other improvised plugs. But if valves are installed on the first floors, water can break through on the second floor. Up to the third floors, the pressure is usually not enough, and if it is strong enough, it will simply destroy the blockage and the water will go into the pipe.
So, it’s worth installing a check valve if:
- Your apartment is located on the first or second floor.
- You live in an individual home: a cottage, a dacha, a private house.
- The house was built a long time ago and there has been no major repair of the sewer system or replacement of risers.
- According to neighbors, there are frequent cases of sewer blockages in the house.
In this case, the small costs of purchasing and installing protective devices will pay off handsomely, allowing you not to worry about sudden costs and hassle.
If your home has a common riser valve installed, it can reduce the risk of flooding. But in problem apartments it is better to install separate valves on each drain to be completely sure.
Device
In 2021, there are many options for such a unit. They differ in materials, sizes and shapes, locking methods and many other parameters. But all types of valves have the same purpose - to cut off sewer water in the pipe that rushes sharply in the opposite direction.
Almost any design has the following elements:
- The pipes through which drained water enters and leaves the valve.
- A handle that closes the valve forcibly. It can be used when cutting off drains at night, or when trying to unclog a sewer system.
- A removable cover that allows you to inspect the condition of the valve and, if necessary, clean its parts from contamination.
- Locking mechanism. A ball valve is a rubber ball, but membranes, flaps and other devices can also be used.
The valve will not work if the “input” and “output” are reversed. Typically, the direction of movement of the drains in the valve is shown by an arrow marked on the body. Take this into account during installation!
Main types
First of all, valves vary in diameter. In the standards for sewer installation, left over from Soviet times, a diameter of 110 mm is established for risers, and all other pipes have a diameter of 50 mm. Today, non-standard options have appeared, for example, with a diameter of 75 mm, but they are significantly less widespread.
Various materials are used to make shut-off devices. They can be either metal (bronze, brass, stainless or carbon steel) or polymer (PVC, polyethylene). Each option has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Metal products are significantly more expensive. They are durable, but require attention to their condition and periodic maintenance.
- Plastic valves are cheaper. They practically do not corrode. But the mechanical strength of such structures is less.
The design of check (or fan) valves also differs. Here are the most common options:
- The ball valve has a very simple design: a rubber ball is loosely located in the pipe, the diameter of which is slightly larger than the overall diameter of the pipe. When the liquid moves in the forward direction, the ball moves into a special chamber, and when it moves in the opposite direction, the ball, picked up by water, tightly plugs the neck of the pipe. Thanks to such a simple design, there is simply nothing to break in this device.
- Wafer device. The most compact option. This valve is convenient for installation in confined spaces. But if it fails, you will have to disassemble part of the system in order to repair or replace the faulty unit.
- Lift and rotary valves have spring-loaded flaps in their design. Such devices are relatively large, heavy and not cheap. The advantage is the ability to easily disassemble for cleaning, adjustment and minor repairs.
The choice of a specific type of device depends on the budget allocated for repairs, installation location, type of pipe and existing conditions.
How to properly install an air valve for sewerage, read the article: here
Balancing valve
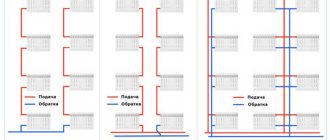
The design of a valve for regulating heating differs from a conventional ball valve in that it can smoothly close the flow area in a few turns. Moreover, after balancing, the position of the valve can be fixed so that no one accidentally violates the settings. This type of control valves is installed at the outlet of the radiator, as shown in the diagram:
Shown here is the connection to a two-pipe horizontal system, most common in private houses and apartments with individual heating. By the way, the principle of installing fittings with a single-pipe scheme remains the same. A regular ball valve is installed on the supply line, and an adjustment valve is installed on the return line. In the case when a two-story house has a system with vertical risers, the installation diagram of the accompanying fittings looks like this:
The principle of product selection is the same as in the previous section
Straight or angular design is accepted depending on the layout of equipment and pipelines; it is also important to use American designs during assembly
Pay special attention to the quality of casting and the thickness of the brass walls of the fittings. If you have networks made of polypropylene pipes, do not rush to buy PPR taps; it is better to install adapters and reliable metal products
Advice. Balancing valves are installed on all radiators, except for the very last one, located at the dead end of the branch. It is enough to install simple ball valves on the connections to it.
How to remove an air lock
Ideally, gases rise to the highest points of the circuit, where air vents are installed, and are released from there by valves operating in manual or automatic mode. In practice, errors in pipeline design or installation lead to the formation of air pockets in hard-to-reach places.
To remove such a plug, you need to find its location - by the murmur of coolant flowing through the air-filled area, by the relatively low temperature of the pipe or radiator, by the ringing sound when tapping the pipes.
Increasing the coolant temperature and/or pressure in the system will help remove the plug from the autonomous heating system. To apply pressure, it is necessary to open the make-up valve and the drain valve closest to the air lock (in the direction of flow). The water entering the system increases the pressure and causes the plug to move forward. After making sure that the plug has come out through the valve (it stops hissing), the system is returned to normal operating mode.
Removing an air lock from the heating system
In more complex cases, they are affected not only by pressure, but also by temperature. The coolant must not be heated above the maximum permissible values, so as not to damage the heating system.
Important! Regular formation of a plug in the same place indicates miscalculations in the project or incorrect installation. It is recommended to install an air vent in the problem area by cutting a tee into the pipeline
What signs indicate the need to install an air valve?
In order to prevent air accumulation, heating engineers suggest using an air valve for heating from the very beginning of operation of the circuit, so heating specialists, in the drawn up heating diagram, give recommendations as to which air vent is suitable for a particular heating system.
However, in some cases, trying to save money on the purchase of this type of control valves, owners refuse to install the devices and thereby provoke a number of problems. To solve them, they have to install an air valve for the heating system after the circuit has been connected and connected to the boiler.
The following signs indicate the presence of air pockets and indicate the need to integrate an air vent into the heating circuit:
- uneven heating of batteries;
- the appearance of “cold spots” on the pipeline;
- poor circulation in the heating system;
- noise in heating devices;
- poor-quality heating of the house.